Category: F
-
Focal sclerosing osteomyelitis
A diffuse radiopaque lesion believed to represent a localized bony reaction to a low‐grade infection of the pulp. It is usually seen at the apex of a tooth (or its extraction site) that has experienced chronic inflammation.
-
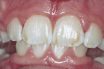
Fluorosis
Condition that occurs because of excessive intake of fluoride either through naturally occurring fluoride in the water, water fluoridation, toothpaste, or other sources. A dental health condition caused by a child receiving too much fluoride during tooth development. Damage to teeth (white to brown mottling of the enamel) and bones caused by an excessive intake…
-
Fluorohydroxyapatite (FHA)
Pyrolytical segmentation of natural algae and hydrothermal transformation of the calcium carbonate (CaCO3) skeleton of algae into FHA (Ca5(PO4)3OHxF1‐x). Particles consist of a pore system (mean diameter 10 μm), periodically separated (mean interval 30 μm) and interconnectedly microperforated (mean diameter of perforations 1 μm).
-
Fluorochrome
Fluorescent substance used as a stain or label for biologic specimens. In implant dentistry, it is used in research to evaluate the kinetics of osteogenesis and osseointegration on implant surfaces. Dyes capable of emitting fluorescence when stimulated by ultra-violet light. A coloring agent that adds a fluorescent glow to an object, e.g., in the staining…
-
Fluoride‐modifying surface treatment
Implant treatment that exposes the surface to a cleansing bath of hydrofluoric acid following treatment with etching or blasting. This technique has been shown to improve biomechanical anchorage and bone integration when compared to control implants treated without the hydrofluoric acid bath.
-
Flowing composite resin
Compared with a conventional composite resin, this type of resin has less filler and less viscosity but improved wettability.
-
Flow cytometry
Measures the physical and chemical characteristics of individual cells as they move past optical or electronic sensors; can be used to detect and characterize specific cells in a mixed population; used to determine the effects of drugs, hormones, chemicals. Technique using an instrument system for making, processing, and displaying one or more measurements on individual…
-
FLO (abbrev)
Feature locating object.
-
Flipper
A prosthesis that is usually considered to be temporary in design. It traditionally has one tooth attached to an acrylic base typically without clasps, although wrought wire clasps may be used for additional retention.
-
Flat panel detectors
A square or rectangular amorphous plate with a scintillator that replaces film, used in cone beam computed tomography.