Category: H
-
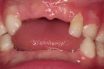
Hypophosphatasia
An inborn error of metabolism characterized by deficient alkaline phosphatase in serum and bone, resulting in the defective formation of bone and cementum. Hypophosphatasia is an uncommon disorder of bone and cartilage formation. Its salient features include poor mineralization of the skull, short ribs resulting in an underdeveloped thorax and respiratory insufficiency, and poorly formed,…
-
Hyponasality
A speech characteristic caused by insufficient resonance of air in the nasal cavity such that the speaker sounds as though he or she has a cold. Also known as denasality.
-
Hypogeusia (hypoageusia)
Reduced sense of taste, including sweet, sour, salty, and bitter substances. Called also hypogeusesthesia.
-
Hypoesthesia
Decreased perception of stimulation by noxious or non‐noxious stimuli. A condition in which the ability to detect sound, taste, smell, or physical contact is abnormally weak.
-
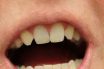
Hypodontia
Congenital absence of one or more, but not all, of the normal complement of teeth. The developmental absence of one or more teeth.
-
Hypertrophy
Nontumor‐associated increase in tissue or organ size related to an increase in constituent cell size. A hypertrophic response may occur as a result of a particular condition. To be distinguished from hyperplasia, which is related to an increase in cell number. Enlargement or overgrowth of an organ. A term used to describe an increase in…
-
Hypertension
Persistent, sustained high blood pressure of 140/90 mmHg or above. Hypertension becomes a surgical risk factor if the condition is uncontrolled. Commonly referred to as “high blood pressure” or HTN, is a medical condition in which the arterial blood pressure is chronically elevated. Persistently high arterial blood pressure. Currently accepted threshold levels are 140 mm…
-
Hypersensitivity
An exaggerated or inappropriate immune response to a pathogen or antigen that is damaging to the host. Classified as immediate (anaphylactic), antibody dependent (cytotoxic), immune complex (Arthus), and delayed (T cell mediated). Altered reactivity to an antigen, which can result in pathologic reactions upon subsequent exposure to that particular antigen. Heightened responsiveness induced by allergic…
-
Hyperplastic tissue
Surplus tissue that is often caused as a response to chronic irritation that stimulates overproduction of the cells in the tissue.
-
Hyperplasia
Excessive enlargement of a tissue or structure due to an increase in the number of cells. Increase in the number of cells produced in an organ or body tissues. Growth in a tissue or organ through an increase in the number of cells. Over proliferation of normal cells within a normal tissue structure. Abnormal multiplication…