Mindblown: a blog about philosophy.
-
Bilirubinuria
Presence of bilirubin in the urine. May be indicative of a liver or blood disorder. The presence of bilirubin (a yellow- or orange-tinged pigment in the bile) in the urine.
-
Azotemia
Presence of urea in the blood. An excess of urea or other nitrogenous bodies in the blood. Elevation of urea and other nitrogenous waste products in the blood due to renal failure. Presence of an abnormally high level of nitrogen-bearing materials (e.g., urea) in the blood. Abnormal concentration of urea and nitrogenous substances in the…
-
Atropine
Anticholinergic agent that counteracts effects of parasympathetic stimulation. An alkaloid obtained from atropa belladonna inhibits the action of the craniosacral division of the autonomic nervous system. An alkaloid substance derived from the poisonous plant belladonna and used, among other things, to enlarge the pupil of the eye, to reduce salivary and bronchial secretions during anaesthesia…
-
Atelectasis
In a neonate, the failure of the lung to completely expand at birth; generally, a collapsed lung. The collapse may be complete or partial. A collapse of the alveolar air spaces of the lungs. The failure of a lung to expand properly. Incomplete expansion of all or part of the lung in a newborn or…
-

Apnea
Temporary cessation in breathing (occurring during sleep). The cessation of breathing, especially without apparent cause. Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder—specifically, hypersomnia that is associated with apnea, hypoventilation, or both. The disorder causes temporary cessation of breathing that occurs several times a night. Sleep apnea is typically classified as central or obstructive. In central apnea,…
-
Anticholinergic (drug)
Drug or agent that inhibits the action of the neurotransmitter chemical acetylcholine, blocking parasympathetic nerve impulses, with consequent reduction of smooth-muscle contractions and various bodily secretions. A cholinergic blocking agent including atropine, nicotine, which prevents acetylcholine from stimulating the receptor. Medications that retard or block the activity of acetylcholine within the central nervous system (cns)…
-
Angiography
Use of x-rays to show an image, on developed film or video monitor, of the blood vessels. A diagnostic procedure through which the chambers and blood vessels of the heart are examined. An x-ray examination of blood vessels after injection with an opaque dye so that show up clearly on the film. The process of…
-
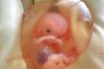
Amniotic fluid
Fluid inside the amniotic sac, the membranous enclosure within the uterus in which the fetus is suspended. A transparent albuminous liquid made by the amnion and the fetus; surrounds and protects the fetus during pregnancy. The fluid secreted by the amnion which immerses the fetus in the uterus prior to birth, amniotic sac. The fluid…
-
Adjuvant analgesic
Any drug whose primary purpose is not generally used or prescribed for pain but can also serve as an analgesic for some pain conditions.
-
Abrade
To chafe; to roughen or remove by friction. To wear away by mechanical action. To rub off, as a skin or covering layer, deliberately or accidentally. The act of wearing away the skin’s surface through rubbing, often resulting in a minor wound known as an abrasion, occurs when skin is scraped against a rough surface.…
Got any book recommendations?