Category: E
-
Endometrial
Having to do with the endometrium (the layer of tissue that lines the uterus). To toe endometrium, toe mucous membrane lining of the uterus (e.g., endometrial carcinoma, cancer of uterine lining). Related to the endometrium, the inner lining of the uterus.
-
Endocardium
The innermost layer of the heart, comprised of endothelial cells. A membrane which lines the heart. Membrane that lines the chambers of the heart and the heart valves. A delicate membrane, formed of flat endothelial cells, that lines the heart and is continuous with the lining of arteries and veins. At the openings of the…
-
Encapsulated
Confined to a specific, localized area and surrounded by a thin layer of tissue. Enclosed in a capsule or in a sheath of tissue. Confined; surrounded by an envelope, capsule, or membrane. Said of certain tumors, abscesses, and medications.
-
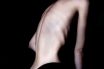
Emaciation
Clinical manifestation of excessive leanness usually caused by disease or a lack of nutrition. Extreme thinness and wasting, caused by disease or undernutrition. The fact of being extremely thin and underweight. The loss of body tissue. Excessive thinness, due to disease (e.g., tuberculosis, cancer) or poor nutrition. Wasting of the body, caused by such conditions…
-
Electroporation
A technique in which electric pulses of intensity in kilovolts per centimeter and of microsecond-to-millisecond duration cause a temporary loss of the semipermeability of cell membranes, thus leading to ion leakage, escape of metabolites, and increased uptake by cells of drugs, molecular probes, and DNA. Some applications of electroporation include introduction of plasmids or foreign…
-
Electrophoresis
An electrochemical process in which macromolecules or colloidal particles with a net electric charge migrate in a solution under the influence of an electric current. A technique for separating molecules based on the differential movement of charged particles through a matrix when subjected to an electric field. The term is usually applied to large ions…
-
Electrons
Stable elementary particles having the smallest known negative charge, present in all elements; also called negatrons. Positively charged electrons are called positrons. The numbers, energies and arrangement of electrons around atomic nuclei determine the chemical identities of elements. Beams of electrons are called cathode rays or beta rays, the latter being a high-energy biproduct of…
-
Elastin
The protein that gives flexibility to tissues. A protein which occurs in elastic fibres. A protein found in connective tissue, ligaments, and vascular tissues. Rich in lysine and glycine. It is a very elastic protein. Connective tissue protein that forms elastic fibers in tissue, particularly the middle layer of arteries (media). Protein forming the major…
-
Efficacy
The extent to which a specific intervention, procedure, regimen, or service produces a beneficial result under ideal conditions. Ideally, the determination of efficacy is based on the results of a randomized control trial. The extent to which an intervention can be shown to be beneficial under optimal conditions. Commonly used synonymously with effectiveness , but…
-
Effector
It is often an enzyme that converts an inactive precursor molecule into an active second messenger. A class of(usually small) molecules that regulates the activity of a specific protein (e.g., enzyme) molecule by binding to a specific site on the protein. Control of (existing) enzyme molecules may be achieved by combination of the effector with…