Category: P
-
Pyorrhea
A description of periodontal disease, not in common use. A purulent discharge that contains or consists of pus. A lay term for gum disease. A pus release often associated with gum inflammation and decay of tooth sockets. It progressively worsens, often requiring the extraction of all teeth.
-
Pyogenic
Pus‐producing substance or agent. Producing pus; pyopoietic (= liquid inflammation product made up of cells and a thin fluid called liquor puris). Causing the formation of pus. Pyogenic bacteria include Staphylococcus aureus. Streptococcus hemolyticus, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. A term applied to those bacteria which cause the formation of PUS and so lead to the formation…
-
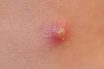
Pustule (pyloric sphincter)
A reaction of tissue to infection that results in a small superficial elevation caused by the collection of pus under the skin. Small, inflamed, pus-filled lesions. Pimple, blister. A small, circumscribed elevation of the skin containing pus. Small, raised area of the skin filled with pus or lymph. Lower opening of the stomach leading into…
-
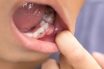
Pus
A generally viscous, yellowish‐white fluid formed in infected and inflamed tissue consisting of white blood cells, cellular debris, necrotic tissue, and bacteria. A mixture of white blood cells and cellular debris resulting from an infection and inflammation. A yellow liquid composed of blood serum, pieces of dead tissue, white blood cells and the remains of…
-
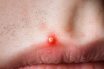
Purulent
Accompanied by or containing pus. Conditions that discharge pus or cause the production of pus; also, human secretions that consist of pus or contain pus. Purulent may describe an inflammation, a wound, or an infection that produces pus.
-
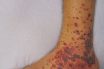
Purpura
Hemorrhage into the tissues with resultant large discoloration (greater than 2 mm in diameter) that does not blanch on pressure. Initial discoloration is red/purple, but later it becomes brown‐yellow as it fades away. Is the appearance of red or purple discolorations on the skin that do not blanch on applying pressure. Also called peliosis. A…
-
Pumice
Sand‐like volcanic glass that is used as a polishing agent in dentistry. Different sized particles proceeding from coarser to finer are used to progressively smooth a hard surface. Materials polished may include natural tooth structure, acrylic, and other restorative materials. An abrasive polishing agent derived from volcanic material. Pumice consists chiefly of complex silicates of…
-
Pulsed mode
Type of operation in which the laser emits radiation energy in the form of pulses.
-
Pulpotomy (pulp amputation)
The surgical removal of the coronal portion of a vital pulp to preserve the vitality of the remaining radicular portion. A partial removal of pulp, the soft tissue that is located in the crown section of the tooth. A pulpotomy is generally performed on the primary tooth of a child to save the tooth until…
-
Pulpitis
A state of inflammation of the dental pulp that can be reversible or nonreversible. Characterized by odontalgia, necrosis of the pulp, and inflammation of the periodontal membrane. In advanced stages, an abscess will form. Pulpitis is the inflammation of the dental pulp, which encompasses the blood vessels and nerves within a tooth. Inflammation of the…