| Ammoniacum Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Ammoniacum |
| Scientific Name: | Dorema ammoniacum |
| Origin | Iran, Central Asia, Afghanistan, Sibiria and northern Russia |
| Shapes | Achenes |
| Taste | Acrid |
| Health benefits | Beneficial for chronic bronchitis, asthma, catarrh, swellings of the joints, indolent tumors, cough, induce sweating, menstruation |
| Name | Ammoniacum |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Dorema ammoniacum |
| Native | Iran, Central Asia, Afghanistan, Sibiria and northern Russia |
| Common Names | Gum ammoniac, Gummi-resina ammoniacum, Ammoniac, Ammoniac-plant, Ammoniakum |
| Name in Other Languages | English: Ammoniac, Ammoniac-plant, Ammoniakum French: Dorème ammoniac German: Ammoniacum, Ammoniakharzpflanze Italian: Ammoniaco Swedish: Dorema |
| Plant Growth Habit | Clump-forming perennial plant |
| Growing Climates | Loess loams in desert areas, dry rocky areas |
| Plant Size | 2½ or 3 meters (8 or 9 ft.) |
| Leaf | Have tripinnate leaves that are alternate. The elliptic leaflets are petiolate |
| Flower | Plant produces compound umbels of white five-stellate flowers |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Achenes |
| Flavor/ aroma | Faintly fetid, unpleasant odor, which becomes more distinct on heating |
| Taste | Acrid |
| Plant Parts Used | Gum resin exuding from the flowering and fruiting stem |
Plant Description
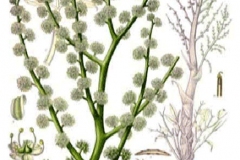
Ammoniacum is a clump-forming perennial plant that normally grows about 2½ or 3 meters (8 or 9 ft.) tall. The plant is found growing in loess loams in desert areas and dry rocky areas. The plant has tripinnate leaves that are alternate. The elliptic leaflets are petiolata. The plant produces compound umbels of white five-stellate flowers. Fertile flowers are followed by achene.
Its whole stem is pervaded with a milky juice, which oozes out on an incision being made at any part, which is pressed into blocks and then ground into a powder. This juice speedily hardens into round tears, forming the “tear ammoniacum” of commerce. “Lump ammoniacum”, the other form of the substance, consists of aggregations of tears, frequently incorporating fragments of the plant itself, as well as other foreign bodies.
Ammoniacum has a faintly fetid, unpleasant odor, which becomes more distinct on heating; externally, it possesses a reddish-yellow appearance, and when the tears or lumps are freshly fractured they exhibit a waxy luster. It is chiefly collected in central Persia, and comes to the European market by way of Bombay. Internally it is used in conjunction with squills in bronchial affections. In asthma and chronic colds it is found useful, but it has no advantages over a number of other substances of more constant and active properties.
Traditional uses and benefits of Ammoniacum
- Ammoniacum has been used in Western herbal medicine for thousands of years and is still seen as an effective remedy for various complaints of the chest.
- Gum resin is found in cavities in the tissues of stems, roots and petioles.
- It often exudes naturally from holes in the stems caused by beetles though this is not as pure as that obtained from the plant tissues.
- Resin is antispasmodic, carminative, diaphoretic, mildly diuretic, expectorant, poultice, stimulant and vasodilator.
- It is often used internally in the treatment of chronic bronchitis (especially in the elderly), asthma and catarrh.
- Externally, it is used as a plaster for swellings of the joints and indolent tumors.
- Gum is used as a plaster for white swellings of the joints and for indolent tumors.
- Its use is of great antiquity and is mentioned by Hippocrates.
- It has been found especially useful in chronic affections of the respiratory organs, especially among the aged, or those in whom the expectoration is scanty, as in cough, asthma, etc.
- It has likewise been found advantageous in profuse mucous discharges.
- It has also been recommended in hysteria, but is inferior to some other of the fetid gum-resins, as asafetida.
- Ammoniacum may be of service in small doses, in the headache resulting from disease of the frontal sinuses, in affections of the optic nerve, in catarrhal affections of the throat, nasal passages, eyes, ears and stomach, mucous diarrhea, and in pains in the limbs accompanying disease of more or less of the mucous tissues.
- Applied externally in the form of plaster, it irritates the skin, frequently producing a papular eruption.
- It is still listed in the British Pharmacopoeia as an antispasmodic and as an expectorant that stimulates the coughing up of thick mucus.
- It is a specific treatment for chronic bronchitis, asthma, and persistent coughs.
- Ammoniacum is also occasionally used to induce sweating or menstruation.
Other Facts
- A medicinal gum or resin called ‘Ammoniacum’ is exuded from insect damaged stems.
- It is also used in perfumery and in porcelain cement as well as for plasters.
Precautions
- There are no serious side effects reported till now. However, it is always advisable to use this herb under the supervision of a homeopathic practitioner.
- Applied externally in the form of plaster, it irritates the skin, frequently producing a papular eruption.
References:
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2775465
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=505942#null
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Dorema+ammoniacum
https://www.botanical.com/botanical/mgmh/a/ammon032.html
https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=DOAM2
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxon/taxonomydetail?id=14547
http://tn-grin.nat.tn/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=14547
http://en.hortipedia.com/Dorema_ammoniacum
http://temperate.theferns.info/plant/Dorema+ammoniacum
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/DOMAM
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ammoniacum
http://www.naturalmedicinalherbs.net/herbs/d/dorema-ammoniacum=ammoniacum.php
https://practicalplants.org/wiki/Dorema_ammoniacum
https://www.henriettes-herb.com/eclectic/kings/dorema-ammo.html