Category: R
-
Ridge augmentation
A procedure used to increase the size, shape, or quality of an edentulous dental ridge or space that has typically lost ideal contour after loss of the dentition (or failure to develop dentition). In periodontics, increasing the width or height of the bony foundation (the alveolar ridge) in which the teeth are seated. The procedure…
-
Ridge atrophy
Decrease in volume of a ridge due to resorption of bone.
-
Ridge
The remainder of the alveolar process after tooth extraction. A long raised part on the surface of a bone or organ. Projecting edge, crest, or rim (e.g., pectoral ridge, crest of the largest tubercle in the bone of the upper part of the arm). An elongated projecting structure or crest.
-
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
RNA component of the ribosome that provides a mechanism for translation of messenger RNA (decoding) during protein synthesis. The nucleic acid component of ribosomes, making up two-thirds of the mass of the bacteria Escherichia coli ribosome, and about one-half of the mass of mammalian ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA accounts for nearly 80 percent of the RNA…
-
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
Polymer composed of ribonucleotides; three types of RNA function in translation of information from genes (DNA) to proteins. In some viruses, RNA is also the genetic material. One of the two nucleic acids found in all cells. The other is deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Ribonucleic acid transfers genetic information from DNA to proteins produced by the…
-
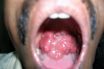
Rhinosporidiosis
In immunocompromised individuals, this disease is caused by Rhinosporidium seeberi, which is a Candida species responsible for oral mycoses and may cause oral infections (thrush) in AIDS patients or other debilitated humans. Candida species are designated as “opportunistic” pathogens since they are often found as members of the normal oral flora. An infection of the…
-
RhBMP (abbrev)
Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein.
-
RFA (abbrev)
Resonance frequency analysis.
-
Revolutions per minute (RPM)
Speed at which a shaft turns. It is recorded as the number of complete (360°) revolutions the shaft makes in a minute.
-
Reversible splint
A device used for, or method of, splinting or fixing teeth that does not change or alter the structure of the involved teeth.