Category: F
-
Fibrous encapsulation
Layer of fibrous connective tissue formed between a dental implant and surrounding bone.
-
Fibrous ankylosis
Decreased movement of a joint due to proliferation of fibrous tissue. Ankylosis due to the formation of fibrous bands within a joint.
-
Fibrous adhesion
A fibrous band or structure by which parts not normally connected adhere to each other.
-
Fibrous
Composed of or containing fibers. Composed of or resembling fibers. (Of flesh of cap or stem) Composed of stringlike, rather tough tissue. Made of fibres, or like fibre.
-
Fibrosis
A subsurface collagenous soft tissue replacement that occurs as a result of chronic inflammation. The tissue appears and feels thick and dense. Fibrosis may occur as a result of chronic inflammation around dental implants that support prosthetic crowns. The tissue becomes thick and enlarges with collagen deposition in the surrounding gingival tissue. There is usually…
-
Fibroosseous integration
Direct attachment of bone to fibrous tissue without a definable intervening tissue. Compare: Osseointegration. The interposition of healthy dense collagenous tissue between implant and bone. Also known as fibroosteal integration.
-
Fibronectin
Adhesive glycoprotein with a high molecular weight (450 kD), composed of two disulfide‐linked polypeptides. Functional domains of the molecule have an affinity for cells and the extracellular matrix components. It is found on cell surfaces, in connective tissues, blood, and other body fluids. Fibronectins are important in connective tissue, where they cross‐link to collagen, promote…
-
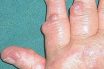
Fibromatosis
Group of tumor‐like lesions that have an infiltrative nature and can be locally aggressive, making them difficult to remove completely. They can recur following surgery but do not metastasize to other parts of the body. Fibromatoses have also been known to undergo spontaneous regression and completely disappear. The simultaneous development of many fibromata. The formation…
-
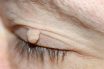
Fibroma
Fibrous connective tissue that is a benign neoplasm; peripheral. A benign type of growth composed of fibrous tissue. A small benign tumor formed in connective tissue. Nonmalignant tumor of connective tissue. A benign or nonmalignant tumor composed largely of fibrous connective tissue. These smooth, usually painless, growths under the skin or in the bone are…
-
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF)
Family of growth factors with mitogenic properties for fibroblasts and mesoderm‐derived cell types. They have important roles in angiogenesis, neurogenesis, wound healing, and tumor growth. In humans, more than 20 proteins have been identified as members of the FGF family. FGF‐2, or basic FGF (bFGF), has been the most studied member of the FGF family…