Category: V
-
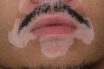
Vitiligo
A chronic skin disease that causes loss of pigment, resulting in irregular pale patches of skin. It occurs when the melanocytes, cells responsible for skin pigmentation, die or are unable to function. Also called leucoderma. A condition in which destruction of melanocytes in small or large circumscribed areas results in patches of depigmentation often having…
-
Vitamin P
A substance or mixture of substances obtained from various plant sources, identified as citrin or a mixture of bioflavonoids, thought to but not proven to be useful in reducing the extent of hemorrhage.
-

Vitamin K
A group of fat soluble vitamin and consist of vitamin K1 which is also known as phylloquinone or phytomenadione (also called phytonadione) and vitamin K2 (menaquinone, menatetrenone). Vitamin K plays an important role in blood clotting. Deficiency is very rare but can cause bleeding diathesis. Mostly fat-soluble and heat stable. Essential for normal blood clotting.…
-

Vitamin E (Tocopherols)
Is the collective name for a group of fat-soluble compounds and exists in eight chemical forms (alpha-, beta-, gamma-, and delta-tocopherol and alpha-, beta-, gamma-, and delta-tocotrienol). It has pronounced antioxidant activities stopping the formation of Reactive Oxygen Species when fat undergoes oxidation and help prevent or delay the chronic diseases associated with free radicals.…
-

Vitamin D
A group of fat-soluble, prohormone vitamin, the two major forms of which are vitamin D2 (or ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (or cholecalciferol). Vitamin D obtained from sun exposure, food, and supplements is biologically inert and must undergo two hydroxylations in the body for activation. Vitamin D is essential for promoting calcium absorption in the gut…
-
Vitamin B12
A water-soluble vitamin, also called cobalamin as it contains the metal cobalt. It helps maintain healthy nerve cells and red blood cells, and DNA production. Vitamin B12 is bound to the protein in food. Deficiency causes megaloblastic anaemia. Water-soluble, heat stable in neutral solutions. Essential for normal development of red blood cells and treatment of…
-
Vitamin B9
Also called folic acid, an essential water-soluble vitamin. Folate is especially important during periods of rapid cell division and growth such as infancy and pregnancy. Deficiency during pregnancy is associated with birth defects such as neural tube defects. Folate is also important for production of red blood cells and prevent anemia. Folate is needed to…
-
Vitamin B 7
Also called biotin or vitamin H, an essential water-soluble vitamin, is involved in the synthesis of fatty acids amino acids and glucose, in energy metabolism. Biotin promotes normal health of sweat glands, bone marrow, male gonads, blood cells, nerve tissue, skin and hair, Deficiency causes dermatitis and enteritis.
-
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
Water-soluble vitamin, exists in three major chemical forms: pyridoxine, pyridoxal, and pyridoxamine. Vitamin B6 is needed in enzymes involved in protein metabolism, red blood cell metabolism, efficient functioning of nervous and immune systems and hemoglobin formation. Deficiency causes anaemia and peripheral neuropathy. Soluble in water, stable to heat, but not light. Functions as a co-enzyme.…
-
Vitamin B5
Also called pantothenic acid, a water-soluble vitamin that function as coenzyme in fatty acid metabolism. Deficiency causes paresthesia. A vitamin that acts as an immune stimulant, It also stimulates the production of adrenal chemicals important for healthy nerves. Vitamin B5 can improve the body’s ability to withstand stressful conditions. It is found in offal, brewers’…