Category: C
-
Cross‐sectional slice
A thin, reformatted section of computed tomography scan data representing the alveolar process perpendicular to a panoramic curve of the patient’s mandible or maxilla.
-
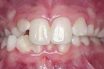
Cross‐bite occlusion
Occluding tooth contact in which the natural or artificial mandibular teeth overlap the maxillary teeth. Also called reverse articulation.
-
Cross‐bite
A dental condition where a mandibular tooth is located facial to the opposing tooth. Normal dentition locates the mandibular dentition lingual to the maxillary dentition.
-
Cross‐arch stabilization
Resistance against dislodging or rotational forces obtained by using a partial removable dental prosthesis design that uses natural teeth on the opposite side of the dental arch from the edentulous space to assist in stabilization.
-
Cross‐arch balanced articulation
The simultaneous contact of the buccal and lingual cusps of the working side maxillary teeth with the opposing buccal and lingual cusps of the mandibular teeth, concurrent with contact of the nonworking side maxillary lingual cusps with the mandibular buccal cusps.
-
Crohn’s disease
Also known as regional enteritis, a chronic, granulomatous disease of unknown cause involving any part of the gastrointestinal tract, but commonly involving the terminal ileum. Oral lesions may be granulomatous in nature. A chronic inflammatory disease of the digestive tract, particularly the small intestine and colon. Chronic inflammatory disease of the bowel, of unknown origin,…
-
Critical‐size(d) defect (CSD)
Smallest osseous defect that does not completely heal by spontaneous bone regeneration. Its size varies by anatomic location and species.
-
Critical bending moment
The moment at which the external nonaxial load applied overcomes screw joint preload, causing loss of contact between the mating surfaces of the dental implant screw joint components.
-
Cribriform plate
In dentistry, the alveolar bone proper. Another example is the horizontal plate of bone of the ethmoid sinus, which is perforated by numerous foramina that allow passage of nerves through the bone. The top part of the ethmoid bone which forms the roof of the nasal cavity and part of the roof of the eye…
-
Cribriform
Perforated like a sieve, for example, the cribriform plate of the ethmoid sinus. Having small holes like a sieve.