Month: June 2020
-
Isometric
Muscle actions that occur when tension is developed in the muscle without movement at the joint or a change in the muscle length. The tension remains constant because the length of the muscle does not change. Movement against an immovable force; static; a muscle contraction in which the tension increases, but muscle length remains the…
-
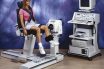
Isokinetic
A type of muscular action in which movement occurs at the joint, as in an isotonic action; however, the tension remains constant, as in an isometric action. Contraction in which the tension developed by the muscle while shortening at constant speed is maximal over the full range of motion. In exercise, the term isokinetic is…
-
Irregular bone
A bone with a complex shape, such as a vertebra.
-
Iron deficiency anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells, which provide oxygen to body tissues. Iron deficiency anemia is a decrease in the number of red cells in the blood caused by too little iron. Anemia resulting from a low hemoglobin level and a low hematocrit level. Symptoms…
-
Iron deficiency
Depleted iron stores, although not to the level of anemia. Inadequate intake of iron; characterized by anemia.
-
Inversion
Turning the sole of the foot inward or medially. Applied to sucrose, means its hydrolysis to glucose and fructose (invert sugar). A turning inward, as of the eyelid or the foot. The fact of being turned towards the inside. Abnormal condition in which an organ is turned inward or inside out (e.g., the uterus after…
-
Intrinsic reinforcement
Motivation resulting from the activity itself being the reward.
-
Interval training
Consists of harder bouts of exercise (work cycles) interspersed with easier bouts of exercise (recovery cycles). An aerobic and/or anaerobic workout that consists of three elements: a selected work interval (usually a distance), a target time for that distance, and a predetermined recovery period before the next repetition of the work interval. Alternate periods of…
-
Internal locus of control
Belief that one is personally responsible for what happens and for the outcomes in their own life. A person’s belief that he or she, not outside forces or other people, is largely responsible for what happens to him or her in life. A general disposition to expect that one’s actions will lead to predictable outcomes…
-
Internalization
When a person is engaging in an activity for self-fulfillment; when reached, compliance is likely to occur. The process whereby moral codes are adopted by the person so that they control his or her behavior even when there are no external rewards or punishments. Unconscious process of adopting and absorbing the beliefs, values, and attitudes…