Category: S
-
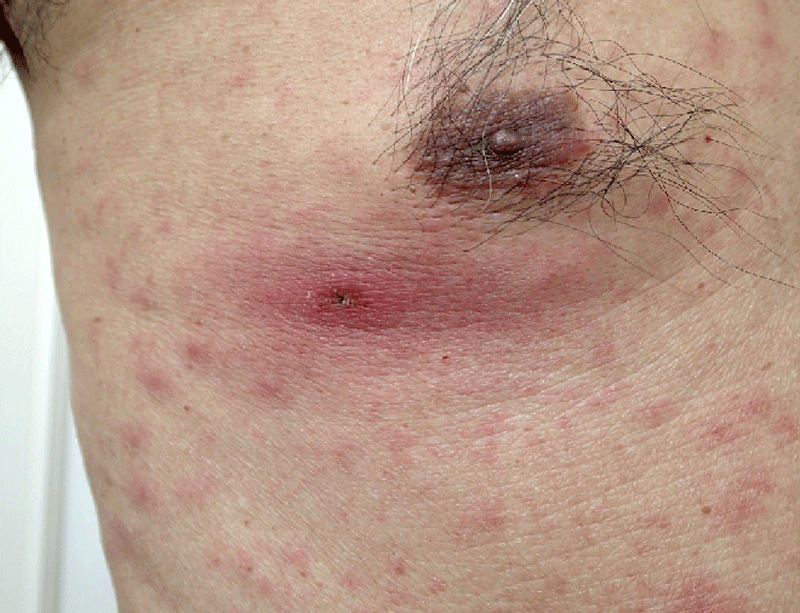
Scrub typhus
Disease of eastern Asia, surrounding islands, and Australia, caused by Rickesttsia organisms transmitted to humans by mites. Symptoms include a dark lesion at the site of the bite, lymph node enlargement, fever, muscle ache, rash, and in severe cases cardiovascular and nervous system involvement. A disease, widely distributed in SE Asia, caused by the parasitic…
-
Scopolamine patch
Small transdermal disc that contains the medication scopolamine and is placed behind the ear to prevent motion sickness; the disc delivers the medication over a period of three days; side effects include blurred vision, dryness of the mouth, and drowsiness.
-
Scavenger
Drug or cell that removes disintegrated tissues or abnormal compounds in the body. Anti-oxidant drugs function as free-radical scavengers, removing them from the body. Certain types of white blood cells remove foreign material or bacteria from the body, much as a scavenger bird would clean the carcass of a dead animal.
-
Sanitarium
Institution for treatment of persons with long-term or chronic disorders. Prior to modem antibiotics, persons with tuberculosis were placed in a TB sanitarium. Also, colloq. for an institution that treats persons with mental disorders. An institution for the treatment and recuperation of persons having physical or mental disorders. Promoting, to conditions that are conducive to…
-
Salivary duct
Duct through which saliva passes from a Salivary gland to the mouth. A duct is a passageway that facilitates the transportation of saliva from the salivary gland to the mouth. This slender tube plays a vital role in the oral cavity by conveying the saliva produced by the salivary glands to its intended destination. It…
-
Salicylate poisoning
Toxic condition caused by the ingestion of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) or other salicylates; it is characterized by vomiting, headache, rapid breathing, tinnitus, low blood sugar, electrolyte imbalance, and in severe cases by convulsions, respiratory arrest, and death. Treatment includes induced emesis and/or gastric lavage, saline cathartics, correction of electrolyte imbalance, and possibly dialysis. Some physicians…
-
Safe sex
Use of sexual practices believed to decrease the chances of acquiring sexually transmitted diseases, esp. acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Generally, this involves avoidance of promiscuity, abstinence from orogenital and rectal sex, and the use of condoms. A term used to describe any sexual activity that poses no risk of contracting or transmitting a sexually…
-
Sacral vertebra
Any of the five segments of the vertebral column that fuse in the adult to form the sacrum. One of the five fused vertebrae forming the sacrum.
-
Cervical disc syndrome
Abnormal condition caused by compression of cervical (neck region) nerve roots, resulting from trauma or degenerative disease or other factors, that produces pain in the neck region, often radiating to the shoulder, arm, and hand, paresthesia, and some muscular weakness. Treatment may involve analgesics, immobilization of the area to allow rest, traction, and, if severe,…
-
Synthetic media
Culture media of defined and reproducible chemical composition, used for research purposes. Such media consist of simple sources of carbon and nitrogen plus trace elements. The metabolism of a given bacterium can thereby be studied by the omission or substitution of specific growth factors, such as amino acids, minerals, vitamins or carbohydrates.