 An enterovirus occasionally found in association with ulcerative oral lesions.
An enterovirus occasionally found in association with ulcerative oral lesions.
Any of a group of viruses that produce a variety of symptoms and diseases including the common cold, meningitis, pericarditis, and myocarditis. Infection occurs primarily in the summer months.
Any of a group of viruses that cause a variety of infectious diseases, including a mild form of meningitis and hand-foot-and-mouth disease. The most common symptoms of an infection include flulike malaise, fever, and muscle aches. There may also be coughing, nasal congestion, diarrhea, and vomiting.
Any of a group of viruses, the first of which was isolated in 1948 from two children in Coxsackie, New York. There are 23 group A and 6 group B coxsackieviruses. Most coxsackievirus infections in humans are mild, but the viruses produce a variety of important illnesses, including aseptic meningitis, herpangina, epidemic pleurodynia, epidemic hemorrhagic conjunctivitis, acute upper respiratory infection, and myocarditis.
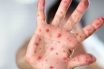
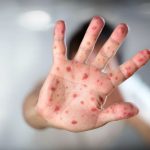
Within the family of viruses known to cause a wide array of diseases, coxsackieviruses hold a significant position. These viruses can be broadly classified into two main types: A and B. Among the type A infections, the most familiar one is hand, foot, and mouth disease, a prevalent childhood ailment characterized by the formation of blisters around the mouth, hands, and feet. On the other hand, type B viruses have the potential to induce severe illnesses such as meningitis, pericarditis, and pneumonia.