| Coat Button Quick Facts | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name: | Coat Button | ||
| Scientific Name: | Tridax procumbens | ||
| Origin | Mexico, Central America and tropical South America | ||
| Colors | Dark brown to black | ||
| Shapes | Hard achene narrowly obconical, and 2.0-2.5 mm long, with 15-20 patent, 0.12-0.24 inches (3-6 mm) long | ||
| Health benefits | Good for colds, inflammation, vaginitis, stomach pains, diarrhea, fever, cough, back ache, epilepsy, bronchial catarrh, ulcers, anal fistula, and hemorrhoids | ||
| Name | Coat Button |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Tridax procumbens |
| Native | Mexico, Central America (i.e. Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras and Nicaragua) and tropical South America (i.e. Venezuela, Bolivia, Colombia and Peru) |
| Common Names | Coat buttons, coatbuttons, Mexican daisy, tridax, tridax daisy, wild daisy, dagad-phul |
| Name in Other Languages | Assamese: Kurakuri bana (কুৰকুৰি বন), putali bana (পুতলী বন), tridhara (ত্রিধারা) Australia: Tridax daisy Bengali: Tridhara (ত্রিধারা), kanaiya (কানাইয়া), kanaphuli (কানফুলি), paradesi bhanara (পরদেশি ভাঙড়া), tridaksa (ত্রিদক্ষ), tridhara (ত্রিধারা) Brazilin: Erva de touro Burmese: Mive sok ne-gya Central America: Hierba del toro Chinese: Chángbǐng jú (長柄菊), yǔ máng jú (羽芒菊), Kotobukigiku Colombia: Cadillo chisaca Cuban: Romerillo de loma, Romerillo Dagbani: Alepele bindi English: Coat-buttons, Tridax daisy, Tridax, dagad-phul, wild daisy, Mexican daisy Fijian: Tubua leka, tumbualeka, voti French: Herbe calille German: Niederliegender Dreibiß Ghana: Nantwi bini Gujarati: Ghaburi (ઘાબુરી), pardeshi bhangaro (પરદેશી ભાંગરો) Hindi: Ghamra, Khal Muriya, Tal Muriya, kanphuli (कानफुली), kumra (कुमढ़ा) Indonesian: Gletang, Gletangan, Sidowlo, Tar sentaran, cemondelan, glentangan, gobesan, katumpang, londotan, orang aring Irula: Mukuthi poo, Railpoo Jamaican: Bakenbox Japanese: Kotobukigiku (コトブキギク) Javanese: Songgolangit, Sidawala Kachchhi: Vilati bhangaro (વિલાતી ભંગરો) Kannada: Jayanthi, Addike soppu (ಅಡ್ಡಿಕೆಸೊಪ್ಪು) Attige soppu (ಅಟ್ಟಿಗೆ ಸೊಪ್ಪು), Gabbu sanna shaavanthi (ಗಬ್ಬು ಸಣ್ಣ ಶಾವಂತಿ), Netta gabbu shaavanthi (ನೆಟ್ಟ ಗಬ್ಬು ಶಾವಂತಿ), Teeke (ತೀಕೆ), Sanna Gida Madagascar: Anganiay Malayalam: Chiravanak, cheeravanakk (ചിരവനാക്ക്), kumminippachcha (കുമ്മിണിപ്പച്ച), kurikutticheera (കുറികൂട്ടിചീര), mukutti pu (മുകുത്തി പൂ), muriyampachchila (മുറിയമ്പച്ചില), otiyacheera (ഒടിയൻചീര), reyipuchcheti (റെയിൽപൂച്ചെടി), sanipuv (സാനിപൂവ്), telukkutti (തേളുക്കുത്തി), Railpoochedi, Thelkuthi, Odiyancheera, Sanipoovu Malaysian: Kanching baju Marathi: Kambarmodi (कंबरमोडी), bandukiche phul (बंदुकीचे फूल), dagadi paala (दगडी पाला), ekdandi (एकदांडी), jakhamjudi (जखमजुडी), kambarmodi (कंबरमोडी), tantani Mexico: Flor amarilla Myanmar: Mive sok ne-gya Nepali: Husure jhaar (हुसुरे झार), kurakure jhaar (कुरकुरे झार), putalee jhaar (पुतली झार), ramne jhaar (रम्ने झार) Nigerian: Igbalobe, Muwagun, Muriyam pachila, Jayanti, Vettukaaya-thala Odia: ବିଶଲ୍ଯ କରଣୀ bishalya karani Portuguese: Erva-de-touro Rajasthani: Kagla ri mehndi (कागला री मेहंदी) Russian: Trydaks lezhachyy (тридакс лежачий) Sanskrit: Jayanti veda (जयन्ती वेद), kshudra sevantika (क्षुद्र सेवन्तिका) Santali: ᱛᱨᱤᱫᱷᱟᱨᱟ Spanish: Cadillo chisaca, flor amarilla, hierba del toro, panquica, rosella, mata gusano, romerillo de loma Swedish: Tridax Tamil: Vettukaaya, Puntu (வெட்டுக்காயப் பூண்டு), kinarruppacan (கிணற்றுப்பாசான்), vettukkaya-p-puntu (வெட்டுக்காயப் பூண்டு), Thata poodu, Kenathuppoondu, Seruppadithalai, Seruppadithazhai, Vettukkaaya-thalai Taiwan: Kotobuki-giku Telugu: Gaddi chemanthi (గడ్డి చామంతి) Thai: Tin tukkae (ตีนตุ๊กแก) Tulu: Nela sevanthige (ನೆಲ ಸೆವಂತಿಗೆ) Urdu: Zagh mai hayat USA: Tridax daisy Vietnamese: Cúc mui |
| Plant Growth Habit | Semi-prostrate, spreading, herbaceous, perennial, procumbent annual herb |
| Growing Climates | Found in annual crops, roadsides, pastures, fallow land, meadows, waste grounds, railways, riverbanks, dikes and dunes and occasionally in lawns, perennial crops and nurseries |
| Plant Size | 8-30 inches (20-75 cm) long |
| Root | Strong taproot |
| Stem | Cylindrical, solid and highly hispid, covered with multicellular hairs of 1 mm, tuberculate at the base |
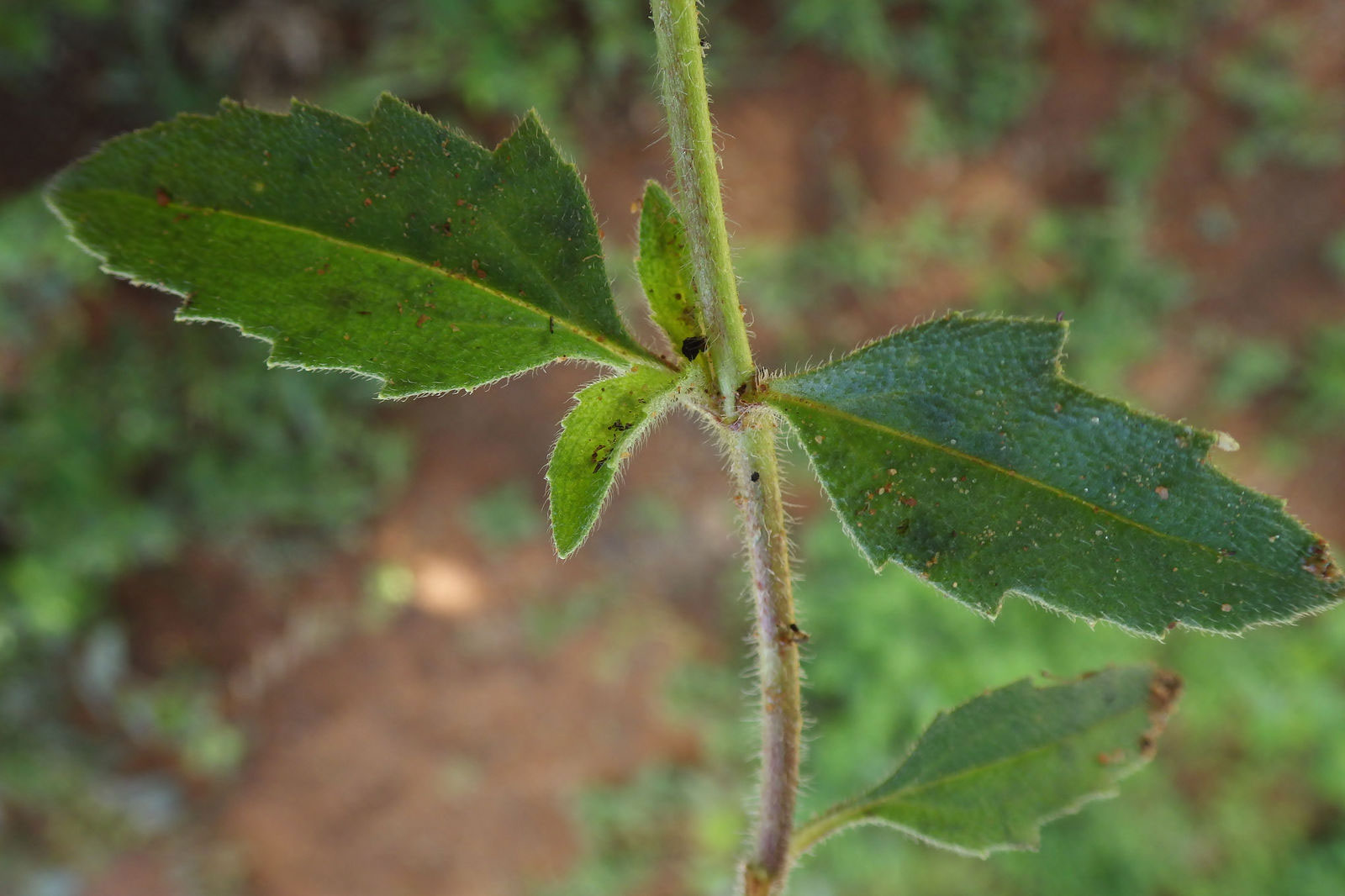
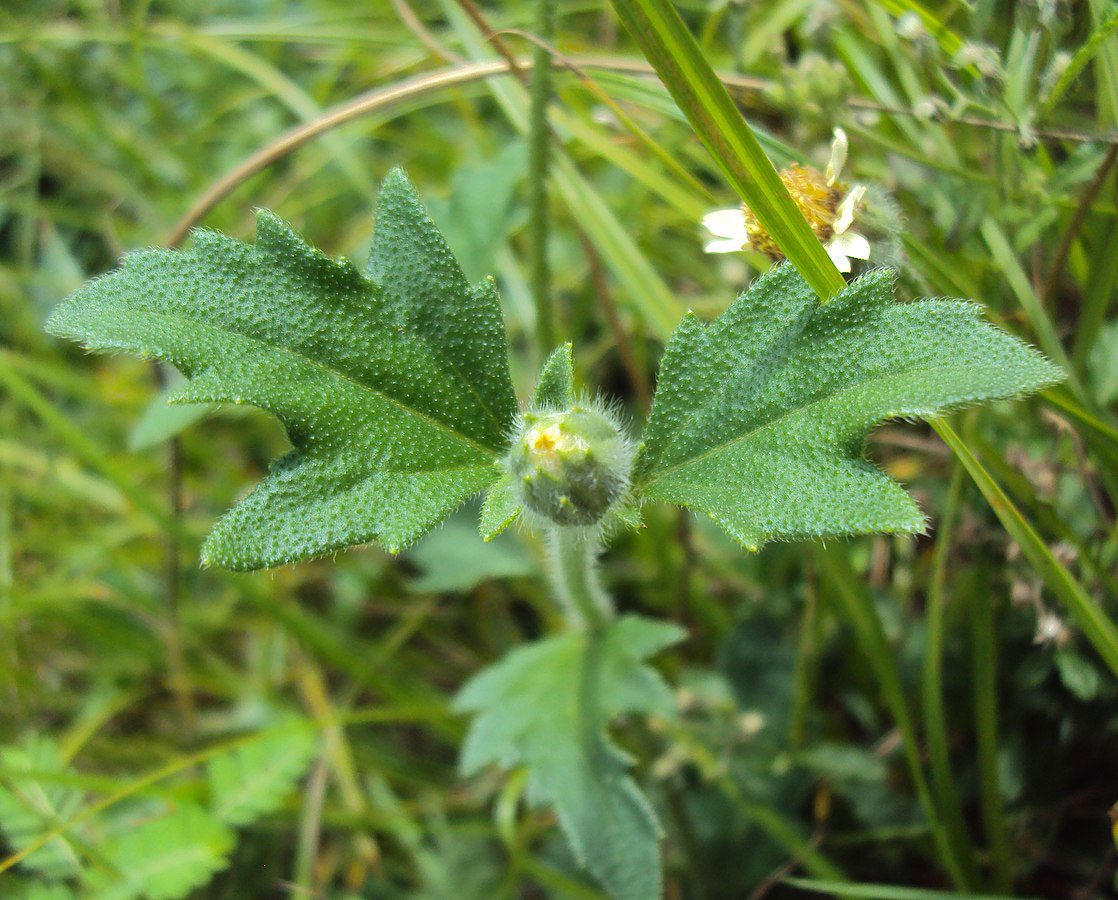
| Leaf | Opposite, simple, fleshy, pubescent, and carried by a concave petiole, 0.8-2.5 cm long. Leaf blades are thick, soft and dark green. The lamina is oval to lanceolate, 2.5 to 6 cm long and 2 to 5 cm wide, base attenuate in corner and with strongly and irregularly serrated margin |
| Flowering season | May to December |
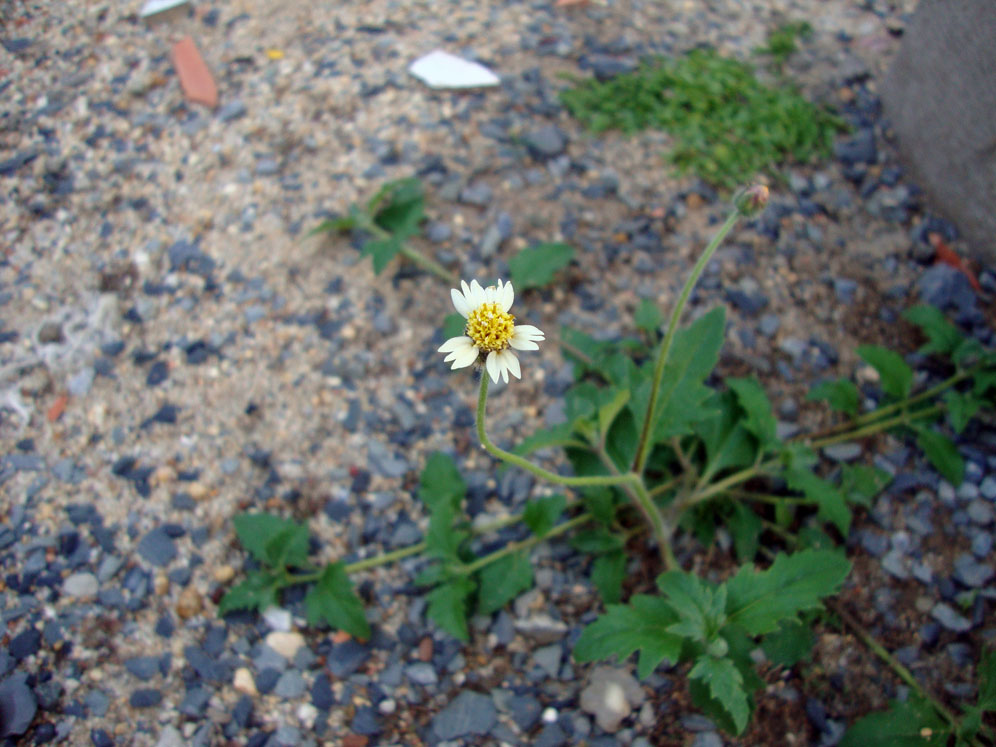
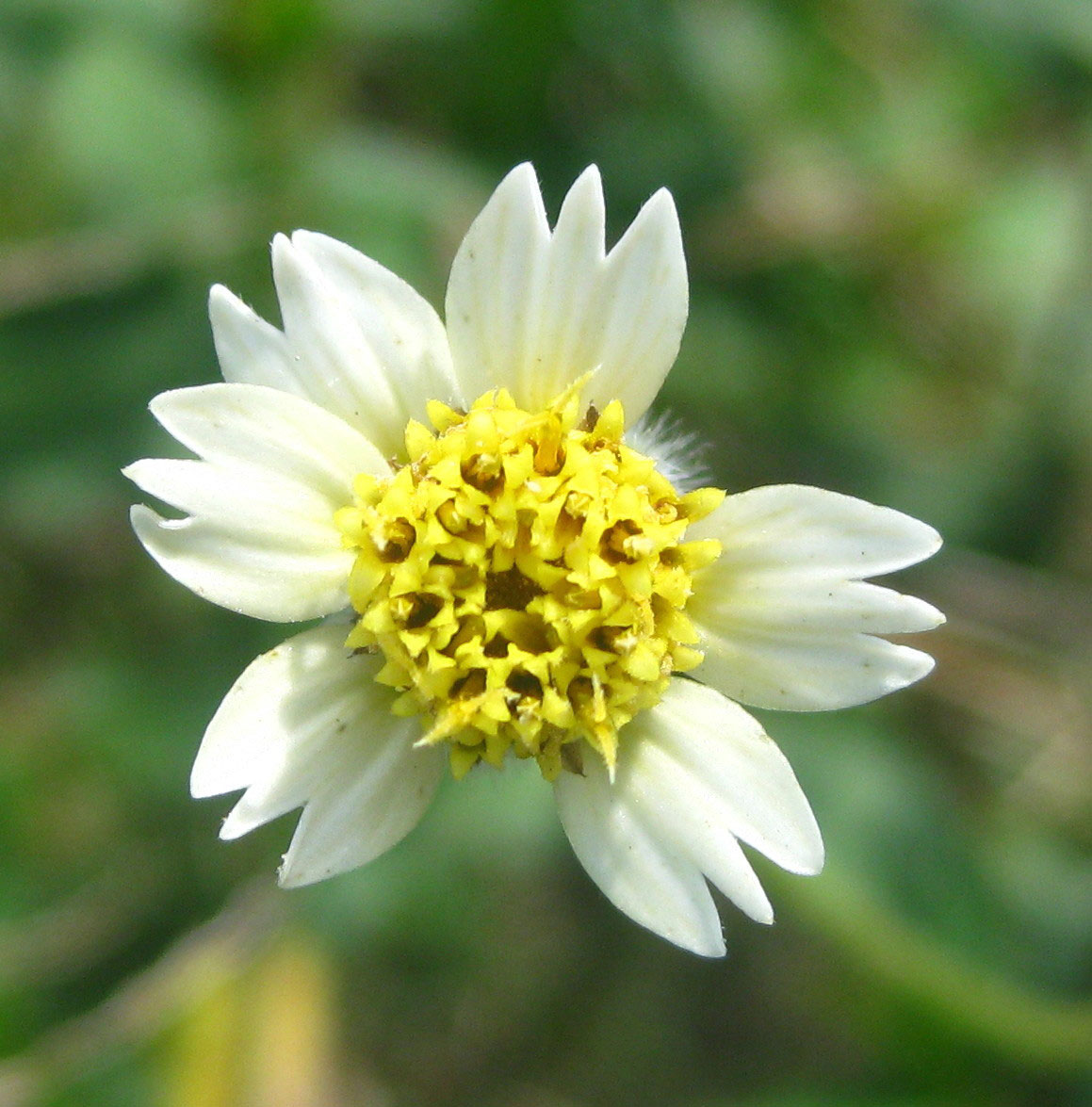
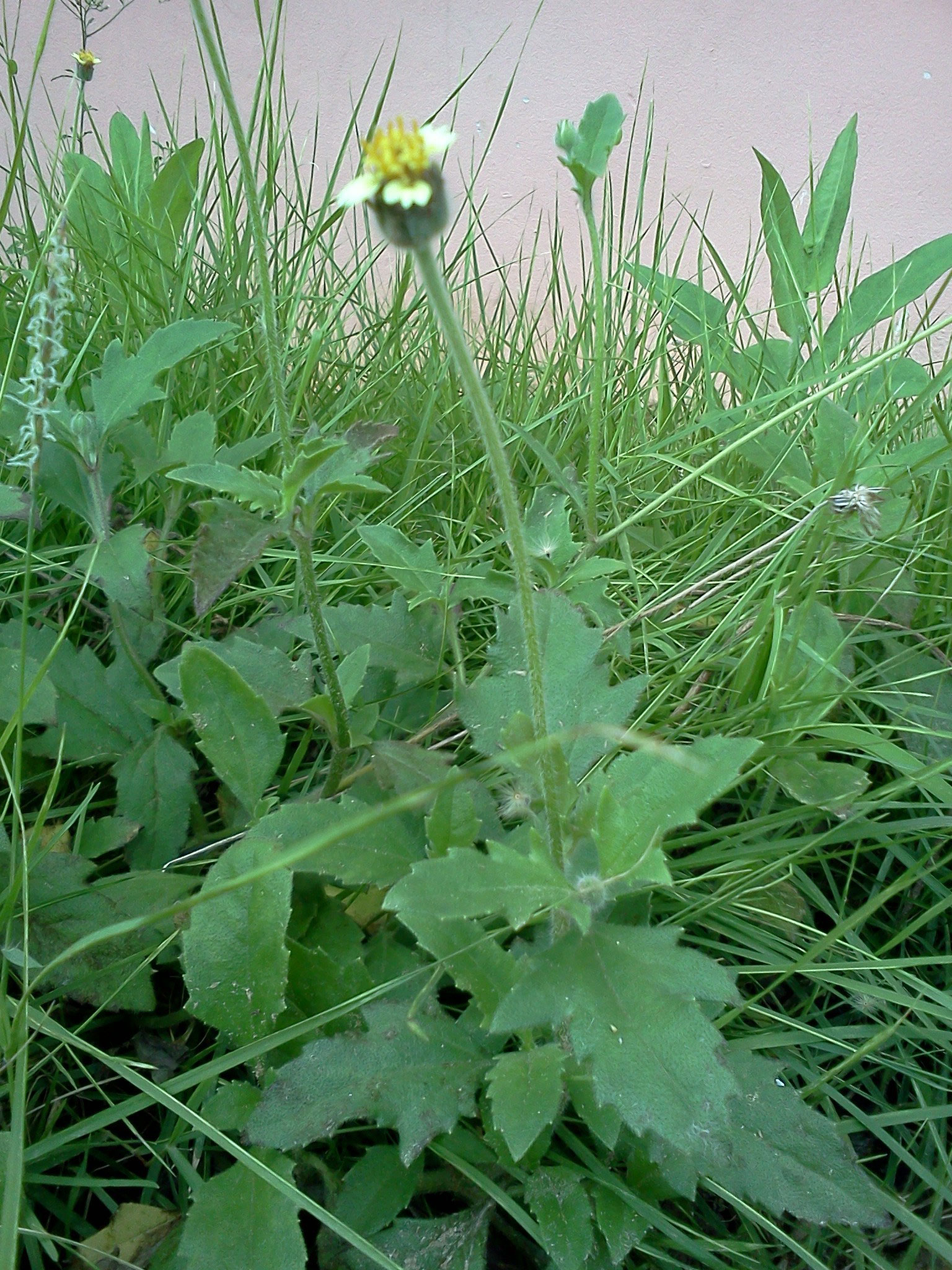
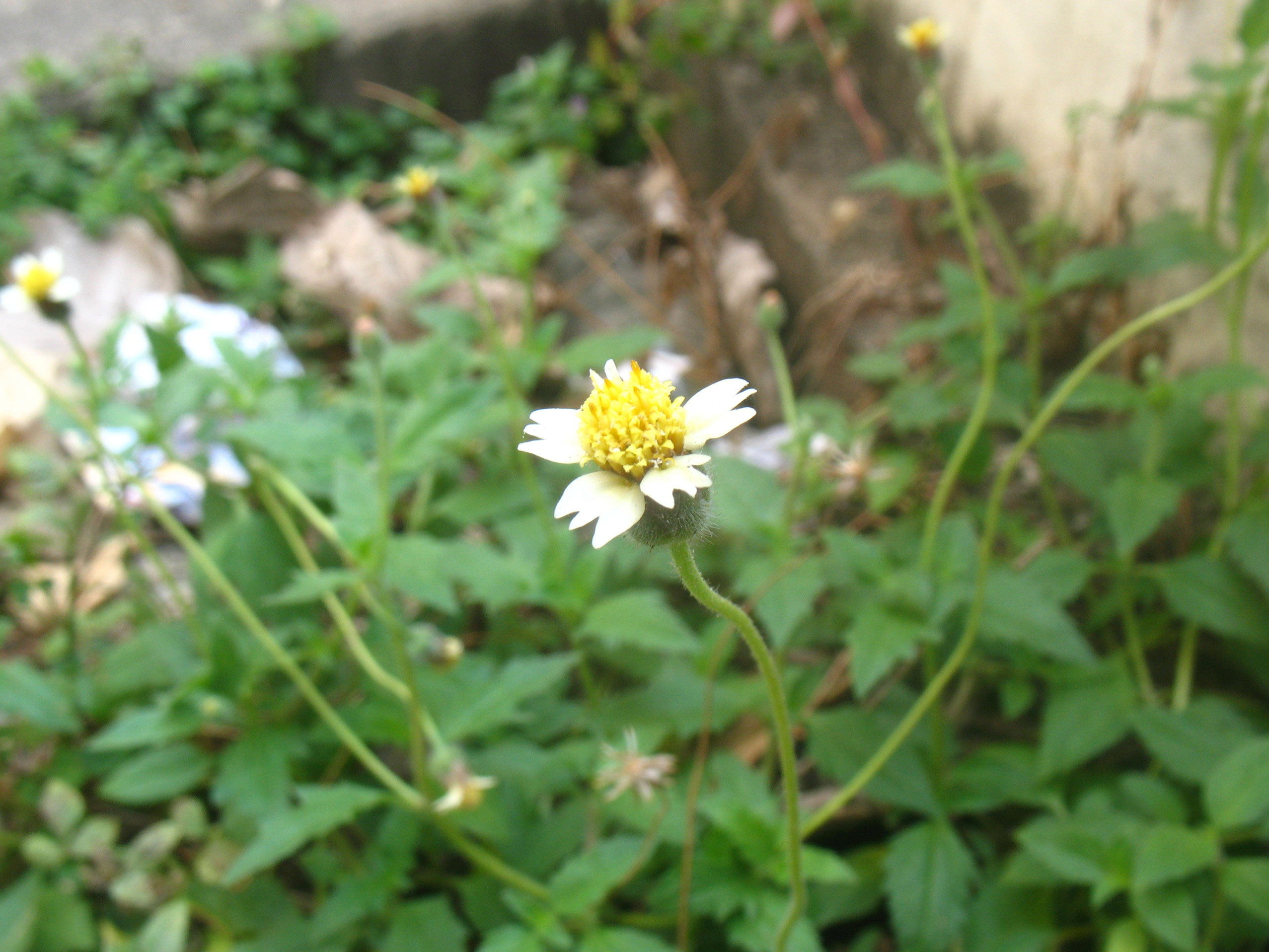
| Flower | The flower is tubular, yellow centered white or yellow flowers with three-toothed ray florets. They are about 0.4-0.6 inches (1-1.5 cm) wide, and held on a 4-12 inches (10-30 cm) long stalk. |
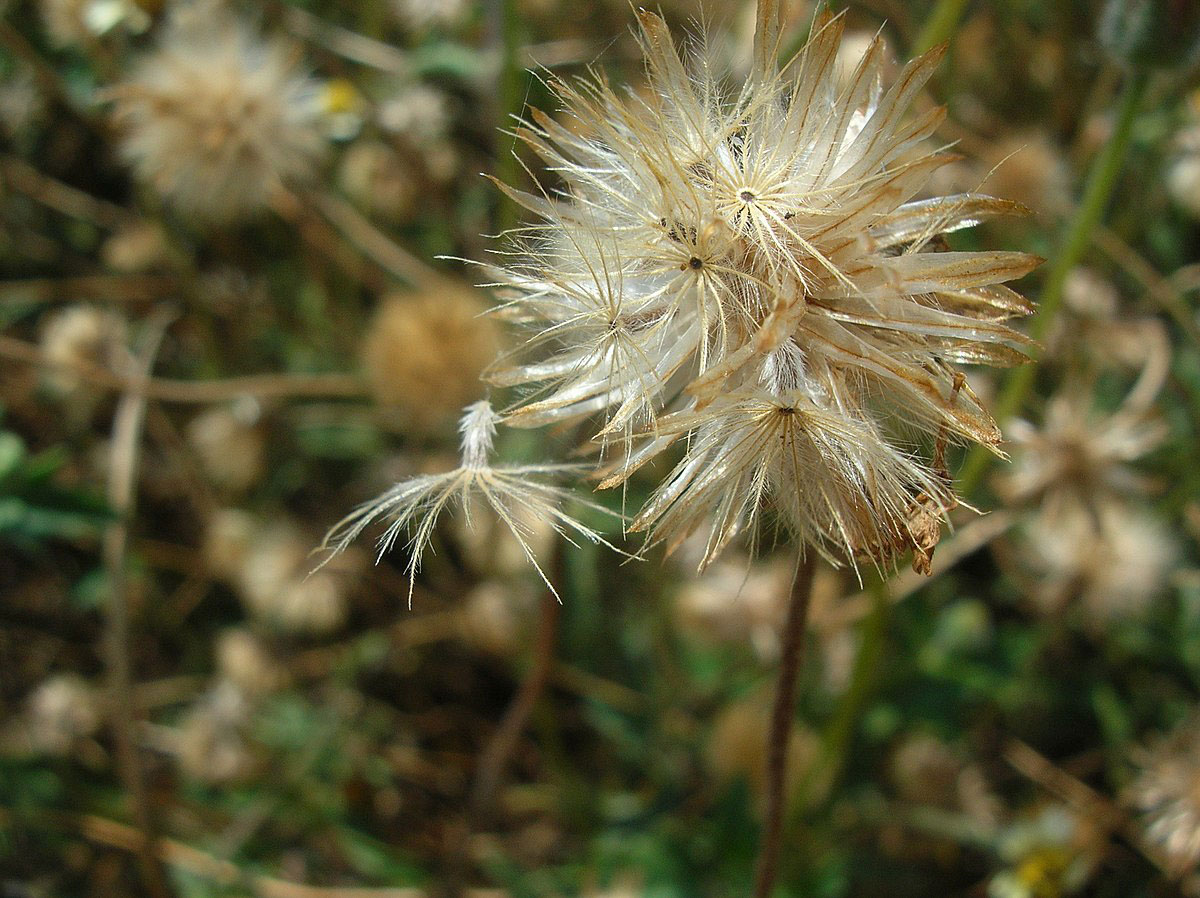
| Fruit Shape & Size | Hard achene, narrowly obconical, and 2.0-2.5 mm long, with 15-20 patent, 0.12-0.24 inches (3-6 mm) long, rather stiff, feathered, unequal bristles and having a feathery, plume like white pappus at one end. |
| Fruit Color | Dark brown to black, |
| Seed | Numerous, small with tuft of silky hairs on one side for wind dispersal. |
| Plant Parts Used | Whole plant, Leaves, stems, flowers |
| Propagation | By seed |
| Culinary Uses |
|
| Precautions |
|
Plant Description
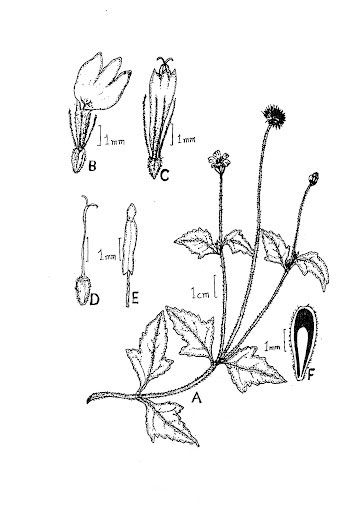
Coat Button is a semi-prostrate, spreading, herbaceous, perennial, procumbent annual herb that normally grows about 8-30 inches (20-75 cm) tall. Stem is cylindrical, solid and highly hispid, covered with multicellular hairs of 1 mm, tuberculate at the base. Hairs are more scattered towards the base and attenuated towards the top. The stems produce new roots at the leaf nodes. The plant has strong taproot. The plant is found growing in found in annual crops, roadsides, pastures, fallow land, meadows, waste grounds, railways, riverbanks, dikes and dunes and occasionally in lawns, perennial crops and nurseries.
Leaves
Leaves are opposite, simple, fleshy, pubescent, and carried by a concave petiole, 0.8-2.5 cm long. Leaf blades are thick, soft and dark green. The lamina is oval to lanceolate, 2.5 to 6 cm long and 2 to 5 cm wide, base attenuate in corner and with strongly and irregularly serrated margin. Both sides are hispid, with tuberculate based bristles. Pubescence is most abundant on the underside. 2-3 lateral veins are present on each side of the midrib.
Flowers
At the end of the long stems, is a capitulum inflorescence, comprising at the periphery of 4 to 7 spreading flowers. Flower looks like daisy .The flower is tubular, yellow centered white or yellow flowers with three-toothed ray florets. They are about 0.4-0.6 inches (1-1.5 cm) wide, and held on a 4-12 inches (10-30 cm) long stalk. It has two types of flower: ray florets and disc florets with basal palcentation. Sometimes the flowers are 3 lobed with long, penduncled heads. Flowering and fruiting occurs throughout the year, but from May to December is the time that it is fully in bloom.
Fruit
Fertile flowers are followed hard achene dark brown to black, narrowly obconical, and 2.0-2.5 mm long, with 15-20 patent, 0.12-0.24 inches (3-6 mm) long, rather stiff, feathered, unequal bristles and having a feathery, plume like white pappus at one end. Calyx is represented by scales or reduced to pappus.
Microscopy of Coat Button
| Part of Plant | Morphology | Observation |
|
Leaf |
Color | Green |
| Odor | Characteristics | |
| Taste | Acrid | |
| Size | 3-7 cm long and 1-5 cm wide | |
| Shape | Lanceolate to ovate | |
| Texture | Short | |
| Fracture | Easy | |
| Apex | Acute | |
| Margin | Irregularly toothed | |
| Arrangement | opposite | |
| Appearance | Rough and scabrous | |
|
Stem |
Color | Green |
| Odor | Characteristic | |
| Taste | Acrid | |
| Size | 23-46cm | |
| Shape | Cylindrical | |
| Texture | Smooth | |
| Fracture | Soft | |
|
Root |
Color | Brown |
| Odor | Characteristic | |
| Taste | Acrid | |
| Size | 15-32cm | |
| Shape | Tortuous | |
| Texture | Rough | |
| fracture | Soft |
Traditional uses and plant preparation of Coat Button
| Location | Preparation/extract | Plant ailment uses | |
|
Guatemala |
Leaves: juice | · Anemia, colds, inflammation, hepato-pathies, vaginitis, stomach pain, diarrhea, mucosal inflammation, skin infections, bleeding. | |
| Leaves: poultice, dried infusions Stems: dried | · Reduce inflammation, gastrointestinal and respiratory infections, high blood pressure, diabetes | ||
| Whole plant: dried | · Protozoal infections, treatment of chronic ulcers caused by leishmaniasis, gastrointestinal disorders | ||
| India | Leaves: dried and other herbs
ingested orally, juice |
· Diabetes, insect repellent, used to treat diarrhea, and to help check for hemorrhages, as well as hair loss. Jaundice, healing of wounds, inflammation | |
| Africa | Whole plant: blending with other
herbs adding salt and water |
· Treating mastitis in livestock | |
|
Africa |
Ghana | · Decoction with Phyllanthus amarus
· Aqueous extracts |
· Anti-malarial, antibacterial, wound-healing
· Anti-plasmodial activity |
| Nigeria | Whole plant: dried | · Fever, Typhoid fever, cough, back ache, stomach ache, diarrhea, epilepsy | |
| Benin | Whole plant: dried | · Rabbit or livestock feed | |
| Togo | Leaves: dried | · Dressing wounds, pain, malaria and abdominal and gastrointestinal mycosis | |
Traditional uses and benefits of Coat Button
- In Indian traditional medicine, it is used as anticoagulant, repellent, antidiarrheal, anti-dysenteric.
- Leaf juice is used on fresh wounds, to stop bleeding, and as hair tonic in tonic.
- It is used for liver disorders, arthritis, and heartburn also for hair growth in Ayurveda.
- Local Yoruba population uses the leaves for treatment to reduce blood pressure In Nigeria.
- Leaf juice is used for colds, inflammation, vaginitis, stomach pains and diarrhea in Guatemala.
- Whole plant used for protozoal infections and treatment of chronic ulcers.
- Dried whole plant is used for fever, cough, back ache, diarrhea and epilepsy in Africa.
- Dried leaves are used for malaria, gastrointestinal mycosis, and for dressing wounds.
- Traditionally, the plant has been in use in India for wound healing and as an anticoagulant, antifungal, and insect repellent.
- Juice extracted from the leaves is directly applied on wounds.
- Its leaf extracts were used for infectious skin diseases in folk medicines.
- It is used in Ayurvedic medicine for liver disorders, hepato-protection, gastritis, and heartburn.
- The plant is also used as treatment for boils, blisters, and cuts by local healers in parts of India.
- The plant can be used for wound healing, staunching bleeding and treatment of diarrhea, backache and bronchial catarrh.
- Coat buttons has been used to treat skin diseases and heal wounds, as an anticoagulant, fungicide, as a hair tonic, insect repellant and to treat diabetes.
- It is useful in the treatment jaundice, bronchial catarrh, diarrhea, dysentery, inflammation, ulcers, anal fistula, and hemorrhoids.
- Leaf juice can be used to cure fresh wounds, to stop bleeding.
- Leaf extract cures liver disorders.
- In Jamaica, it is used for fever and for the treatment of catarrh.
- Plant is also used in the treatment of gastrointestinal and respiratory infections, high blood pressure, and diabetes.
- The plant is also used to stop bleeding, and for liver disorders, arthritis, heartburn, and as a hair tonic to promote hair growth.
- Leaf juice is used for colds, inflammation, vaginitis, stomach pains, and diarrhea in Guatemala.
- Whole plant is used for protozoal infections, and for the treatment of chronic ulcers.
- In Nigeria, the entire plant is used to treat typhoid fever, cough, fever, stomachache, backache, diarrhea, and epilepsy.
- The leaves are antiseptic, haemostatic and parasiticide.
- They are used as a treatment against bronchial catarrh, dysentery, and diarrhea.
- A fine paste of the leaves is applied externally to reduce swelling of hemorrhoids and to stop bleeding.
- The leaf sap is applied topically to sores and ulcers.
- The juice extracted from the leaves of the plant is applied directly on the Wounds.
- The leaf extracts are used for infectious Skin diseases.
- A paste of leaves is used externally to reduce swelling of Hemorrhoids and stop Bleeding.
- The leaf sap of the plant applied topically cures Sores and Ulcers.
- It is used to treat Liver disorders, Gastritis and Heartburn.
- It is used to treat Boils, Blisters and Cuts.
- In Guatemala, T. procumbens is used as an antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral treatment as well as for vaginitis, stomach pain, diarrhea, mucosal inflammations, and skin infections.
- The leaf juice is used to treat wounds and stop bleeding.
- In Guatemala, the entire plant is used for the treatment of protozoal infections.
- Decoction of the leaves is used against pain, to treat malaria, and against abdominal and gastrointestinal mycosis.
- It is known as an insect repellent, used to treat diarrhea, and to help check for hemorrhages in India
Other Facts
- In Africa, plant is used for treating mastitis in livestock.
- The leaf juice possesses insecticidal and parasiticidal properties.
- Smoke produced by burning the plant is used to repel mosquitoes.
- The leaves are used as a hair restorative.
Prevention and control
Cultural Control
Coat Button does not have the great powers of regeneration possessed by some other perennial Compositae and can be easily controlled by cultivation and hand pulling.
Chemical Control
Herbicides reported to give control of T. procumbens include ametryne, atrazine, 2, 4-D and diuron, Avirosan (dimethametryn + piperophos) and oxadiazon in rice, bromacil, metobromuron + metolachlor in cowpea, MCPA and 2, 4-D in sisal and oxyfluorfen in groundnut.
References:
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=38575#null
http://www.hear.org/pier/species/tridax_procumbens.htm
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/55072
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/TRQPR
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/gcc-42420
http://www.stuartxchange.com/CoatButtons
http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Tridax%20Daisy.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tridax_procumbens
https://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/33338#brief
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Tridax%20procumbens
https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=TRPR5