Category: T
-
T test
Statistical test often used to compare two groups on the mean value of a continuous response variable. The test is used when the variables have normal distribution. A statistical test to determine whether a difference is significant.
-
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
RNA that transports an amino acid to the ribosome, according to the code specified in the messenger RNA (mRNA), for incorporation into a polypeptide during protein synthesis. A class of relatively small RNA (ribonucleic acid) molecules of molecular weight 23,000 to about 30,000. tRNA molecules act as carriers of specific amino acids during the process…
-
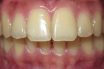
Thin periodontal biotype
Periodontal biotype characterized by a thin periodontal tissue at the facial aspect of teeth or oral implants. This biotype is prone to gingival recession following mechanical or surgical manipulation.
-
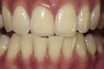
Thick periodontal biotype
Periodontal biotype characterized by a thick and wide keratinized tissue at the facial aspect of teeth and oral implants. This biotype is prone to pocket formation instead of gingival recession in the presence of periodontal disease.
-
Traumatic l
A self‐inflicted (factitious), accidental, or iatrogenic injury which may manifest as recession, abrasions, ulcerations, lacerations, erythematous or white lesions, or combinations of several of these features.
-
Tooth extraction and i. l
Implant placed and put into function at the time the natural tooth is extracted.
-
Transseptal fiber
Collagenous fibers that run interdentally from the cementum just apical to the base of the junctional epithelium of one tooth over the alveolar crest to insert into a comparable region of an adjacent tooth. Any of the collagenous fibers that extend between the teeth and are embedded in the cementum of adjacent teeth.
-
Traumatic (hemorrhagic bone) c
A radiolucent lesion in the bone without a radiopaque border; a cavity of disputed cause, lined by extremely thin or no tissue, which may contain fluid (blood or serum). It is assumed to have been caused by trauma. Teeth, if present, are vital. Not a true cyst.
-
Temporary c
Binding or luting agent intended for short‐term use, e.g., zinc oxide (powder) eugenol (liquid) mixture.
-
Topical a
Anesthetic effect produced by the application of an anesthetic agent to a surface area.