The act of squeezing a passage in the body.
Constriction of a tubular structure that prevents passage of material; for example, strangulation of the bowel prevents the passage of feces. Also refers to constriction of the blood supply to an organ, resulting in lack of oxygen, such as a strangulated hernia.
Strata, layer of tissues or cells (e.g., the layers of the skin).
Interruption of blood supply to a loop of intestine trapped inside a hernia (a protrusion of soft tissue through the muscle wall that normally contains it). Symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. A strangulated hernia often requires emergency surgery. Otherwise, gangrene (death of tissue) may develop.
The closure of a passage, such as the main airway to the lungs (resulting in the cessation of breathing), a blood vessel, or the gastrointestinal tract.
The constriction of a passage or tube in the body that blocks the blood flowing to and from it, and thus disturbs the working of the affected organ. It is usually caused by compression or twisting. Strangulation customarily occurs when part of the intestine herniates either inside the abdomen or outside as in an inguinal hernia. If a section of the intestine twists, this may strangulate and is known as a volvulus.
The compression or constriction of a part, as the bowel or throat, causing suspension of breathing or of the passage of contents. Congestion accompanies this condition.
Ischemia is a condition characterized by the compression or constriction of a blood vessel, segment of the intestine, or another body part to such an extent that adequate blood circulation is impeded.
The narrowing, typically caused by twisting or compression, of a tube or passage within the body obstructs blood circulation and disrupts the normal functioning of the organ involved. An instance of this could be strangulation linked to a hernia.
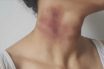
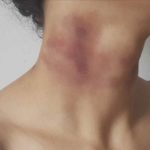
Strangulation of the neck is a critical, life-endangering incident, either unintentional or intentional, that entails the compression of the jugular veins, impeding the outward flow of blood from the brain, along with constriction of the windpipe that hampers normal breathing. This situation leads to the victim losing consciousness, followed by brain impairment and ultimately, demise due to oxygen deprivation.
The action of blocking or obstructing, resulting in the stoppage of blood flow to a specific area.