| Cupuassu Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Cupuassu |
| Scientific Name: | Theobroma grandiflorum |
| Origin | Amazon basin in the southern and eastern Pará |
| Colors | Brown |
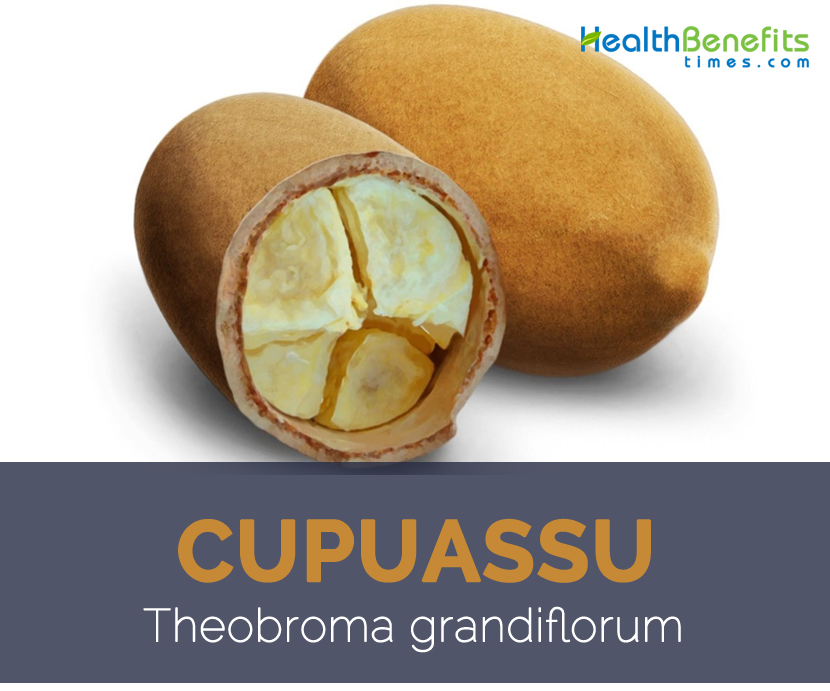
| Shapes | Oblongish, obovate, sub globose to ellipsoidal, large, 20–25 cm long by 6–10 cm wide, |
| Flesh colors | Yellowish white |
| Taste | Often compared to chocolate, banana, melon or bubble gum. |
| Calories | 120 Kcal./cup |
| Major nutrients | Total Fat (38.86%) Vitamin E (0.53%) |
Cupuassu scientifically known as Theobroma Grandiflorum is normally pronounced as (koo-poo-ah-soo). Cupuassu belongs to the cocoa family and grows to a height of 12-20 meters (30-65 feet). The fruit of the tree, which is called by the same name, has been a primary food source for natives in the rainforest for centuries and has a creamy, exotic pulp at the center of a large melon. Cupuassu is known in the Amazon as “the pharmacy in a fruit” and could be considered one of the most nutritionally beneficial super fruits ever introduced to the marketplace. As a cousin of the cacao fruit, cupuassu has a prized tropical flavor combining elements of chocolate, bananas, pear, passion fruit and pineapple.
Plant
Cupuassu is an erect, evergreen, much-branched tree usually ranges from 5 to 15 meters (16 to 50 feet) in height, though some can reach 20 meters (65 feet). Tree prefers a very humid environment and need lots of water for good growth. They have brown bark and tricomic branches. Leaves are simple, entire, alternate, coriaceous, narrowly ovate- to obovate-elliptic, 25–35 cm long and 6–10 cm wide, base rounded to shallowly cordate, apex long acuminate with a 9–10 pairs of lateral veins, bright-green, pubescent upper surface and grey underside. As they mature, their leaves change from pink-tinted to green, and eventually they begin bearing fruit. Flower is bisexual, small, pentamerous, occurring in 3–5 flowered cymose inflorescence on trunk and main branches. Cupuassu fruits are oblongish, obovate, sub globose to ellipsoidal, large, 20–25 cm long by 6–10 cm wide and weight between 1–2 kg (2–4 lb.), and covered with a thick (4–7 mm), hard exocarp. The exterior of the fruit is thick and very sour in taste, while the flesh is very sweet and has approximately 20 to 30 seed pods. Seeds are sub globose, 2 cm across, covered in white testa, cotyledons fleshy, non endospermous.
The white pulp of the cupuassu is uniquely fragrant (described as a mix of chocolate and pineapple), and It is frequently used in desserts, juices and sweets. The juice tastes primarily like a pear, with a hint of banana. Cupuassu is touted as a possible super fruit flavor. Commercial production of cupuassu includes food supplements, pills, drinks, smoothies and sweets. The pulp is also used in cosmetics products such as body lotions, as it is highly hydrating, similarly to cocoa butter. Cupuassu pulp is often used for making juice, ice cream, smoothies, mousse, jellies, chocolates called “cupualte” and liquor. The seeds are used for producing “cupualte”, a product with similar characteristics to chocolate, but which contains nutritional value and is healthier.
History
Cupuassu is native to the Amazon basin in the southern and eastern Pará, covering the areas of the middle Tapajós, Xingu and Guamá, and reaching the northeast of Maranhão in Brazil (Cuatrecasas 1964). It is extensively cultivated in the north of Brazil, with the largest production in Pará, followed by Amazonas, Rondônia and Acre. It is also cultivated in Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, and Costa Rica.
Cupuassu is wildly popular in Brazil as well as other parts of South America despite taking a back seat to cacao during the past century. For centuries, natives of the rainforest have used the fruit of the cupuassu tree as a main source of food and it continues to be a delicacy in the more populated towns of South America.
Today, cupuassu pulp is often used for making juice, ice cream, smoothies, mousse, jellies, chocolates called “cupualte” and liqour. The seeds are used for producing “cupualte”, a product with similar characteristics to chocolate, but which contains nutritional value and is healthier.
Nutritional Value
Apart from their taste often compared to chocolate, banana, melon or bubble gum, cupuassu is a good source of nutrients, vitamins and minerals. Consuming 13.6 gram of cupuassu oil offers 13.6 g of Total Fat and 0.08 mg of Vitamin E.
Health Benefits of Cupuassu Fruit
Cupuassu fruit has phytonutrient polyphenols (theograndins). It is also heavy with vitamins B1, B2, B3 (Niacin), fatty and amino acids, and at least nine antioxidants (including Vitamins A and C). Being from the cocoa family, Cupuassu also has high flavonoid content. There are many health benefits to Cupuassu, most of which are tied to the fruit’s extremely powerful phytonutrient polyphenols, anti-oxidants, essential nutrients, vitamins, and others mentioned earlier. These have a myriad of nutritional benefits, which will be discussed more thoroughly below.
- Cupuassu is very rich in antioxidants and it is even regarded as a full breakfast among people in South America.
- The fruit has the comparable flavor of cocoa, that’s why it is utilized in making jams, jellies, and breads.
- It contains no caffeine and thus, it is capable of keeping the body hydrated and moisturized.
- The fruit is an abundant source of vitamins A, C, B1, B2, and B3. In addition, it is great for the bones, ligaments, and tendons as a result of its high amino acids content, as well as calcium and selenium.
- People in South America, particularly the Brazilian ladies used the fruit to assist them in labor pains and stomach problems.
- The fruit has therapeutic advantages that help keep the body’s defense mechanisms healthy and strong.
- Phytonutrient polyphenols are present in cupuassu, but not in many other fruits. This compound is extremely helpful in the treatment of respiratory illnesses.
- Cupuassu acts as an all-natural medicine for erection dysfunction.
- The fruit helps combat free radicals- the reason behind cancers and other life-threatening problems.
- It helps maintain the body’s cholesterol at normal levels and prevents the occurrence of cardio-related problems.
- If you have kids who are selective when it comes to food, the fruit could be the best solution as it can be given by means of powder, yogurt, ice cream, or juice. At the same time, the fruit can help them improve the power of their memory.
- For the ladies, cupuassu can increase the health of their skin and can treat acne breakouts.
- Aside from fortifying the coronary heart, it can also safeguard the artery walls from damage, which may lead to heart diseases.
- When cupuassu is combined with acai fruit, it gives serious energy in motion.
- The seeds of Cupuassu can relieve pain in the different parts of the body. Those who opt for natural remedies to ease pain should slowly chew the seeds of the fruit.
- Cupuassu fruit is great for kids as it improves memory power.
- The Cupuassu has a great advantage for health, as it helps to fight free radicals; they are the main responsible for various cancers.
- The fatty acids present in Cupuassu, help reduce bad cholesterol and keep the good cholesterol, carrying, extremante beneficial in maintaining a healthy heart.
- Cupuassu aid in healthy weight loss, addition of vitamins and minerals, so-called fruit contains soluble fiber pectin, which aids in weight loss, because it produces a sociogenic effect, found in many anti-obesity drugs.
- Cupuassu leaves have soothing action, combat bronchitis and kidney infections.
- The Cupuassu has anti-inflammatory action.
How to Eat
- The delicious fruit pulp is eaten raw or prepared into a wide variety of beverages, juices, ice cream, yoghurt, sorbet, preserves, sweets, jams, jellies, puddings and other desserts.
- Seeds have a high amount of fat and provide a good cocoa butter and can be used to produce chocolate and chocolate-like foodstuffs.
- Cupuassu can replace cocoa in many day-to-day foods, especially for children, such as chocolate milk.
- Cupuassu seeds can be made into cupulate, which looks and tastes just like chocolate but is cheaper and more resistant to heat.
Traditional uses and benefits of Cupuassu
- Ibeansî (seeds) were often given to people to chew to cure abdominal pains.
- Juice would be blessed by shamans and given to pregnant women, newlyweds who wanted children and others for various maladies.
- Vitamins and minerals present in the fruit acts as boosters for the gastro-intestinal system.
- Cupuassu when mixed with acai fruit will give you serious synergy in motion.
- The fruit stimulates the immune system increasing stamina and energy equivalent to that caused by other artificial caffeine sources.
- It also strengthens your cardiovascular system and protects the artery walls from damage which can cause heart diseases.
- Fatty acids present in the fruit reduce the bad cholesterol and keeps the good cholesterol which helps in maintaining a healthy heart.
- Cupuassu has a huge concentration of antioxidants which neutralizes the free radicals in the body’s tissues.
- Antioxidants improve the circulation and lower the blood pressure and helps in eliminating the free radicals.
- It is also helpful in curing diabetes, cataract problems and coronary heart diseases.
- It is also often used as a pain killer.
- It is traditionally used by women who experience difficult births and labor pains.
Other Facts
- The timber is commonly used for construction and joinery.
- Brazil declared Cupuassu to be the national fruit and the name to be ineligible for trademark.
- Cupuassu is available in many forms: shampoo, lotion, butter, ice cream, as a juice, as straight pulp, or even as the fruit itself.
- Cupuassu is called “the pharmacy in a fruit” because of its nutritional value and the effectiveness in curing and preventing sickness.
- It is also cosmetic products such as body lotions which reduces the signs of aging and makes you look younger.
- Seeds are used in making cupuassu butter- one of the world’s newest skin-softeners.
Precautions
Cupuassu is generally safe for most adults when consumed in moderation.
While the theacrine content of a single serving of cupuassu may not provide the same stimulating properties as caffeine in a cup of coffee, those who are sensitive to stimulants, or who are on medications that may be stimulating (such as anti-depressants), should use caution and consume cupuassu in small amounts at first to see how they respond to it.
Cupuassu Facts
Cupuassu is a tree that grows in the rainforest canopy in South America with the Latin name Theobroma Grandiflorum. The Cupuassu belongs to the cocoa family and grows to a height of 12-20 meters (30-65 feet). The fruit of the tree, which is called by the same name, has been a primary food source for natives in the rainforest for centuries and has a creamy, exotic pulp at the center of a large melon. Fruit oblongish, obovate, sub globose to ellipsoidal, large, 20–25 cm long by 6–10 cm wide, weighing up to two kg, woody, hard, pubescent, rough, brown, fall to the ground when ripe. The endocarp is yellowish white, pulpy, soft, aromatic, and acid-sweet enclosing 25–50 superposed seeds in five rows. It is covered with a hard exocarp which is 4 to 7 mm thick. The pulp of the fruit is very fragrant and smells like banana. Cupuassu looks like a cross between a papaya and coconut. It has an aromatic and buttery pulp with approximately 35 hazelnut-sized seeds. As a cousin of the cacao fruit, cupuassu has a prized tropical flavor combining elements of chocolate, bananas, pear, passion fruit and pineapple.
| Name | Cupuassu |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Theobroma grandiflorum |
| Native | Amazon basin in the southern and eastern Pará |
| Common Names | Brazilian Cocoa, Copoasu, Large-Flowered Cocoa, Cupuasu, Cupuacu, cupuazú, cupu assu |
| Name in Other Languages | Brazil : Copoasu, Cupuaçú, Cupuaçuzeiro, Cupuarana, Cupu-Assu Cupuassu, Cupuassú, Cupu Do Mato, Copoaçú, Pupu, Pupuaçú ( Portuguese ); English: theobroma Colômbia : Bacau, Kopoazu; Costa Rica : Cacau Silvestre, Pataiste, Tete Negra; Czech : Kakaovník Velkokvětý; Portuguese : Cupuaçú, Cupuassú; Suriname : Lupu; Spanish: Copoasú, Copoasú, Copuazú, Cupassú, Cupuarana, Cupuasú. |
| Plant Growth habit | Erect, evergreen, much-branched tree |
| Growing Environment | Prefers a very humid environment and need lots of water for good growth. |
| Plant Size | 5 to 15 meters (16 to 50 feet) |
| Bark | Brown bark |
| Leaf | Simple, entire, alternate, coriaceous, narrowly ovate- to obovate-elliptic, 25–35 cm long and 6–10 cm wide, base rounded to shallowly cordate, apex long acuminate with a 9–10 pairs of lateral veins, bright-green, pubescent upper surface and grey underside. |
| Flower | Bisexual, small, pentamerous, occurring in 3–5 flowered cymose inflorescence on trunk and main branches. |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Oblongish, obovate, sub globose to ellipsoidal, large, 20–25 cm long by 6–10 cm wide, |
| Fruit Color | Brown |
| Fruit Weight | Between 1 to 2 kilos |
| Flesh Color | Yellowish white, pulpy, soft, aromatic |
| Flavor/Aroma | Smells like banana. |
| Taste | Often compared to chocolate, banana, melon or bubble gum. |
| Seed | Sub globose, 2 cm across, covered in white testa, cotyledons fleshy, non endospermous. |
| Season | January to April |
| Major Nutrition | Total Fat (lipid) 13.6 g (38.86%) Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) 0.08 mg (0.53%) |
| Calories in 1 tbsp ( 13.6 g) | 120 K cal |
References:
http://www.amafruits.com/cupuacu
http://www.fruitsinfo.com/cupuacu-tropical-fruits.php
http://www.raysahelian.com/cupuacu.html
http://www.vitaminclass.com/cupuacu-benefits/
http://www.buzzle.com/articles/cupuacu-fruit.html
http://www.natures-health-foods.com/cupuacu.html
http://www.womenfitness.net/cupuacu_pharmacyFruit.htm
http://www.byoaudio.com/note/C1NKS2B9
http://healthiestsuperfoods.com/cupuacu-health-benefits/
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=101891
http://www.plantnames.unimelb.edu.au/Sorting/Theobroma.html
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=506108#null
Comments
comments