Diabetes is a common disease that affects the way your body processes sugar. It can lead to serious health issues, including heart disease and stroke if left untreated. There are two types of diabetes: type 1 (previously known as juvenile diabetes) and type 2 (also called adult-onset). Type 1 is an autoimmune condition that typically presents in childhood or adolescence. Type 2 develops when insulin isn’t produced properly by the pancreas or when cells don’t respond to insulin properly. Read on to learn different ways to manage diabetes:
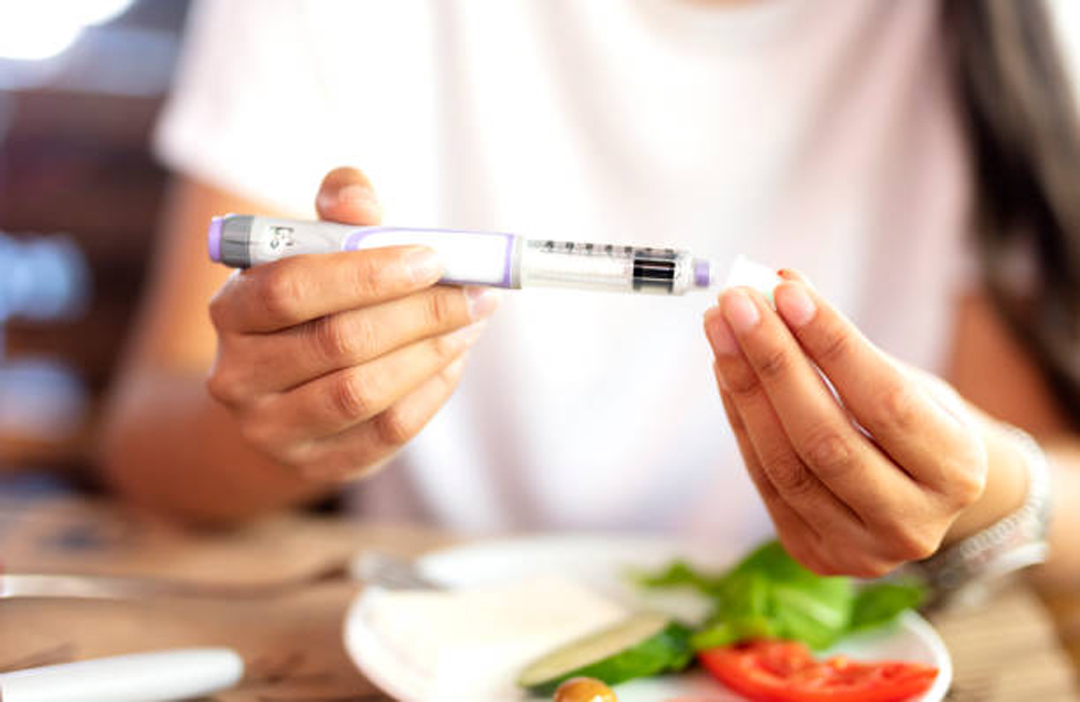
Monitor your blood sugar levels
Monitoring your blood sugar levels is one of the best ways to manage Type 2 diabetes. Monitoring helps you identify and manage changes in glucose levels, which can help prevent health problems such as high blood pressure and eye problems. You should check your glucose level at least once a day, but how often you check depends on the type of diabetes you have, as well as any medical care provider recommendations.
Eat a healthy diet
Eating a healthy diet will help you manage your diabetes. A balanced diet that includes a variety of nutritious foods, such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains and beans, can help you manage your blood glucose levels. According to Tandem Diabetes’ experts, “You should avoid alcohol and sugary drinks because they contain carbohydrates that affect blood glucose levels.” You can also eat lean meats, fish and poultry that are low in saturated fats and cholesterol to help control your weight and reduce the risk of heart disease related to diabetes.
Exercise regularly
Exercise can be a powerful tool for people with diabetes. It can help lower blood sugar levels, lose weight and reduce the risk of complications from diabetes. Exercise is also thought to help improve sleep quality, emotional well-being and overall health. Exercise can even improve your life expectancy! Studies have shown that people with type 2 diabetes who exercise regularly may have better blood sugar control than those who don’t exercise at all.
Don’t smoke or drink alcohol
You may not realize it, but smoking and drinking alcohol can make your diabetes worse. Your doctor will tell you that smoking is a risk factor for heart disease, which is a major cause of death among people with diabetes. Additionally, drinking alcohol can increase the risk of developing high blood sugar levels.
Take your medication
To help you remember to take your medication, set the alarm or reminder on your phone. Plan to take it about 30 minutes before meals and with food. You may also want to include your medication with water and/or exercise in order to make sure that you are getting all of the benefits from taking it regularly. If you feel like something is wrong with how your body is reacting to a certain medicine, talk with your doctor right away so they can adjust the dosage or recommend another type of medication altogether.
Manage stress
Stress can affect your blood sugar levels in a couple of ways. If you’re stressed out and have low blood sugar, it’s best to eat something sugary right away (like a candy bar or some fruit). In the case of high blood sugar, if your stress level is at an all-time high, try eating something salty or fatty to bring down those levels. Stress management techniques such as meditation are known to help people with diabetes manage their stress levels better overall.
These were a few tips that can help you manage stress. It is recommended that you visit your doctor regularly and get their opinion before trying out anything new.
Differences between type 2 and type 1 diabetes
- In type 2 diabetes, the primary disorder is a problem with the action of insulin, which is no longer effective in controlling metabolism. This is called “insulin resistance” and is usually related to being overweight and inactive. Insulin resistance means that insulin cannot act normally to keep blood sugars in the desired range. Type 2 diabetes is a progressive disease that will require the eventual use of insulin.
- In response to insulin resistance, increased amounts of insulin are made initially. This is the opposite of type 1 diabetes, where the insulin levels are low or absent. Over time, the amount of insulin produced by individuals with type 2 diabetes decreases. This happens as the pancreas fails to keep up with the body’s higher demands for insulin. Even though there is less insulin being produced by the pancreas and the patient may need to take insulin injections, the individual still has insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. One type does not turn into the other type.
- Laboratory measurements sometimes help in deciding if someone has type | or type 2 diabetes. ISLET CELL ANTIBODIES ARE NOT PRESENT IN TYPE 2 DIABETES. In type 1| diabetes ICA antibodies are usually present. Measurements of C-peptide, an insulin related protein, may be normal or elevated in type 2 diabetes, but are generally low in type 1. However, sometimes it takes monitoring the individual with diabetes for a while to differentiate between the two types.
Causes
Inheritance (genetics)
Type 2 diabetes has a stronger risk for inheritance than type 1 diabetes. In almost all cases, a parent and/or grandparent will also have the disease. In the case of identical twins, if one twin develops type 2 diabetes, the other twin has an 80 percent chance of also developing the disease. In type 1 diabetes, an identical twin has a 35-50 percent chance of developing the disease. In type 2 diabetes, there are many different potentially-inherited (genetic) defects, which vary between families. There is not just one common defect in all families. Children who are born to mothers with type 2 diabetes, or mothers with gestational diabetes, have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes in childhood. Children born with a low birth weight for length (“small for date”) are also at an increased risk for developing type 2 Diabetes.
Lifestyle
Most (but not all) people with type 2 diabetes are overweight and do not lead active lives. According to a study of a sample of U.S. children, the obesity prevalence has increased from around 5% in 1963 to 17% in 2003 to 2004. In the past two decades, the obesity related cost of illnesses during childhood increased from 35 million to 127 million US dollars. Factors that can play a role in obesity include genetics, certain medications, eating on the run, recreational eating, eating foods higher in fat, increased portion size, increased TV and video time, and decreased physical activity.
Insulin resistance usually occurs with excessive weight and decreased physical fitness. Insulin resistance means that the body loses its sensitivity to insulin. The insulin doesn’t work as well to allow sugar to pass into the cells. In some cases, the increased insulin that the body makes to try to overcome the resistance causes darkening of the skin (called acanthosis nigricans). The most common areas for this darkening are the neck, armpits and/or the elbows. By losing weight (eating fewer calories and exercising more), the sensitivity to insulin may return again and the dark skin coloring may lessen or disappear.
Comments
comments