Month: August 2020
-
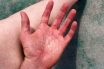
Blood pooling
A condition caused by ceasing vigorous exercise too abruptly so that blood remains in the extremities and may not be delivered quickly enough to the heart and brain.
-
Ballistic
Bounce or explosive movement, unsustained.
-
Aortic stenosis
A narrowing of the valve opening between the lower left chamber of the heart and the aorta. A condition in which the aortic valve is narrow, caused by rheumatic fever. Narrowing or stricture of the aortic valve, due to congenital malformation or the result of disease (e.g., rheumatic fever), that obstructs the flow of blood…
-
Anoxia
A deficiency of oxygen, most frequently occurring when blood supply to any part of the body is completely cut off. Generally, lack of sufficient oxygen in the blood. Below-normal oxygen in body tissues. Lack of oxygen in blood or tissues; it may be local due to inadequate oxygen delivery to a localized area or may…
-
Anoxemia
A deficiency of oxygen in the blood. A diminished or inadequate oxygen concentration in the blood. A condition in which there is less than the normal concentration of oxygen in the blood. Insufficient oxygenation of the blood. An insufficient supply of oxygen in the blood.
-
Anemia
A condition in which there is a reduced number of erythrocytes or decreased percentage of hemoglobin in the blood. A condition characterized by a decreased amount of hemoglobin in the blood. The most common type is iron-deficiency anemia (usually due to a diet low in iron), in which red blood cells are reduced in size…
-
Amphiarthrodiai
A type of articulation joined by hyaline cartilage, classified as either permanent or stationary joints and slightly move-able.
-
All-or-none law
A muscle contracts to its fullest potential or not at all. Pertains to the fact that once a stimulus exceeds the threshold, further increases in the stimulus will not increase the amplitude of the action potential. The weakest stimulus capable of producing a response produces the maximum contraction of cardiac and skeletal muscle cells, and…
-
Alkalosis
When the blood has a lower hydrogen ion concentration than normal and an excessive base (bicarbonate ions) in the extracellular fluids. Excessive alkalinity of body fluids due to accumulation of alkalines or reduction of acids. A condition that results when the body loses too much carbon dioxide or acid as the result of forced breathing…
-

Aerobic exercise
A method of conditioning the cardiorespiratory system by using a variety of activities that create an increased demand for oxygen over an extended period of time. Continuous rhythmic exercise using the large muscles of the body over an extended period of time. Aerobic exercise increases the body’s demand for oxygen, thereby adding to the workload…