Category: R
-
Ruffini cylinder
A receptor thought to correspond to warmth.
-
Rudiment
A part or organ that is not fully developed. Remains of a body part that was functional at an earlier stage of life; for example, Meckel’s diverticulum is the rudiment of the embryonic yolk stalk.
-
Rubin’s test
A procedure to check for obstructed fallopian tubes. Carbon dioxide is inserted into the uterus to determine whether it passes into the abdomen. A test to see if the Fallopian tubes are free from obstruction [After Isador Clinton Rubin (b. 1883), US gynaecologist]. Test that determines the patency of the fallopian tubes, used to help…
-
Rubeola
One form of measles caused by a virus and tends to last for 1-3 weeks. Characterized by nasal discharge, reddened eyes, swollen eyelids, fever, cough, Koplik’s spots on the buccal surfaces of the mouth, and a red skin rash. Alternate term for measles, as opposed to rubella (German measles).
-
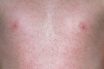
Rubella
One form of measles caused by a virus and characterized by fever, skin rash, sore throat, and other symptoms, lasting from about 3 days to 1 week is most dangerous during the first trimester of pregnancy as it can cause miscarriage, stillbirth, or birth defects. The disease can be prevented by inoculating females before they…
-
Rubefaction
A condition of inducing increased blood flow and a redness to the skin, such as with a counterirritant drug.
-
Resistance transfer factor
Bacterial epi-some associated with resistance to certain antibiotics. A genetic factor in bacteria that controls resistance to certain antibiotic drugs. The factor may be passed from one bacterium to another. This makes it possible for nonpathogenic bacteria to become resistant to antibiotics and to transfer that resistance to pathogens, thereby establishing a potential source for…
-
Route of administration
The method by which a drug is introduced into the body.
-
Round shoulders
A defect in posture in which the tips of the shoulders are drawn forward in front of the gravity line.
-
Roughage
Dietary fiber. Undigestible fibres and starches found particularly in cereals, fruits and vegetables which, though not nutritious, help the movement of food down the digestive tract, and contribute to easy passage of stools by keeping them bulky and soft. A coarse, bulky food, high in fiber, which is nondigestible and stimulates bowel movement: e.g.. cellulose.…