Category: D
-
Dyskinesia
The impairment of the power of voluntary movement, resulting in fragmentary or incomplete movements. Any disturbance of movement; may be induced by medication. Poor coordination, clumsy, inappropriate movements in a person without detectable cerebral palsy. The inability to control voluntary movements. Dyskinesia is a collection of movement disorders involving impairment of central nervous system motor…
-
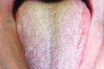
Dysgeusia
Any change, disturbance or distortion in the sense of taste. Impaired taste. Also known as parageusia. Distortion of the sense of taste – a common side-effect of some drugs. Abnormal taste perception. Impairment or perversion of the gustatory sense so that normal tastes are interpreted as being unpleasant or completely different from the characteristic taste…
-
Dysfunction
To not function properly or normally as a cell or within an organ. In dentistry, a dysfunction means any abnormality between the physical nature of the teeth, bones, or joints within the oral cavity and their function as mediated through muscles or nerves affecting the oral cavity and causing abnormal functioning. Abnormal functioning of a…
-
Dysesthesia
An abnormal and unpleasant sensation that is either spontaneous or evoked. Dysesthesia includes paresthesia but not vice versa. An unpleasant abnormal sensation produced by normal stimuli. Perception of an irritating sensation in response to normal stimuli due to nerve dysfunction. Experiencing difficulty in performance of voluntary movements. The abnormal and sometime unpleasant sensation felt by…
-
Dynamic relations
Relations of two objects involving the element of relative movement of one object to another, as the relationship of the mandible to the maxillae.
-
Dynamic loading
Situation in which the loading of an implant is continually changing, as would happen during occlusal function. Both the magnitude and direction of applied force are in constant flux.
-
DXA (abbrev)
Dual‐energy X‐ray absorptiometry.
-
Durometer
An instrument that measures the hardness of a material.
-
Duplicate denture
A second denture that is identical in all aspects to the in‐use or functioning denture.
-
Ductility
The ability of a material to withstand permanent deformation under a tensile load without rupture; ability of a material to be plastically strained in tension. A material is brittle if it does not have appreciable plastic deformation in tension before rupture.