Author: Glossary
-
Netherton syndrome ichthyosis
Netherton syndrome (NS) is a rare, congenital, hereditary disorder characterized by ichthyosis (an abnormality of skin development that manifests as scaling and redness), several distinct anomalies of hair, and a tendency toward a variety of allergic illnesses. Skin findings are usually evident within two weeks after birth.
-
Lamellar recessive ichthyosis
Lamellar ichthyosis (LI) is one of the two major forms of hereditary, autosomal recessive, congenital disorders of keratinization, the process by which skin tissues form and are eventually shed from the body’s surface. Abnormalities are present at birth or shortly thereafter. The incidence of LI has not been determined. The mode of inheritance is autosomal…
-
Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans ichthyosis
Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans (KFSD) is a form of ichthyosis characterized by hardening of the skin around the hair follicles eventually leading to baldness (alopecia) and scarring. During infancy, keratosis begins on the face and moves to the extremities and trunk by childhood. Around puberty, alopecia of the scalp and eyebrows develops. KFSD is a…
-
Harlequin type ichthyosis
Harlequin fetus (HF) is a rare disorder of keratinization, the process by which skin tissue forms and eventually sloughs off the body. It most likely represents several genetic mutations that have common clinical findings.
-
Erythrokeratolysis hiemalis ichthyosis
Erythrokeratolysis hiemalis (EH) or keratolytic winter erythema (KWE) is an autosomal dominant skin disorder characterized by circles of erythema (redness or inflammation of the skin) and hyperkeratosis (excessive skin lesions in which there is overgrowth and thickening of the skin). With age, the symptoms grow milder, eventually disappearing all together. This disorder is mostly seen…
-
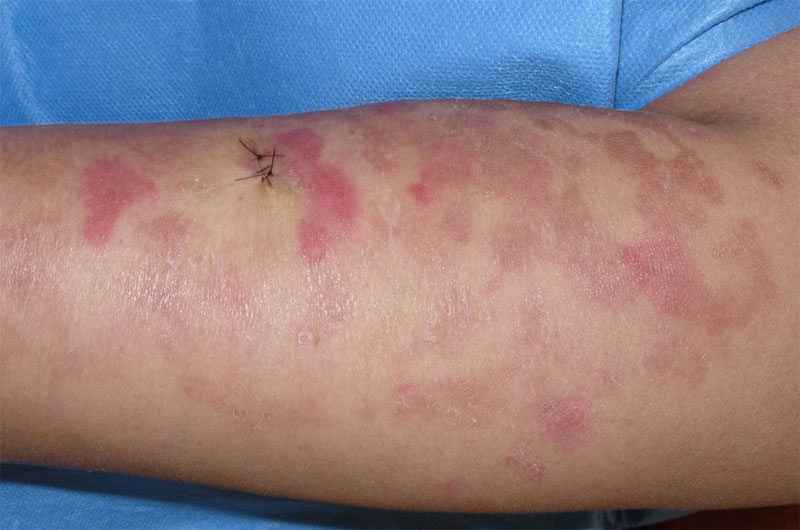
Ichthyosis erythrokeratodermia variabilis
Ichthyosis erythrokeratodermia variabilis (IEV) is one of a diverse group of disorders of skin keratinization (the process in which skin cells form and are eventually shed). It is distinguished from the other members of the ichthyosis group by its unique clinical features and pattern of inheritance.
-
Erythrokeratodermia progressiva symmetrica ichthyosis
A form of ichthyosis, erythrokeratodermia progressiva symmetrica (EPS) is a very rare hereditary skin disorder characterized by keratotic (hardened red) plaques distributed over the body and the extremities. However, the chest and abdomen area are normally void of any plaques. Cornification normally appears during the first year of life; some cases involving EPS have been…
-
Ichthyosis congenita
Ichthyosis congenita is an inherited skin disorder characterized by generalized dry and rough skin. All babies who suffer from an autosomal recessive congenita ichthyosis are collodion babies at birth. Collodion babies are born with a translucent or opaque membrane that covers the entire body and lasts for days to weeks. Congenita ichthyosis presents on a…
-
Child syndrome ichthyosis
CHILD (congenital hemidysplasia with ichthyosis erythroderma and limb defects) syndrome is an inherited disorder that is usually present at birth. It is characterized by skin anomalies and limb defects on one side of the body.
-
Chanarin dorfman syndrome
Chanarin Dorfman syndrome is a hereditary disorder of lipid metabolism almost always accompanied by dry, scaly skin (ichthyosis). Myopathy (degeneration of the muscles) and fat deposits appearing in the white blood cells also are commonly seen in patients with Chanarin Dorfman syndrome. This is a highly uncommon autosomal recessive genetic condition that impacts fat metabolism.…