Category: T
-
Traveler’s diarrhea
Diarrhea caused by ingesting contaminated water or food while traveling in areas with poor sanitation. Abdominal cramps, fever, dehydration, nausea, and vomiting may also occur. In many cases, over-the-counter medications control diarrhea. Dehydration can be treated by drinking adequate clear liquids. Because watery diarrhea can rapidly cause a loss of body fluids and crucial body…
-
Type A botulinum toxin
A neurotoxin produced by certain strains of the bacterium Clostridium botulinum, also known as botulism toxin. When consumed in food, botulinum toxin, type A can cause paralysis and death. The neurotoxins produced by Clostridium botulinum are among the most potent poisons known. In a purified form, botulinum toxin, type A (known as Botox) has been…
-
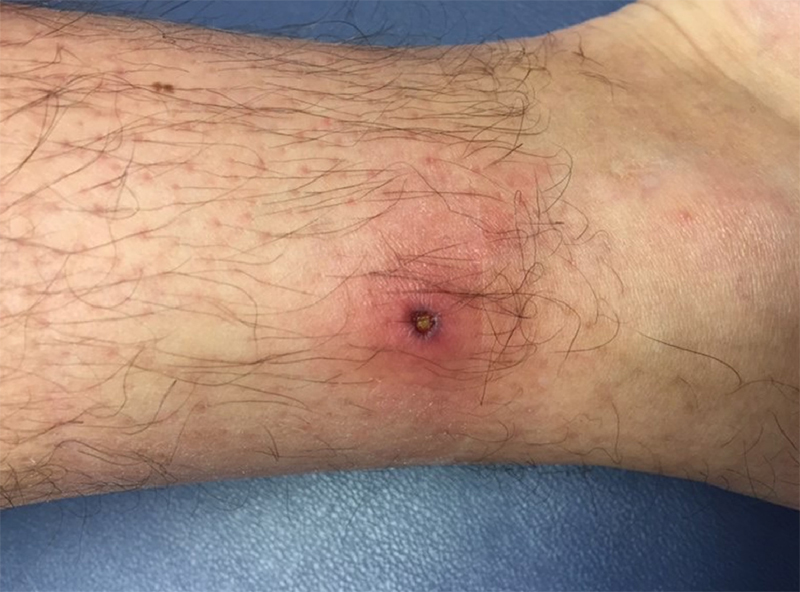
Tick bites
Ticks are often very tiny and hard to see. Some ticks transmit organisms that cause serious illnesses, including Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever. If a person is bitten by a tick, the first thing to do is to remove it promptly and carefully, using tweezers while wearing protective rubber gloves, if possible, to…
-
Typing
Classifying blood, tissues, cells, disease-causing organisms, and other materials so they can be compared with standards. A laboratory method of determining the antigenic characteristics (type) of a blood or tissue sample, i.e., of determining whether or not the blood or tissue taken is likely to cause a reaction if introduced into another person with whom…
-
Type and crossmatch
A blood test done before a blood transfusion is administered. The donor’s blood as well as the recipient’s blood is tested to be sure both are of the same blood type; donor and recipient blood samples are then mixed to confirm that their bloods are compatible, and will not clot when the transfusion is given.…
-
Typhoid agglutinin test
A test done on serum to diagnose the presence of typhoid fever.
-
Tuning-fork tests
Tests in which a tuning fork is used to measure hearing function and bone-conduction sensitivity in various neurologic (nervous system) examinations. Tests for hearing are performed to distinguish between conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. In the Weber test, a vibrating tuning fork is placed on the forehead. If conductive hearing loss is present, the sound…
-
Tumor doubling time
The length of time it takes a cancerous cell mass to double in bulk (cell mass). These measurements are important in calculating cancer therapy.
-
Tularemia agglutinin test
A test done to determine the presence of tularemia, an infectious disease spread through contact with infected rabbits.
-
Tubo-ovarian abscess
A pus-filled area in the fallopian tube and the ovary. This may occur in women who have pelvic inflammatory disease (one or more sexually transmitted diseases that travel through the genital tract). This condition causes intense pain in the abdominal area, requiring surgical treatment.