Category: L
-
Leukotoxin
A toxin produced by certain bacteria, including Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, which is toxic to leukocytes, particularly polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Also known as leukocidin.
-
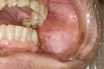
Leukoplakia
A nonspecific white patch in the oral cavity which will not rub off. Condition characterized by white spots or patches on mucous membranes, especially of the mouth and vulva. A white patch that may develop on mucous membranes such as the cheek, gums, or tongue and may become cancerous. A precancerous condition in which white…
-
Leukopenia
Reduction in the number of leukocytes in the blood below 5000 per cubic mm. A decrease in the number of circulating white blood cells. A decrease below normal levels in the number of white blood cells (leukocytes), most commonly provoked by certain drugs, such as anticonvulsants. Also known as neutropenia. An abnormally low number of…
-
Leukocyte
Blood cell that is colorless, lacks hemoglobin, and contains a nucleus. Leukocytes are involved with host defense and are classified in two large groups: granular leukocytes (basophils, eosinophils, and neutrophils) and nongranular leukocytes (lymphocytes and monocytes). Called also white blood cell. White blood cell (WBC). There are five types of leukocytes: three granulocytes with granules…
-
Leukemia
A generalized neoplastic disorder of the blood‐forming tissues, primarily those of the leukocyte series. Cancer of blood-forming tissue. A progressive, maglinant disease of the blood-forming organs, marked by distorted proliferation and development of leukocytes and their precursors in the blood and bone marrow. Cancer of the blood and lymphatic systems. There are two kinds of…
-
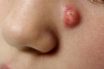
Lesion
Any pathological change to a tissue or organ, local in nature, caused by injury, surgical procedures, chemicals, or infection that may result in a loss of normal function. An area of abnormal tissue change. Any discontinuity or disruption of tissue caused by disease or trauma. A break in the cellular integrity of a tissue or…
-
Leptotrichia ssp
Gram‐negative, nonmotile, anaerobic, rod‐shaped bacteria found in marginal and subgingival plaque.
-
Lengthening of the clinical crown
A surgical procedure performed to increase the extent of supragingival tooth structure by apically repositioning the gingival tissue around the tooth; often includes removing a portion of the surrounding alveolar bone. This procedure is typically performed for restorative or esthetic purposes.
-

Leaf gauge
A device consisting of a set of blades or leaves of graduated thicknesses that is placed in the oral cavity to make accurate measurements between two points or to provide a metered separation.
-
Le Fort osteotomy
Surgical sectioning of the maxilla from the rest of the skull. Le Fort I osteotomy sections the midface through the walls of the maxillary sinuses, the lateral nasal walls, and the nasal septum, just superior to the apices of the maxillary teeth. Le Fort II osteotomy is similar to Le Fort I, except that instead…