Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-
Accompaniments
Salads, bread, vegetables, pickles, jams or relishes items that accompany the main meal.
-
Acceptance number (C)
The maximum number of deviants permitted in a sample of a lot that meets a specification.
-
Acceptance
An experience, or feature of experience characterized by a positive attitude. May be measured by preference or liking for specific food item. The process in qualitative research by which subjects being observed become sufficiently accustomed to the observer that their behavior is normal, qualitative evaluation; qualitative variable. According to Dr. Elisabeth Kubler-Ross, the fifth and…
-
Acceptable quality level (AQL)
Minimum number of parts or containers that must comply with quality standards.
-
Absorbent
A substance having the ability to soak up and retain other substances. An agent that takes up water or fluid and increases in bulk, adsorbent. An agent that binds chemical substances to its surface, absorbent. Being capable of adsorption.
-
Xylose
Pentose (five-carbon) sugar found in plant tissues as complex polysaccharide; 40% as sweet as sucrose. Also known as wood sugar. Pentose which has not been metabolised. A pentose sugar (i.e. one with five carbon atom’s) that is involved in carbohydrate interconversions within cells. A sugar containing five carbon atoms involved in the metabolic conversion of…
-
Xylitol
A five-carbon sugar; said to have an effect in suppressing the growth of some of the bacteria associated with dental caries. Sugar-alcohol (polyol). A five-carbon sugar alcohol that has a sweet taste and has chemical properties similar to those of sucrose. It may be used in place of sucrose as a sweetener. The use of…
-
Xanthosis
Yellowing of the skin associated with high blood concentrations of carotene. Yellow colouring of the skin, caused by eating too much food containing carotene. Abnormal yellowish discoloration. A yellowing of the skin seen in carotenemia resulting from ingestion of excessive quantities of carrots, squash, egg yolk, and other foods containing carotenoids. The condition is usually…
-
Xanthophylls
Yellow-orange hydroxylated carotene derivatives. The yellow-orange pigments found in plant foods such as corn, peaches and squash. A yellow pigment found in green leaves. An example of a xanthophyll is lutein. A yellow pigment derived from carotene. It is present in some plants and egg yolk.
-
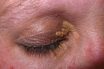
Xanthelasma
Yellow fatty plaques on the eyelids, due to hypercholesterolaemia. The formation of little yellow fatty tumours on the eyelids. Condition marked by the formation of yellowish fatty deposits around the eyes, occurring chiefly in the elderly. A yellow-orange bump beneath the surface of the skin (xanthoma) on the eyelids made of cholesterol deposits. Xanthelasmas are…
Got any book recommendations?