Category: R
-
Resorbable
The ability of an autogenous graft to dissolve physiologically. Natural or synthetic material that can be removed by a cellular process, osteoclasts, or foreign body giant cells and macrophages.
-
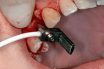
Resonance frequency analysis (RFA)
Determination of the relative stiffness of an implant within the bone via attachment of a resonance frequency transducer containing two piezoceramic elements to an implant. One piezo element is excited by an electrical signal, and the resulting vibration is measured by the second element. The higher the resulting frequency (in kHz), the stiffer the implant‐to‐bone…
-
Resolution
In dentistry or medicine, the return to health or improvement of a pathologic state. In digital imaging, a pixel that is the smallest recognizable point found in the master image. The subsidence of an inflammatory process. The amount of detail which can be seen in a microscope or on a computer monitor. A point in…
-
Resistance form
The features of a tooth preparation that enhance the stability of a restoration and resist dislodgment along an axis other than the path of placement.
-
Resistance
Ability of a human, organism, or inert material to resist the damaging effects of chemical, microbiological, or mechanical agents. The force to be overcome by a lever. One’s conscious or unconscious psychological defense against bringing repressed (unconscious) thoughts into conscious awareness. In weight lifting, the weight to be lifted or the work load. The ability…
-
Resin crown
A resin restoration that restores a clinical crown without a metal substructure.
-
Resin‐bonded splint
A fixed splint made of heavy wire, fibrous resin materials and/or cast metal that is bonded to the labial or lingual surface of natural teeth with an acid etch technique. It is used to stabilize traumatically displaced or periodontal compromised teeth.
-
Resin
Organic substance that forms a plastic material following polymerization initiated by heat or chemical activation. It is usually transparent or translucent, not water soluble, and named according to chemical composition, physical structure, or means of activation or curing. Hardened exudate from wounded stem or leaves that is soluble in alcohol but not in water. A…
-
Resilient attachment
A special attachment intended to give a combination tooth and soft tissue‐borne removable dental prosthesis sufficient flexure to allow for its placement without introducing unnecessary stress on the abutments.
-
Residual ridge resorption
The phenomenon of diminishing volume and density of the residual ridge after the teeth are removed.