Category: L
-
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
A reproductive hormone that acts upon the ovaries to stimulate ovulation. It is secreted by the pituitary gland. This is a sugar-bearing protein manufactured by the anterior pituitary. Like a lot of the pituitary hormones, it surges on and off, since constant secretion would overload and deaden receptors. In women, it builds up after menses,…
-
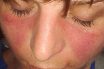
Lupus
An autoimmune disease of the body, in which anti-DNA antibodies bind to DNA. The resulting complexes (of DNA and antibodies) travel to the kidneys via the bloodstream, and become lodged in kidneys, where they cause inflammatory reactions (that can lead to kidney failure). A chronic disease of unknown cause, which can cause changes in many…
-
Lumen
The interior (opening through which blood flows) e.g., within a blood vessel. Space within an artery, vein, intestine, or other tubular structure. The cavity or channel within a blood vessel. An SI unit of light emitted per second. The inside width of a passage in the body or of an instrument such as an endoscope.…
-
LPAAT Protein
A protein consisting of lysophosphatidic acid acyl transferase (enzyme), which (when present in plant) causes production of triglycerides (in the seeds) possessing saturated fatty acids in the “middle position” of the triglycerides’ molecular (glycerine) “backbone.” For example, canola (rapeseed) plants genetically engineered to contain LPAAT protein are able to produce high levels of saturated fatty…
-
LOX Null
Refers to soybeans that do not contain lipoxygenase enzymes (thus, they result in a “null” test reading).
-
Low-tillage crop production
A methodology of crop production in which the farmer utilizes a minimum of mechanical cultivation (i.e., only two to four passes over the field instead of the conventional five passes for traditional crop production). The plant residue remaining on field’s surface helps to control weeds and reduce soil erosion, but it also provides sites for…
-
Low-stachyose soybeans
Those soybean varieties that contain lower levels of the relatively indigestible stachyose carbohydrate (and thus higher levels of easily digestible other nutrients) than traditional varieties of soybeans. Low-stachyose soybeans are particularly useful for feeding of monogastric animals (e.g., swine, poultry).
-
Loop
A single-stranded region at the end of a hairpin in RNA (or single-stranded DNA). It corresponds to the sequence between inverted repeats in duplex DNA. A curve or bend in a line, especially one of the particular curves in a fingerprint. A curved piece of wire placed in the uterus to prevent contraception. A bend…
-
Locus
The position of a gene on a chromosome. The position on a chromosome that is occupied by a gene. An area or point where an infection or disease is to be found. A position on a chromosome occupied by a gene. The position of a chromosome occupied by a gene or its allele. Loci, specific…
-
Liposomes
Also called lipid vesicles or vesicle. Aqueous (i.e., watery) compartments enclosed by a lipid bilayer. They can be formed by suspending a suitable lipid, such as phosphatidyl choline, in an aqueous medium. This mixture is then sonicated (i.e., agitated by high-frequency sound waves) to give a dispersion of closed vesicles (i.e., compartments) that are quite…