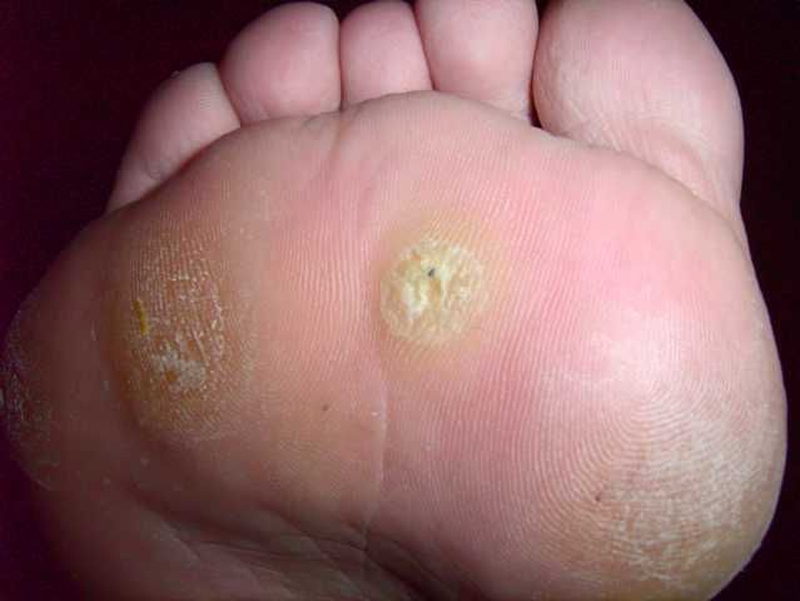
 A wart on the sole of the foot.
A wart on the sole of the foot.
Wart occurring on the sole of the foot that, because of pressure, develops a callus (hardened) ring around its soft center and becomes painful. Treatment includes cryosurgery, electrodesiccation (cauterization), and application of topical acids.
Viral lesion on the foot.
A hard, rough-surfaced area on the sole of the foot that is caused by a virus.
A wart occurring in the skin on the sole of the foot, usually at the base of the toes.
A wart on a pressure bearing area, especially the sole of the foot.
A tough, calloused, and rough patch found on the sole of the foot is the result of an infection by a virus known as a papillomavirus. These growths, commonly referred to as plantar warts or verrucas, can appear individually or in groups. The wart typically becomes flattened and embedded within the skin, potentially causing discomfort or pain during walking. Most often, these infections are acquired from contaminated surfaces in places like swimming pool areas and communal showers.
Numerous plantar warts may naturally vanish over time, yet some endure for extended periods or temporarily vanish only to reappear. These warts can be eliminated through cryosurgery or by using adhesive plasters or gels containing salicylic acid.
A viral skin growth that typically develops on the underside of the foot. This type of wart is often sensitive to pressure and can cause pain while walking. It is also referred to as verruca plantaris.