Category: X
-
Xiphoid process
The bottom part of the breastbone which is cartilage in young people but becomes bone by middle age. Smallest of the three parts of the sternum (breastbone), articulating with the body of the sternum and with the seventh rib. The lowermost section of the breastbone: a flat pointed cartilage that gradually ossifies until it is…
-
Xiphisternal plane
An imaginary horizontal line across the middle of the chest at the point where the xiphoid process starts.
-
Xenotransplantation
The process of transplanting organs from one species to another, especially from animals to humans. Transplantation of organs from one species to another for example, from pigs to humans. The use of organs from appropriately cloned animals was seen as a possible solution to the shortage of human organs for transplantation. However, research has shown…
-
Xanthopsia
A disorder of the eyes, making everything appear yellow. Abnormality of vision in which objects appear to have a yellowish hue; sometimes occurring in jaundice or drug toxicity. The condition in which all objects appear to have a yellowish tinge. It is sometimes experienced in digitalis poisoning. A condition in which objects appear to be…
-
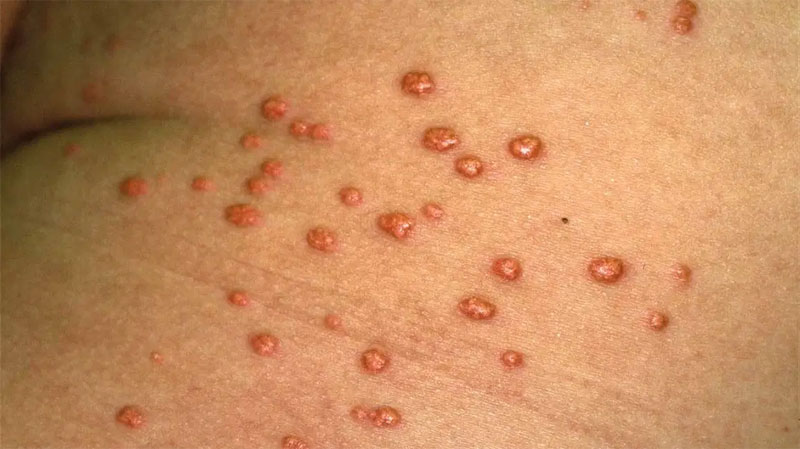
Xanthomatosis
A condition in which several small masses of yellow fatty substance appear in the skin or some internal organs, caused by an excess of fat in the body. Condition in which a disorder of lipid metabolism leads to the formation of yellowish fatty deposits in the skin and internal organs. A condition in which fatty…
-
Xanthochromia
Yellow colour of the skin as in jaundice. A test done on CSF to determine whether yellow color—due to a breakdown of red blood cells—is present, which may indicate hemorrhage, jaundice, very high protein levels, or a traumatic spinal tap. Yellow discoloration, such as may affect the skin (for example, in jaundice) or the cerebrospinal…
-
Xyletol
A sugar alcohol. made from birch trees, with sweetness equal to that of sucrose and caloric values the same as glucose. No longer used in the United States.
-
X-linked gene
A gene known to be located on the X chromosome. A gene on the X chromosome for which there is no corresponding gene on the Y chromosome. X-linked genes (e.g., the gene for red-green color blindness) are expressed but in males even these genes are recessive because there is no corresponding gene to dominate them.…
-
Xiphoid
The smallest and most dependent part of the breast bone.
-
Xerosis
An abnormal dryness, as in conjunctiva or skin. Extreme dryness of skin or mucous membrane. Abnormal dryness of the conjunctiva, the skin, or the mucous membranes. Xerosis affecting the conjunctiva is due not to decreased production of tears but to changes in the membrane itself, which becomes thickened and gray in the area exposed when…