Category: L
-
Lenticular opacity
Also known as or related to cataract.
-
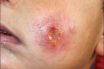
Leishmaniasis
A disease caused by protozoan parasites that belong to the genus Leishmania and is transmitted by the bite of certain species of sand fly. Infection with Leishmania, a parasitic protozoa. A disease caused by the parasite Leishmania, one form of which causes disfiguring ulcers, while another attacks the liver and bone marrow. Infection, most common…
-

Lectins
Are sugar-binding proteins that are highly specific for their sugar moieties. They play a role in biological recognition phenomena involving cells and proteins. Carbohydrate-binding proteins. Proteins from legumes and other sources which bind to the carbohydrates found at cell surfaces. They therefore cause red blood cells to agglutinate in vitro, hence the old names haemagglutinins…
-
LDL receptor (LDLr)
A low-density lipoprotein receptor gene.
-
Laxation
Bowel movement.
-
Laryngitis
Is an inflammation of the larynx. Inflammation of the lining of the larynx causing hoarseness. Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the larynx and swelling of the vocal cords, characterized by loss or hoarseness of voice, cough, and sometimes difficult breathing. It may be acute, caused by bacterial or viral infection or irritation (e.g., from…
-
Larvacidal
An agent which kills insect or parasite larva.
-
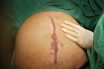
Laparotomy
A surgical procedure involving an incision through the abdominal wall to gain access into the abdominal cavity laparotomized. A type of tubal ligation procedure. A surgical operation to cut open the abdominal cavity. Any surgical procedure in which an incision is made into the abdominal wall, often done for exploration (e.g., to examine abdominal organs).…
-
LAK cell
A lymphokine-activated killer cell i.e. a white blood cell that has been stimulated to kill tumour cells.
-
Lactic acidosis
Is a condition caused by the buildup of lactic acid in the body. It leads to acidification of the blood (acidosis), and is considered a distinct form of metabolic acidosis. Condition where lactate levels are elevated above normal; occurs in the muscles of exercising people, in uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, and also in patients with mitochondrial…