 A tuberculin test in which the test material is injected under the skin.
A tuberculin test in which the test material is injected under the skin.
A test for tuberculosis, in which a person is given an intracutaneous injection of tuberculin.
Skin test to determine past or present infection with tuberculosis. A protein derivative of tubercle bacillus is injected intradermally; a hardened red area appearing 1-3 days after injection signifies a positive reaction and past or present exposure to the tubercle bacillus.
A skin test to detect the presence of, or exposure to, tuberculosis. Normal value: negative reaction if there is no disease or exposure.
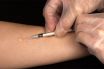
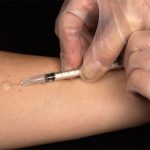
A test for tuberculosis. It comprises injecting into the superficial layers of the skin (i.e. intradermally) a very small quantity of old tuberculin which contains a protein antigen to TB. A positive reaction of the skin swelling and redness indicates a previous infection, at some time in the past, with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. However, this does not necessarily indicate the presence of active disease.
An intradermal (intracutaneous) injection of 0.1 ml of intermediate strength purified protein derivative (PPD). The needle is removed after a brief delay in order to minimize leakage of the PPD at the puncture site. Within 48 to 72 hr, hardening (induration) of the injected area, whose diameter is greater than 10 mm Hg, provides unequivocal evidence of current or previous infection with tuberculosis. In persons infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), an indurated area whose diameter is 5 mm or more should be considered evidence of a positive test result. HlV-infected patients who do not react to PPD or to control antigens (i.e., persons who are anergic) should be considered positive as well, esp. if they come from demographic groups known to have high rates of infection with tuberculosis (e.g., homeless people, Asian-born individuals, among any others).