Category: K
-
Kosher
The selection and preparation of foods in accordance with traditional Jewish ritual and dietary laws. Foods that are not kosher are traife. The only kosher flesh foods are from animals that chew the cud and have cloven hoofs, such as cattle, sheep, goats, and deer; the hindquarters must not be eaten. The only fish permitted…
-
Korsakoff’s psychosis
Failure of recent memory, although events from the past are recalled, with confabulation; associated with vitamin B1 deficiency, especially in alcoholics. Characterized by disorientation, failure of memory, and substituting imagined episodes for the loss of memory. It results from a combination of excessive alcohol intake and a deficiency of niacin. Symptoms of neuropathy associated with include…
-
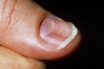
Koilonychia
Development of (brittle) concave finger nails, commonly associated with iron deficiency anaemia. A condition in which the fingernails are brittle and concave, caused by iron-deficiency anaemia. Deformation of the nail bed with thin, concave edges; often associated with iron deficient anemia; also called “spooning of the nails”. A condition in which thinning of the nail…
-
Kjeldahl determination
Widely used method of determining total nitrogen in a substance by digesting with sulphuric acid and a catalyst; the nitrogen is reduced to ammonia which is then measured. In foodstuffs most of the nitrogen is protein, and the term crude protein is the total ‘Kjeldahl nitrogen’ multiplied by a factor of 6.25 (since most proteins…
-
Kilo
As a prefix for units of measurement, one thousand times (i.e. 103); symbol k. A kilogram, the equivalent of 2.2 pounds. The usual package of marijuana sold in Mexico.
-
KGY
Kilogray, a unit of radiation intensity.
-
Keys score
Method of expressing the lipid content of a diet, calculated as 1.35 X (2 X % energy from saturated fat – % energy from polyunsaturated fat) + 1.5 √ (mg cholesterol /lOOO kcal).
-
Ketonuria
Excretion of ketone bodies in the urine. A state in which ketone bodies are excreted in the urine. A condition characterized by excessive levels of ketones in the urine. In diabetes mellitus, fatty acid oxidation is incomplete. As a result, acetone, β-hydroxybutyrate, and acetoacetate, products of incomplete fatty acid oxidation, accumulate. These are the ketone…
-
Ketone bodies
Acetoacetate, p-hydroxybutyrate and acetone; acetoacetate and acetone are chemically ketones; although 3-hydroxybutyrate is not, it is included in the term ketone bodies because of its metabolic relationship with acetoacetate. Fatty acid derivatives that can function as energy sources in the body include β-oxybutyric acid, acetoacetic acid, and acetone. Ketone compounds formed from fatty acids. Products…
-
Ketogenic diet
A diet poor in carbohydrate (20-30 g) and rich in fat; causes accumulation of ketone bodies in tissue. A diet with a high fat content, producing ketosis. A special high-fat diet, used in some cases of epilepsy. A diet that promotes the formation of ketone bodies in the tissues. A ketogenic diet is one in…