Month: January 2020
-
Compensating curve
The curve created by the alignment of the occlusal and incisal surfaces of artificial teeth that compensates for the condylar path when the mandible moves from centric to eccentric positions and provides for a balanced occlusion. The compensating curve corresponds to the curve of Spee in a natural dentition.
-
Compatible
Refers to the interchangeability of prosthetic components of one implant system to another. Able to fertilise each other. Able to function together without being rejected. In transfusions and grafting, capable of being used without immunological reaction. In the context of the interaction between a host and pathogen, the potential for disease to develop is dependent…
-
Compact bone
Concentrically arranged dense bone solidly filled with inorganic salts and organic ground substance with the presence of small spaces called lacunae filled with osteocytes (bone cells). Hard portion of bone that forms the diaphysis and epipysis. A type of bone tissue which forms the hard outer layer of a bone. The hard, dense bone made…
-
Commissure splint
A device placed between the lips that helps increase the separation between them. Such a device is often used when surgical, electrical, or chemical damage of the lips has caused contracture or restriction of the lips. Also known as a lip splint.
-
Commissure
A meeting point or junction between two anatomic structures, such as the corners of the mouth. The place of joining (e.g. the faces of joining carpels). Bundle of nerve fibers passing from one side to the other side of the brain or spinal cord. A structure which joins two similar tissues, e.g. a group of…
-
Comminuted fracture
A complex bone fracture characterized by breaks in several places in the same area, crushed and/or splintered. A fracture where the bone is broken in several places. A fracture in which the bone is broken into more than two pieces. A crushing force is usually responsible and there is often extensive injury to surrounding soft…
-
Comminute
The reduction of food into small parts, comminution. To reduce to small fragments, usually by mechanical means macerate.
-
Commercially pure titanium (CP‐Ti)
Biocompatible metal commonly used for dental implants. It is an alloy of approximately 99 wt.% titanium and small amounts (from 0.18 to 0.40 wt.%) of oxygen with trace amounts (less than 0.25 wt.%) of iron, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen. Commercially pure titanium is classified in multiple grades. The amount of oxygen determines the grade of…
-
Comfort cap
Element designed to fit over a component such as the transmucosal abutment. Intended to cover the component to protect the intraoral tissues from a detectable edge and/or prevent damage to the exposed surfaces of the component.
-
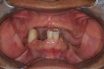
Combination syndrome
The clinical changes observed when an edentulous maxillary arch is opposed by a mandible with retained anterior teeth that may or may not be extruded and missing posterior teeth. Over time, there is a loss of bone in the premaxilla and in the edentulous posterior mandible, overgrowth of the maxillary tuberosities, and hyperplasia of the…