Category: A
-
Alkali (or base)
A compound that takes up hydrogen ions and so raises the pH of a solution. A compound that reacts with acid to form salt and water, acid.
-
Aldosterone
A steroid hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex; controls the excretion of salts and water by the kidneys. A hormone from the adrenal gland that causes the kidney to retain sodium and excrete potassium. An adrenal hormone that plays a major role in the regulation of sodium and potassium metabolism. A hormone secreted by the…
-
Alcohol units
For convenience in calculating intakes of alcohol, a unit of alcohol is defined as 8 g (10 ml) of absolute alcohol. A unit is a commonly utilized measure to quantify the alcohol content in a single alcoholic beverage. It is defined as 10 milliliters of pure alcohol. To determine the number of units in a…
-
Additive
Any compound not commonly regarded or used as a food which is added to foods as an aid in manufacturing or processing, or to improve the keeping properties, flavour, colour, texture appearance, or stability of the food, or as a convenience to the consumer. The term excludes vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients added to enrich…
-
Acute phase reaction
Increase or decrease in the concentration of certain proteins, or other substances, including micronutrients, in blood serum, following infections or tissue- inflammatory reactions. This reaction represents the body’s normal response in counteracting the deleterious effects of a noxious stimulus, but the changes in distributions of proteins and nutrients between body compartments can confound attempts to…
-
Acute phase proteins
A variety of serum proteins synthesised in increased (or sometimes decreased) amounts in response to trauma and infection, so confounding their use as indices of nutritional status. Blood proteins produced in the liver that function in the innate immune response. APPs are important in the response to infection and inflammation. Any of the plasma proteins…
-
Active transport
Energy-requiring transport of solutes across cell membranes, against the prevailing concentration gradient. Cell-mediated, energy-requiring translocation of a molecule across a membrane in the direction of increasing concentration (i.e., opposite of natural tendency). In physiology, an energy- producing process by which certain nutrients are pumped from one compartment to another against a concentration gradient. Active transport…
-
Acrylamide
A chemical that can be generated when the amino acid asparagine is heated above 100°C in the presence of sugars. The amide of acrylic acid, C3H5NO. Acrylamide is used in many types of gel electrophoresis to separate and to identify proteins.
-
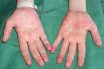
Acrodynia
Dermatitis seen in animals deficient in vitamin B6. There is no evidence for a similar dermatitis in deficient human beings. A disease of infancy and early childhood marked by pain and swelling in, and pink coloration of, the fingers and toes and by listlessness, irritability, failure to thrive, profuse, perspiration, and sometimes scarlet coloration of…
-
Acrodermatitis enteropathica
Severe functional zinc deficiency due to failure to secrete an as yet unidentified compound in pancreatic juice that is required for zinc absorption. Rare disease in children aged 3 weeks to 18 months that may be fatal if untreated. The genetically determined cause is malabsorption of zinc. Onset is insidious with failure to thrive, diarrhea,…