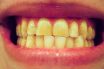
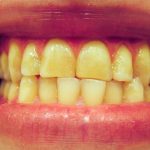
 The parafunctional grinding, clenching, or clamping of teeth.
The parafunctional grinding, clenching, or clamping of teeth.
A habit that consists of the involuntary recurrent or spasmodic nonfunctional grinding, clenching, or clamping of teeth in other than desired functional movements of the mandible (chewing), which results in occlusal damage. Also known as tooth grinding, occlusal neurosis.
Grinding of the teeth that occurs unconsciously while awake or during Stage 2 sleep. It may be secondary to anxiety, tension, or dental problems.
The action of grinding the teeth, as a habit.
Bruxism is the medical term for unintentional, forcible grinding and clenching of the jaw and teeth (ViaHealth, 2001). Etiology is not known, but certain anatomical and psychological factors may lead to the onset of bruxism (KidsHealth, 2001). Bruxism usually occurs at night during sleep and is often associated with stress (Teethgrinding, 2000). It also commonly occurs in children with cerebral palsy.
Grinding of teeth, especially at night. A bad bite, or malocclusion, can cause children to grind their teeth; a dentist may recommend a bite plate to protect the teeth from damage at night or may refer the patient to an orthodontist to correct the problem. Bruxism can also result from tension or from worms.
Rhythmic or spasmodic grinding of the teeth, especially during sleep; often caused by emotional tension.
Teeth-clenching or-grinding, usually occurring during sleep.
A habit of grinding the teeth, usually while asleep and without being aware of it. The teeth may feel uncomfortable on wakening. It is common in children and is usually of no significance. In adults it may be associated with stress or a malpositioned or overfilled tooth. The underlying cause should be treated but, if unsuccessful, a plastic splint can be fitted over the teeth.
Involuntary habit of excessive teeth clenching or grinding that can lead to abrasive wear on the teeth, headaches, and/or temporomandibular pain and dysfunction syndrome.
The persistent act of involuntarily clenching and grinding one’s teeth, particularly occurring during periods of sleep.
Bruxism refers to the rhythmic grinding or clenching of teeth, typically occurring during sleep. The primary factors contributing to this condition are emotional stress and slight discomfort when the teeth come into contact with each other. Prolonged bruxism can lead to the gradual wearing down of teeth.