Category: B
-
Biuret test
A chemical test for proteins based on the formation of a violet colour when copper sulphate in alkaline solution reacts with a peptide bond. A method for measuring protein in the serum. The presence of biuret can be detected by the addition of sodium hydroxide and copper sulfate solutions to the sample. A rose to…
-
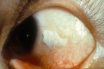
Bitot’s spots
Irregularly shaped foam-like plaques on the conjunctiva of the eye, characteristically in vitamin A deficiency, but not considered to be a diagnostic sign without other evidence of deficiency. Small white spots on the conjunctiva, caused by vitamin A deficiency [Described 1863. After Pierre A. Bitot (1822-88), French physician.] Shiny foam-like spots on the white of…
-
Bisfuran polycyclic compounds
Compounds with several rings including more than two 5-membered oxygen-containing rings.
-
Birth canal
The bony birth canal comprises the passage through the pelvic bones; there is a soft tissue component to the birth canal in the form of the vagina and its supporting tissues. The uterus, vagina and vulva. The widened cervix and vagina through which a baby passes on its way from the uterus during childbirth. Passage…
-
Biological value (BV)
The proportion of absorbed nitrogen that is retained for maintenance and/or growth. An index of protein value or quality that reflects the percentage of absorbed dietary nitrogen used by the body. The efficiency of utilization of a protein by the body, expressed as a percentage of the food nitrogen retained to the food nitrogen absorbed.…
-
Bioinformatics
The application of computational techniques to extract meaning from complex biological data. The utilization of computer science to gather, categorize, and scrutinize biochemical and genetic data.
-
Biofortification
Food fortification achieved by plant breeding or genetic modification to give a higher content of nutrients.
-
Bio-electrical impedance (BIE)
Amethod of measuring the proportion of fat in the body by the difference in the resistance to passage of an electric current between fat and lean tissue.
-
Biocytin
The main form of the vitamin biotin in most foods, bound to the amino acid lysine.
-
Bioassay
Biological assay; measurement of biologically active compounds (e.g. vitamins and essential amino acids) by their ability to support growth of microorganisms or animals. A test which uses animals or microorganisms for determining the biological activity of certain substances or the presence or concentration of nutrients in the food. Determination of the relative strength or bio-activity…