| Camwood Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Camwood |
| Scientific Name: | Baphia nitida |
| Origin | Coastal region of central west Africa |
| Shapes | Compressed pod that are 8–16.5 cm long and 1–1.5 cm wide, pointed at both ends usually containing 2 - 4 brown, flat seeds |
| Health benefits | Good for rheumatic pains, sprains, swollen joints, gastrointestinal problems, asthma, sterility, painful menstruation, jaundice, diabetes, constipation and headache |
| Name | Camwood |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Baphia nitida |
| Native | Coastal region of central west Africa |
| Common Names | Barwood, Dolo, Doro, African Sandalwood, shiny camwood |
| Name in Other Languages | Afrikaans: Camwood Albanian: Camwood Amharic: Kamiwidi (ካምውድ) Arabic: Khashab alwird (خشب الورد) Armenian: P’aytanyut (փայտանյութ), Nerkatsarr (Ներկածառ) Azerbaijani: Camwood Bengali: Camwood Bulgarian: Camwood, анголско дърво (анголско дърво) Burmese: Kabyaar (ကဗျာ) Chinese: Kǎn wǔdé (坎伍德) Croatian: Camwood Czech: Camwood Danish: Camwood Dutch: Camwood English: Camwood, African-sandalwood, Barwood, shiny camwood Esperanto: Camwood Estonian: Camwood Filipino: Kamatis Finnish: Camwood French: Camwood, Bois de cam, Bois rouge, bois de corail dur Georgian: Aklemi (აქლემი) German: Camwood Greek: Camwood Gujarati: Kamavuḍa (કમવુડ) Hausa: Camwood Hebrew: קמווד Hindi: Kainvood (कैंवूड) Hungarian: Afrikai szantálfa Icelandic: Kambur Indonesian: Camwood Irish: Camwood Italian: Camwood Japanese: Kamuuddo (カムウッド) Javanese: Camwood Kannada: Kyāmvuḍ (ಕ್ಯಾಮ್ವುಡ್) Kazakh: Ağaş ağaşı (ағаш ағашы) Korean: Kaem udeu (캠 우드) Kurdish: Kemilî Lao: Camwood Latin: Camwood Latvian: Kamfs Lithuanian: Kampmedis Macedonian: Drvja od drvo (дрвја од дрво) Malagasy: Camwood Malay: Camwood Malayalam: Kyānvuḍ (ക്യാംവുഡ്) Maltese: Canga Marathi: Kĕmavuḍa (कॅमवुड) Mongolian: Temeenii mod (тэмээний мод) Nepali: Kyaamavud (क्यामवुड) Norwegian: Camwood Oriya: କାମ୍ୱୁଡ୍ | Pashto: کیموت Persian: چوب چوب Polish: Drewno leśne Portuguese: Camwood, madeira-de-cam Punjabi: Kaimavuḍa (ਕੈਮਵੁੱਡ) Romanian: Camwood Russian: Bafiya yarkaya (бафия яркая), Angol’skoye derevo (Ангольское дерево) Serbian: Camvood (цамвоод) Sindhi: ڪيم ووڊ Sinhala: Kæmvuḍ (කැම්වුඩ්) Slovenian: Camwood Spanish: Bosque de lata Sudanese: Camwood Swedish: Camwood Tajik: Sutur (шутур) Tamil: Kēmvuṭ (கேம்வுட்) Telugu: Camwood Thai: Camwood Turkish: Afrika’daki bir ağacın sert ve kızıl kerestesi Ukrainian: Camwood Urdu: کیماوڈ Uzbek: O’tin Vietnamese: Gỗ cam Welsh: Camwood Zulu: Camwood |
| Plant Growth Habit | Leguminous, shrubby, hard-wooded, erect small tree |
| Growing Climates | Under storey tree in wetter parts of the coastal regions, in rainforest, in secondary forest, on abandoned farmland |
| Plant Size | Up to 2.5-10 m tall and 45 cm across |
| Leaf | Leaf blade is ovate, elliptical, obovate or lanceolate, 5–21 cm long and 3–9 cm wide, base rounded to cuneate, apex acuminate, slightly leathery and almost glabrous, pinnately veined |
| Flower | White, pea-like and fragrant, having a bright yellow center |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Compressed pod that are 8–16.5 cm long and 1–1.5 cm wide, pointed at both ends usually containing 2 – 4 brown, flat seeds |
| Seed | Flat seeds |
| Propagation | By seeds and cuttings |
| Plant Parts Used | Root, bark, leaf |
| Health Benefits |
|
| Culinary Uses |
|
Plant Description
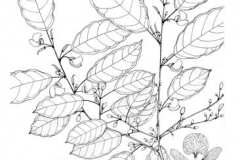
Camwood is a leguminous, shrubby, hard-wooded, erect small tree that normally grows up to 2.5-10 m tall and 45 cm across. The plant is found growing under storey tree in wetter parts of the coastal regions, in secondary forest, in rainforest, and on abandoned farmland. Leaves are alternate, simple and entire. Stipules are quickly caduceus. Petiole is 1–4 cm long, prominently thickened at base and at top. Leaf blade is ovate, elliptical, obovate or lanceolate, 5–21 cm long and 3–9 cm wide, base rounded to cuneate, apex acuminate, slightly leathery and almost glabrous, pinnately veined.
Leaves and bark are thought hemostatic and anti-inflammatory and are used for curing sores and wounds, while the dye from the bark is formed into red body cosmetics. Honey-hunters rub their body with the dye to prevent bee-stings. It is also made into ointments which are applied against stiff and swollen joints, sprains and rheumatism. The plant materials are increasingly being used as a major ingredient in the production of local cosmetic and skincare products.
Flower and fruits
Flowers in axillary fascicles, 1–5-flowered, bisexual and papilionaceous. Pedicel is slender, 3–17 mm and long. Calyx is spathaceous, 8–10 mm long, glabrous but with a tuft of brown hairs at apex. Corolla is standard sub-orbicular, 1–2 cm in diameter, white with a yellow center, wings and keel white with a pocket near the base. Stamens 10, filaments unequal, free, up to 7 mm long; ovary superior, sessile, glabrous, sometimes with a row of silvery hairs along the dorsal margin, 1-celled, style curved, filiform, stigma small. Fertile flowers are followed by compressed pod that are 8–16.5 cm long and 1–1.5 cm wide, pointed at both ends and are about 1–4-seeded. Seeds are almost circular in outline, 1–1.5 cm in diameter and brown colored.
Dry leaf is an ingredient of traditional black soap, while the heartwood, bark and roots are crushed into a paste and used as skin cosmetic. Wood is extremely hard, heavy and durable and is traditionally used to make knife handles, drum sticks, mortars and pestles. It is used for making ornamental fencing in areas of South West Nigeria.
Health benefits of Camwood
Listed below are some of the popular health benefits of using Camwood
1. Heals sunburns and acne
Camwood Powder helps to heal the damages on the skin caused by the sun. It is a natural beauty ingredient used for treating sunburns. Mostly, teenagers have to deal with pimples, acne, eczema and Camwood Powder is a great help when added to their skincare routine.
2. Anti-aging
Camwood is loaded with anti-aging, detoxifying and wrinkle reducing properties. It is considered as a good cosmetic product which helps to remove or reduce the signs of aging. Camwood when mixed with almond oil and coconut oil helps to tighten your skin. Similarly it can also be mixed with several homemade beauty products like face Masks, natural face moisturizers and scrubs for brilliant outcomes.
3. Soothes the skin
Camwood powder is also loaded with natural skin soothing properties that help to enhance skin beautifully. It will help you remove your dead, dull skin, revealing glowing, beautiful inner skin naturally.
4. Bleaching abilities
Camwood when mixed with raw black soap, turmeric and honey, helps to lighten the skin. It helps to keep the skin toned and if escalated, can even bleach the skin.
5. Anti-inflammatory properties
Camwood powder consist of powerful antioxidants and is also an anti-inflammatory agent that helps to improve blood circulation to your face, remove toxins and fight the formation of wrinkle-causing free radicals. It can also be used to treat insect bites and swelling.
Traditional uses and benefits of Camwood
- Camwood has long been used in several traditional African medicines.
- Its leaves have inflammatory, antidiarrheal and analgesic activities.
- An ointment can be made by mixing powdered heartwood with shea butter for rheumatic pains, sprains and swollen joints.
- An ointment made from the leaves has showed anti-inflammatory activity.
- An infusion of the leaves is drunk to cure enteritis and other gastrointestinal problems.
- Powdered leaves when taken with palm wine or food helps to cure venereal diseases.
- Camwood is combined with Senna occidentalis and is drunk against asthma.
- In combination with the leaves of Morinda lucida it is used to treat female sterility and painful menstruation.
- Decoction of the leaves is taken against jaundice and diabetes.
- Leaves and bark have been used as an enema to treat constipation.
- Leaves or leaf juice are used externally against parasitic skin diseases.
- It is used to treat bone fractures when Camwood is mixed with Veld Grape.
- Both leaves and bark are used for healing sores and wounds.
- Bark decoction is drunk to cure epilepsy and cardiac pain.
- Finely ground root bark are mixed with honey and taken against asthma.
- Pounded dried root is mixed with water and oil and applied to a ringworm-like fungus attacking the feet in Ghana and Nigeria.
- Leaves and bark are used for healing sores and wounds in Ghana, Côte d’Ivoire and Nigeria.
- Leaf sap is applied as eye drops against jaundice.
- An extract of young leaves with some salt and red pepper is used as nose drops against headache.
- Bark decoction is drunk to cure cardial pain in Sierra Leone.
Other Facts
- Bark and heartwood are great sources of a high quality red dye used to dye raffia and cotton textiles.
- Twigs are used as chewing sticks.
- Plant responds well to trimming and is grown as a hedge and fence.
- It was considered to have a coloring power 3 – 4 times stronger than the other ‘insoluble’ redwoods by European and American dyers.
- Camwood was used to obtain red colors, reddish to dark brown colors, muddy brown’ and ‘London smoke’, mostly in combination with other dyewoods in Wool Industry.
- Until the beginning of the 20th century, it was used for dark grey and black colors in the wool-cloth industry.
- In UK, it was used to dye silk pink, ‘acid brown’ and ‘light claret’.
- Powdered heartwood is a familiar red body paint in West Africa
- Paste of the heartwood is used as a cosmetic for the skin.
- Water Red liquid obtained by soaking dried and ground roots, is used for painting furniture.
- Yoruba ceremonial masks are painted dark red with a decoction of the wood in South western Nigeria and Southern Benin.
- Heartwood is pale brown when fresh, turning rapidly to dark red or orange upon exposure.
- Wood is extremely hard, heavy and durable, close-grained and of fine texture.
- Wood is used for making tool-handles, farm implements, house posts, rafters, utensils such as walking sticks, mortars, pestles and naves of wheels.
- It was formerly distributed to Europe for turnery and cabinetry.
- In some regions tree is considered sacred, gifted with the power to protect against evil spirits and to attract benevolent ones.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=506240#null
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Baphia+nitida
https://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Baphia+nitida
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baphia_nitida
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Baphia_nitida_(PROTA)
https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=BANI3
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/BAHNI
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/ild-7095