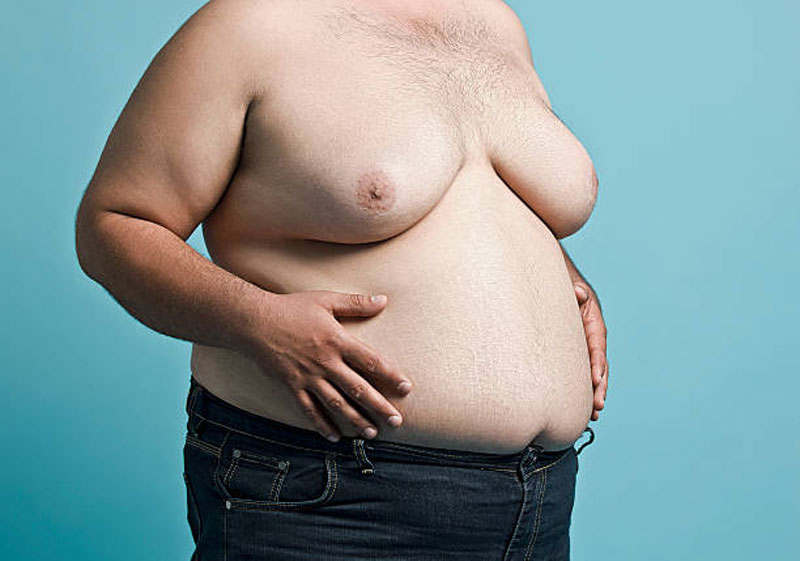
The disease involves abnormal enlargement of breast tissue in male subjects. Said event might occur in either one or both breasts. Medical professionals suggest that this event does occur naturally at several times during a male’s life such as immediately after birth, during puberty and again in mid to old age. That said, the condition usually resolves on its own accord. The disease process occurs when the natural process fails to cease or occurs at another period of one’s life. The following are some of the potential causes of gynecomastia.
Potential Causes
Hormonal imbalances are often pointed out as the main reason. In most cases, an abnormal systemic concentration of certain reproductive and sexual hormones can cause gynecomastia, as written by plastic surgeon Dr. Stephan Baker of Miami, FL. Typically, afflicted individuals experience a significant decrease in testosterone, the chief male reproductive hormone and witness an unusual elevation of internal levels of estrogen, one of the primary female reproductive hormones.
Numerous underlying causes can precipitate the offending hormonal imbalances, as well.
The endocrine system is comprised of glands and organs that produce and secrete various hormones needed by the body to perform various functions. Diseases to organs like the thyroid, hypothalamus, adrenal glands or testicles could ultimately lead to the development of gynecomastia.
Conditions impacting the kidneys and liver could upset systemic hormonal imbalances.
Poor lifestyle choices such as the failure to obtain adequate nutrition and obesity could elicit hormonal changes that precipitate gynecomastia.
A variety of drugs could result in offending hormonal imbalances such as certain preparations used to remedy anxiety, digestive issues like heartburn, anabolic steroids, hormone therapy, specific fertility enhancers and some medications designed to treat bacterial and fungal infections.
Physical Manifestations
For the most part, the only symptom of the disease is a sudden or persistent enlargement of breast tissue. This associated burgeoning might additionally be accompanied by soreness, pain and nipple discharge.
Complications
Most healthcare professionals opine that gynecomastia is not a serious medical illness on its own accord. That said, the presence of said malady might indicate a more serious underlying problem or suggest an adverse reaction to a specific medication being used to remediate such a condition. Ergo, individuals experiencing the manifestations of gynecomastia are strongly encouraged to visit a healthcare provider as soon as possible and undergo a thorough physical examination.
Diagnosis
It is important to reiterate that gynecomastia’s main cause is a significant hormonal imbalance. Therefore, curing said occurrence will require an accurate diagnosis of the specific underlying cause precipitating it. In many instances, physical evaluations will involve intense and careful scrutiny of the patient in question’s testicles and pelvic regions and several different blood tests. That said, a much further examination might also necessitate the usage of diagnostic tools such as Magnetic Resonance Imaging, or MRI scans and the capturing of Computerized Tomography, commonly abbreviated as CT images. In certain cases, breast tissue biopsies may be indicated.
Gynecomastia can mimic other conditions. Conditions producing similar manifestations include the growth of fatty breast tissue, the presence of an infection known as a breast abscess and breast cancer. Additionally, certain forms of testicular cancer sometimes precipitate swelling or growth of breast tissue.
Treatment Options
Several issues factor in determining the most appropriate therapeutic protocol. Arguably, the most significant concern is the ailment’s underlying cause. Once doctors can identify the specific reason the afflicted patient is experiencing hormonal imbalances severe enough to precipitate gynecomastia, specific treatment options can be explored. That said, remedial efforts can include:
Hormone Therapy: Sometimes, restoring the afflicted individual’s testosterone levels or reducing their estrogen levels might cause swollen breast tissue to return to its normal position.
Medications: Properly treating hormone balance-disturbing ailments with medications may dissipate the enlargement of breast tissue.
Change In Medications: Should gynecomastia be attributed to the ingestion of a specific drug, either reducing the dosage of said substance or using a different medication might be indicated.
Surgery: Regardless of the underlying cause, remedial efforts might take time. Unfortunately, the embarrassing nature of the condition will reduce the desire of many stricken subjects to wait for such endeavors to take effect. In these instances, surgical intervention might be necessary.
Should surgical intervention be performed, two types of procedures are typically utilized, liposuction and mastectomy. Liposuction involves the removal of fatty breast tissue. However, the breast gland itself is left in-tact. During a mastectomy, significant portions or the entire breast gland will be removed.
Prevention
Preventing the condition can prove challenging. That said, executing actions such as maintaining a healthy weight, consuming a nutritious diet, closely monitoring the side effects of any prescription medications and ensuring one’s hormonal balances are even and normal might help male subjects avoid the embarrassing condition.
Comments
comments