Category: C
-
Clinical crown
The portion of a tooth that projects above the free gingival margin. The portion of the natural tooth that is exposed in the mouth, from the gingiva to the occlusal plane or the incisal edge.
-
Clinical attachment level
Distance from the cementoenamel junction or implant collar to the tip of a periodontal probe during soft tissue diagnostic probing. Health of the attachment apparatus can affect the measurement.
-
Clindamycin
Lincosamide antibiotic used in the treatment of orofacial infections caused by anaerobic bacteria. It is also active against aerobic bacteria, such as streptococci and staphylococci. Alternative drug used for antibiotic prophylaxis. Pseudomembranous colitis has been reported as a common side effect (0.01–10%) of patients taking this medication. A powerful antibiotic used to treat severe infections…
-
Clicking
A series of clicks, such as the snapping, cracking, or noise evident on excursions of the mandible; a distinct snapping sound or sensation, usually audible (or by stethoscope) or on palpation, which emanates from the temporomandibular joint(s) during jaw movement. It may or may not be associated with internal derangements of the temporomandibular joint.
-

Cleft lip and/or palate
Most common craniofacial anomaly, occurring 1 in 600–700 live births, characterized by failure of fusion between embryologic processes during facial morphogenesis. Failure of fusion between the medial and lateral nasal and the maxillary processes results in a cleft of the lip and/or alveolar process, whereas failure of fusion between the lateral palatine processes results in…
-
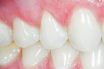
Cleft, gingival
A vertical opening, slit, or fissure in the gingiva.
-
Clearance
A physical state in which physical masses may pass each other without interference. The gap between two bodies. A measure of the body’s ability to eliminate a drug. The process by which the active form of the drug is removed from the bloodstream by either metabolism or excretion. Removal of something, as of wastes, from…
-
Clean technique
Surgical procedure that takes place in a clinic setting. All instruments, implants, grafts, and irrigation solution used are sterile. Surgeons wear sterile gloves, but hospital operating room‐level sterility is not achieved. The surgeons and assistants wear nonsterile attire and the patient is not necessarily covered by sterile drapes.
-
Clavulanic acid
A beta‐lactamase inhibitor sometimes combined with penicillin group antibiotics to overcome certain types of antibiotic resistance. Co-amoxiclav, an antibiotic medication, is formed by combining the penicillin drug amoxicillin with another substance.
-
Clasp
The component of the clasp assembly that engages a portion of the tooth surface and either enters an undercut for retention or remains entirely above the height of contour to act as a reciprocating element. Generally, it is used to stabilize and retain a removable dental prosthesis. A device for holding objects or tissues together.…