Category: A
-
Architecture
A term with an appropriate modifier, commonly used in periodontics to describe gingival and/or bony form.
-
Arch length discrepancy
An incongruent relationship between the arch size of the maxilla or mandible and the teeth present as viewed from the occlusal plane.
-
Arch form
The outline of the dental arch as viewed from a horizontal plane (i.e., ovoid, square, or tapered). The shape of the dental arch when viewed in the horizontal plane.
-
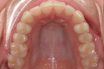
Arch, dental
The curved composite structure of the natural dentition and the alveolar ridge, or the residual bone after the loss of some or all of the natural teeth.
-
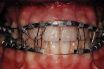
Arch bar
A rigid bar or wire used to stabilize teeth and implants and used for intraarch fixation in the treatment of fractures of the maxilla or mandible.
-
Arch
Bony arc formed by the maxillary or mandibular teeth or residual ridge when viewed occlusally. A curved part of the body, especially under the foot. Bowlike structure or part (e.g., maxillary arch, structure that forms the palate). Any anatomical structure having a curved or bowlike outline.
-
Arachidonic acid
A 20‐carbon essential fatty acid that contains four double bonds (5, 8, II, 14‐ eicosatetraenoic acid); the precursor of prostaglandins, prostacyclins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. Along chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (C20:4 006). A 20-carbon atom of fatty acid with four double bonds. In the body, it is synthesized from the essential fatty acid, linoleic acid. Long…
-
AP spread (abbrev)
Anteroposterior spread.
-
Approximation
The state of being near or close together, as in root approximation. In psychology, shaping.
-
Apoptosis
Morphologic pattern of cell death affecting single cells and marked by shrinkage of the cell, condensation of chromatin, formation of cytoplasmic blebs, and fragmentation of the cell into membrane‐bound apoptotic bodies that are eliminated by phagocytosis. One of the two mechanisms by which cell death occurs (the other being the pathological process of necrosis). Apoptosis…