 Appendicitis is one of the most common surgical emergencies worldwide, occurring when the appendix—a small, tube-like pouch attached to the large intestine—becomes inflamed and filled with pus. While the condition is well-known for the sharp pain it causes in the lower right abdomen, the biological triggers behind it are often misunderstood.
Appendicitis is one of the most common surgical emergencies worldwide, occurring when the appendix—a small, tube-like pouch attached to the large intestine—becomes inflamed and filled with pus. While the condition is well-known for the sharp pain it causes in the lower right abdomen, the biological triggers behind it are often misunderstood.
Appendicitis is almost always the result of an obstruction. The appendix is a narrow tube with a single opening that connects to the cecum (the beginning of the large intestine). When this opening gets blocked, the appendix cannot empty its contents. Mucus backs up, pressure rises, and bacteria naturally present in the gut begin to multiply rapidly. This leads to swelling, infection, and if left untreated, the potential rupture of the organ.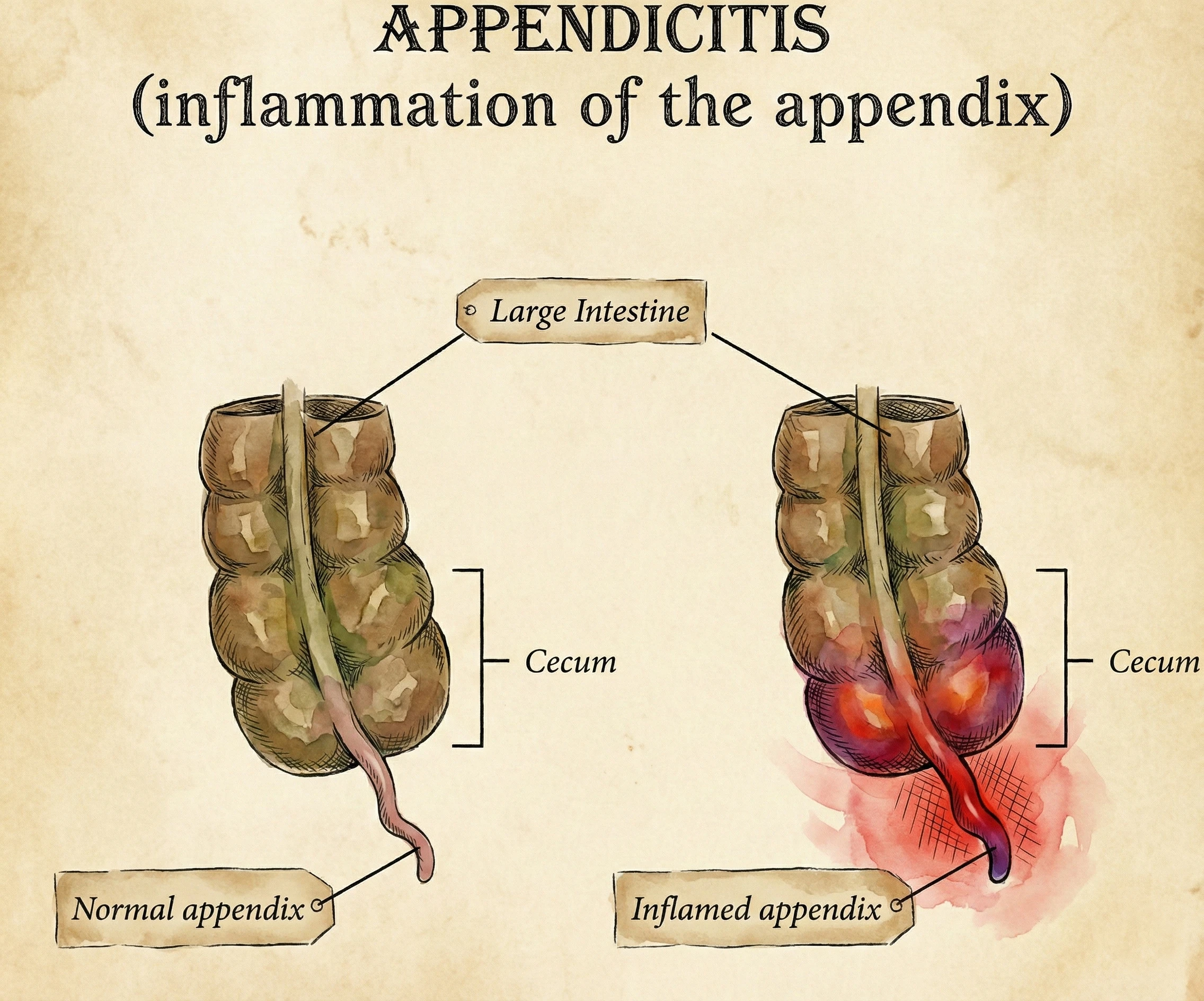
The Leading Cause: Fecaliths (Appendicoliths)
In adults, the most frequent cause of appendicitis is a fecalith, also known as an appendicolith or “appendix stone.”
A fecalith is a hard, calcified piece of stool (fecal matter) that becomes trapped in the appendix. Because the lumen (the inner space) of the appendix is very narrow, even a small piece of hardened stool can act like a plug, completely sealing off the connection to the large intestine. Once this seal is formed, the appendix becomes a closed loop. It continues to produce mucus which has nowhere to go, causing internal pressure to skyrocket and cutting off blood flow to the widespread tissue. This environment is perfect for bacterial overgrowth.
Lymphoid Hyperplasia: The Immune Response
In children and young adults, the most common cause of obstruction is lymphoid hyperplasia. This refers to the rapid enlargement (swelling) of the lymphoid tissue found in the wall of the appendix.
The appendix is rich in lymphatic tissue, which is part of the body’s immune system. When the body fights an infection—such as a viral stomach flu, a respiratory infection, or even measles—this lymph tissue can swell significantly, much like swollen glands in the neck during a cold. Because the appendix is so narrow, this swollen tissue pushes inward, effectively squeezing the tube shut. This blockage initiates the same cycle of inflammation and infection seen with fecaliths.
Parasites and Intestinal Worms
Although much rarer in developed nations, parasites remain a notable cause of appendicitis in many parts of the world. Intestinal worms, particularly Enterobius vermicularis (commonly known as pinworms) or Ascaris lumbricoides (roundworms), can migrate from the intestines into the appendix.
The presence of these parasites can cause appendicitis in two ways: they can physically cluster together to block the lumen, or their presence can damage the lining of the appendix, triggering inflammation and swelling that subsequently closes the opening.
Trauma and Injury
Physical trauma to the abdomen is an infrequent but possible cause of appendicitis. Direct blunt force trauma—such as that sustained in a car accident (seatbelt injury), a hard fall, or a high-impact sports injury—can cause internal bruising or bleeding.
If this trauma affects the appendix, the resulting swelling or blood clot (hematoma) can obstruct the opening. However, strictly speaking, traumatic appendicitis is rare compared to obstructions caused by stool or infection.
Tumors (Neoplasms)
In older adults, a tumor may be the underlying cause of the obstruction. These neoplasms can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
Tumors such as carcinoids or adenocarcinoma can grow within the appendix itself or in the adjacent cecum. As the tumor enlarges, it may press against the opening of the appendix or grow inside the tube, physically blocking the passage. Because the risk of tumors increases with age, doctors may investigate the possibility of an underlying cancer in elderly patients presenting with appendicitis symptoms.
Conclusion
Regardless of the trigger—whether a hardened stone of stool, swollen immune tissue from a flu, or a rare parasitic infection—the mechanism of appendicitis remains a dangerous blockage. Once the appendix is obstructed, the clock starts ticking toward potential rupture.
It is important to note that in many cases, even after surgery, the specific cause of the blockage may remain unidentified. However, understanding these causes highlights that appendicitis is rarely a result of lifestyle choices, but rather a mechanical failure within the digestive tract. Recognizing the symptoms early and seeking immediate medical care remains the only way to safely manage this condition.

