Category: P
-
Positive architecture
When the crest of the interdental gingiva or bone is located coronal to its midfacial midlingual margins.
-
Positioned flap
A flap that is moved apically, coronally, or laterally to a new position.
-
Positional record
Documentation that uses intraoral and extraoral registrations to capture a specified mandibular position.
-
Porphyromonas gingivalis
A gram‐negative, nonmotile, rod‐shaped anaerobic bacterium from the phylum Bacteroidetes. Commonly found in subgingival dental plaque, it is an etiologic agent in the development of chronic periodontal disease. A member of the red complex bacteria.
-
Porous coralline hydroxyapatite
Bone substitute developed from the Porites or Goniopora coral, in which the CaCO3 skeleton of the coral is converted via a hydrothermal process into a hydroxyapatite (HA) substitute with trace levels of beta‐tricalcium phosphate. It is nonresorbable but osteoconductive because of the nonending porous structure.
-
Porous
Property of allowing ingress of fluid or gas within a material or surface; spongelike quality. Full of holes. Containing pores. Referring to tissue which allows fluid to pass through it. Made or constructed of a material that has pores or openings. Porous items are absorbent.
-
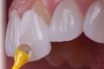
Porcelain laminate veneer
A thin bonded ceramic restoration that restores the facial surface and part of the proximal surfaces of teeth requiring esthetic restoration.
-
Porcelain fracture
The cohesive failure of porcelain. Etiology of the fracture may be imperfections or stresses residual from fabrication, incompatibility with substrate (thermal coefficient of expansion), substructure deformation because of misfit or inadequate structural integrity, or overload caused by occlusion or trauma.
-
Porcelain
A ceramic material formed of infusible elements joined by lower fusing materials. Most dental porcelains are glasses and are used in the fabrication of teeth for dentures, pontics and facings, metal ceramic restorations including fixed dental prostheses, as well as all‐ceramic restorations such as crowns, laminate veneers, inlays, onlays, and other porcelain‐fused‐to‐metal restorations. A hard,…
-
Pontic
An artificial tooth on a fixed dental prosthesis that replaces a missing natural tooth, restores its function, and usually fills the space previously occupied by the clinical crown. An artificial tooth set in a bridge.