Author: Glossary
-
Intestinal pseudo-obstruction
Intestinal pseudo-obstruction (IPO) is a congenital digestive disorder resulting from the inability of the intestines to move food through the digestive tract. The intestine may be abnormally formed, and peristalsis (involuntary wave-like contractions that propel food through the digestive system) is absent or lacking. This condition resembles a true obstruction of the intestine, but no…
-
Insatiable child syndrome
Insatiable child syndrome is characterized by a chronic inability to be satisfied. Usually the child craves specific foods, certain activities, attention from others, or material goods. The child’s insatiability may be organic or could be learned, such as when humiliating experiences leave the child feeling useless and craving for the attention of others.
-
Inhalant abuse
Inhalant abuse involves the voluntary inhalation of gases or fumes in an effort to achieve an intoxicated state. These substances include many household products that are legal to buy and possess, including such things as airplane glue, nail polish remover, and propellants used in certain commercial products, such as whipped cream dispensers. Generally, the vapors…
-
Infantile hypercalcemia
Infantile hypercalcemia, or Williams syndrome, is a congenital disorder that affects a child’s cognitive, physical, and behavioral development. It has been linked to the absence of genetic material on Chromosome 7. The deletion of portions of this chromosome, where elastin is made, results in many of the physical features seen in Williams syndrome.
-
Incontinentia pigmenti
Incontinentia pigmenti (IP) is a rare, hereditary disorder with abnormalities in the skin, skin derivatives (hair, nails, and teeth), eyes, skeleton, and nervous system. The original cases were described in 1925 and occurred in twin sisters. Since then, several hundred affected individuals have been reported.
-
Iga nephropathy
IgA nephropathy (IgAN) is an endochrine (renal) disorder of unknown cause. IgAN occurs when deposits of the protein immunoglobulin A (IgA) enter the kidneys. The IgA protein interrupts the filtering process of the kidneys, causing blood and protein to build in the urine and resulting in swelling of the feet and hands. As this condition…
-
X-linked ichthyosis
X-linked ichthyosis (XLI) is a hereditary disorder of the skin that affects males almost exclusively. Female carriers of the abnormal gene may occasionally demonstrate clinical findings. Corneal opacities (clouding of the clear part of the eyeball that overlies the iris) and cryptorchism (undescended testicles) are also commonly seen in patients with XLI. Ichthyosis (reddened, scaling…
-
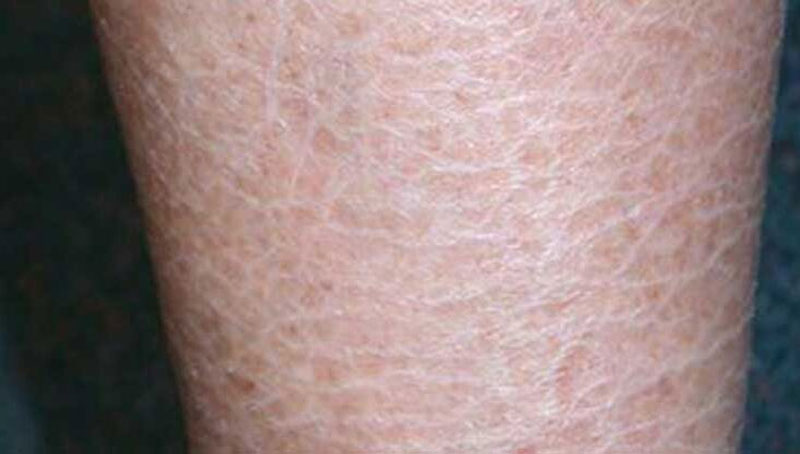
Ichthyosis vulgaris
Ichthyosis vulgaris (IV) is one of a heterogeneous group of disorders of skin cornification or keratinization (the process in which skin cells are produced and eventually shed). It is typified by a specific pattern of scaling of the skin and a unique form of inheritance. A condition characterized by dry, rectangular scales on the skin…
-
Tay syndrome ichthyosis
Tay syndrome is a hereditary disorder characterized by trichothiodystrophy (brittle, sulfur-deficient hair) and dry, scaly skin (ichthyosis). Males and females are equally affected, and Tay syndrome is believed to be an autosomal recessive trait.
-
Sjoren-larsson syndrome ichthyosis
Sjoren-Larsson syndrome (SLS) is a hereditary disorder of the skin and central nervous system. It is characterized by ichthyosis (red, scaly patches of skin), mental retardation, and spasticity (increased muscle tone). A deficiency of the enzyme fatty aldehyde dehydrogenase is the primary defect in SLS.