Category: G
-
Group function
Multiple contact relations between the maxillary and mandibular teeth in lateral movements on the working side whereby simultaneous contact of several teeth acts as a group to distribute occlusal forces.
-
Groove
A long narrow channel or depression, such as the indentation between tooth cusps or the retentive features placed on tooth surfaces to augment the retentive characteristics of crown preparations. Narrow channel or depression in a structure; for example, the costal groove lodges the blood vessels and nerves between two ribs.
-
Grit blasting
Delivery to a dental implant surface of a high‐velocity stream of abrasive particles propelled by compressed air, designed to increase surface area.
-
Grit‐blasted implant surface
Modification of an implant or other surface through the application of sand, aluminum oxide, or other abrasive material by intense air pressure.
-
Grinding‐in
A term used to denote the act of correcting occlusal disharmonies by grinding the natural or artificial teeth (GPT‐1).
-
Gray (Gy)
A unit of absorbed radiation dose equivalent to 100 rad.
-
Granulomatous tissue
A distinctive morphologic pattern of inflammation consisting of histiocytes that have been transformed into epithelioid cells that are surrounded by mononuclear cells, usually lymphocytes.
-
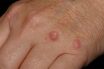
Granuloma
A reactive nodule consisting of modified macrophages resembling epithelial cells surrounded by a rim of mononuclear cells, usually lymphocytes, and often containing giant cells. A relatively small nodular inflammatory lesion containing grouped mononuclear phagocytes, caused by infectious and noninfectious agents. One of a variety of growths of inflamed, granular-appearing tissue. Infiltration of tissue phagocytes, producing…
-

Granulation tissue
Healing tissue that forms in response to any injury or surgical insult of soft tissue and consists of fibroblasts, capillary buds, inflammatory cells, and edema. A mixture of proteins and cells produced by the fibroblast growth that results from a wound. A growth of young capillaries and fibrous tissue cells which is the basis for…
-
Gram positive
Pertaining to bacteria that stain deep purple with Gram stain. These bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer but no lipopolysaccharide in their cell walls. Retaining the stain or resisting decolorization by alcohol in Gram’s method of staining, a primary characteristic of bacteria whose cell wall is composed of a thick layer of peptidologlycan with attached…