Category: R
-
Radiation absorbed dose
A unit of radiation exposure that measures the absorbed dose. The absorption of 100 erg per gram by material exposed to ionizing radiation. The rad is a unit of energy absorbed and therefore differs from the roentgen. The quantity of ionizing radiation, measured in rad or gray (Gy), absorbed by any material per unit mass…
-
Rotator cuff tendonitis
Inflammation of the tendons of the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, or subscapular muscles of the shoulder. A common cause of shoulder pain, thought to be due to inflammation of the intrinsic tendons of the shoulder, esp. that of the supraspinatus. The onset usually follows injury or overuse during activities involving repeated overhead arm motions, as…
-
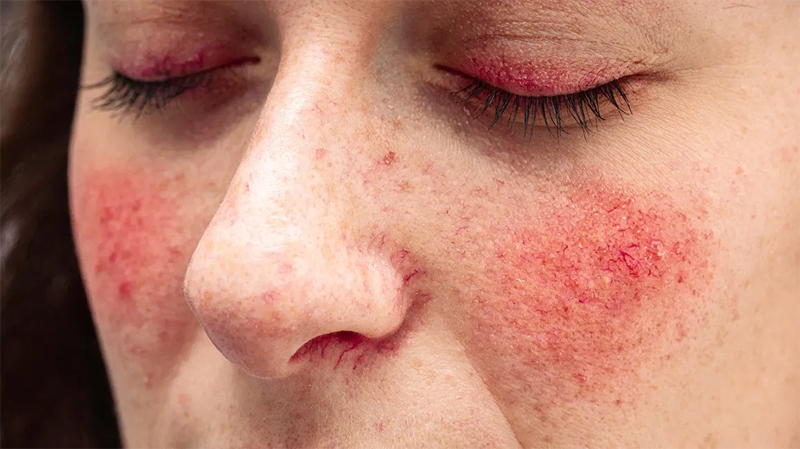
Rosaceiform
The red mask appearance of cheeks, nose, and skin; typical of rosacea.
-
Rosacea
Chronic, noninfectious skin disorder marked by redness on the cheeks, nose, and chin. A skin disease characterized by varying degrees of facial redness due to enlargement and dilation of blood vessels beneath the skin surface; also known as adult acne. Common signs of rosacea are redness, pimples, and the appearance of spidery small blood vessels…
-
Right lung
Structure of respiration located in the right chest and comprised of the superior and inferior lobes.
-
Right coronary artery
Artery supplying blood to the heart tissue. An artery which derives from the right aortic sinus. It supplies blood to the right ventricle, the right atrium, and often, the inferior or posterior wall of the left ventricle of the heart.
-
Right atrioventricular valve
Valve between the right ventricle and the right atrium; tricuspid valve.
-
Rhomboideus muscle
Muscle that raises and adducts the scapula.
-
Rhinorrhagia
Profuse bleeding from the nose.
-
Rheumatic heart
Damage to heart valves as a result of rheumatic fever.