Category: I
-
Intubation
Refers to the placement of a tube into an external or internal orifice of the body. The act of inserting a tube into the larynx to relieve a respiratory obstacle. The therapeutic insertion of a tube into the larynx through the glottis to allow the passage of air. Placement of a tube into an opening,…
-
Intromission
The act of putting one thing into another. Insertion of the penis into the vagina. The insertion of the penis into the vagina sexual intercourse. The introduction of one organ or part into another, e.g. the penis into the vagina. The introduction of one organ or part into another. An example is the insertion of…
-
Intraperitoneal (IP)
The term used when a chemical is contained within or administered through the peritoneum (the thin, transparent membrane that lines the walls of the abdomen). Inside the peritoneal cavity of the abdomen. Given that the entire abdomen is lined with peritoneum, this essentially means within the abdomen.
-
Intoxicant
Substance that produce drunkenness or intoxication. A substance which induces a state of intoxication or poisoning, e.g. an alcoholic drink.
-
Intima
Innermost layer of an artery or vein. The lining of an artery. Innermost lining of a part, especially of a blood vessels. The inner layer of the wall of an artery or vein. It is composed of a lining of endothelial cells and an elastic membrane. The innermost coat lining the arteries and the veins.…
-
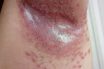
Intertrigo
An inflammation (rash) caused by microbial infection in skin folds. An eruption of the skin due to chafing. Irritation of skin due to rubbing of opposing surfaces. An irritation which occurs when two skin surfaces rub against each other, as in the armpit or between the buttocks. Irritation of two skin surfaces that are in…
-
Interstitium
The space between cells in a tissue.
-
Intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDL)
Is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins (chylomicrons, VLDL, IDL, LDL, HDL) that enable fats and cholesterol to move within the water based solution of the bloodstream. IDL is further degraded to form LDL particles and, like LDL, can also promote the growth of atheroma and increase cardiovascular diseases.
-
Interleukin 8 (IL-8)
A cytokine produced by macrophages and other cell types such as epithelial cells and is one of the major mediators of the inflammatory response.
-
Interleukin-6 (IL-6)
An interleukin that acts as both a pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine. A cytokine (glycoprotein) that is pleiotropic (i.e., stimulates several different types of immune system cells); and is a hematopoietic growth factor.