Category: C
-
Caproic acid
A short-chain fatty acid (C6:0).
-
Capric acid
A medium-chain fatty acid.
-
Canthaxanthin
A red carotenoid pigment which is not a precursor of vitamin A.
-

Canola
A variety of rape which is low in glucosinolates. Canola oil (canbra oil) contains less than 2% erucic acid. Brassica napus or Brassica campestris strains of the rapeseed plant, which were developed by plant breeders after the 1 960’s. This was because oil produced from rapeseed grown prior to 1971 contained 30%-60% erucic acid (high…
-

Canbra oil (canola oil)
Oil extracted from selected strains of rapeseed containing not more than 2% erucic acid. Oil from the rapeseed plant. An oil extracted from a variety of the rapeseed plant renamed canola; good source of a-linolenic acid, an unsaturated fatty acid of the omega 3 family. A light, clear oil derived from the pods of an…
-
Calorimetry
The measurement of energy expenditure by the body. Direct calorimetry is the measurement of heat output from the body, as an index of energy expenditure, and hence requirements. The measurement of heat energy liberated or absorbed in metabolic processes. The measurement of heat change in a person or system. The measurement of heat produced by…
-
Calorimeter (bomb calorimeter)
An instrument for measuring the amount of oxidisable energy in a substance, by burning it in oxygen and measuring the heat produced. An instrument used to measure the amount of heat produced by a weighted sample of food, and thus the food’s energy value. An instrument for measuring the amount of heat produced by a…
-
Calcitriol
The 1,25-dihydroxy-derivative of vitamin D, also known as 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol; the active metabolite of the vitamin. The active hormone form of vitamin D that promotes the absorption of calcium and phosphate in the intestines, decreases calcium excretion by the kidneys, and acts along with parathyroid hormone to maintain bone homeostasis.
-
Calcioi
The official name for cholecalciferol, the naturally occurring form of vitamin D (vitamin D3).
-
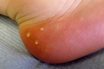
Calcinosis
Abnormal deposition of calcium salts in tissues. May be due to excessive intake of vitamin D. A medical condition where deposits of calcium salts form in joints, muscles and organs. Calcification of the skin and other soft tissues, which particularly affects the skin of the hands. Calcinosis is characterized by swollen hands, pinpicks of red…