Category: A
-
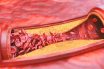
Atherosclerosis
Form of arteriosclerosis characterized by the deposition of atheromatous plaques containing cholesterol and lipids on the innermost layer of the walls of large‐ and medium‐sized arteries. The condition in which an artery wall thickens as the result of a build-up of fatty materials such as cholesterol. Hardening of the arteries. A form of arteriosclerosis in…
-
Asymmetry
Absence or lack of symmetry or balance; dissimilarity in corresponding parts or organs on opposite sides of the body. Differences in corresponding parts on opposite sides of body. Lack of mirror-image correspondence between paired parts or normally similar sides of a body or organ (e.g., having one hand or a side of the face that…
-
Asymmetrical
Characterized by or pertaining to asymmetry. Irregular; not divided into like and equal parts. With the two sides of an organ unequal in size.
-
Astringent
An agent that causes contraction of the tissues, arrests secretion, or controls bleeding. A substance that contracts blood vessels and certain body tissues (such as mucous membranes) with the effect of reducing secretion and excretion of fluids and/or has a drying effect. Tightens mucous membranes and skin, reducing secretions and bleeding from abrasions. (Taste) making…
-

Aspergillus
Fungus responsible for maxillary sinus fungal infections (aspergillosis). A genus of fungi, including many common molds, some of which cause infections of the respiratory system in man. The species A. fumigatus causes aspergillosis. A. niger is commonly found in the external ear and can become pathogenic. A group of fungi including the common moulds. Several…
-

Aseptic
Free from infection or septic material; sterile, free from pathogenic microorganisms. Free of disease or spoilage causing organisms. Free from contamination by hannful bacteria, viruses or other micro-organisms. Sterilised, or involving sterilisation, and therefore without infection. Sterile; absence of pathogens. Devoid of microorganisms that can cause illness.
-
Asepsis
Free from infection. The prevention of contact with microorganisms. The absence of viable organisms. The complete absence of bacteria, fungi, viruses, or other microorganisms that could cause disease. Asepsis is the ideal state for the performance of surgical operations and is achieved by using sterilization techniques. A technique to produce a germ-free environment to protect…
-
Asaccharolytic
The inability of an organism to catabolize carbohydrates. Generally relates to sugar metabolism.
-

Artificial limb
Artificial replacement for part or all of a human arm or leg. A manufactured prosthetic replacement for an arm or leg, worn when all or part of the limb has been lost due to injury, accident, disease, or birth defect. A person requiring an artificial limb can discuss his or her needs and preferences with both…
-
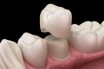
Artificial crown
A metal, plastic, or ceramic restoration that covers three or more axial surfaces and the occlusal surface or incisal edge of a tooth artificial denture. A replacement for the loss of the natural crown of a tooth. There are several types, usually made of porcelain or plastic. For example, the sheath like jacket crown covers…