| Deodar Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Deodar |
| Scientific Name: | Cedrus deodara |
| Origin | Afghanistan, Tibet, Nepal, Pakistan, and India |
| Colors | Initially green and purplish, later turning a reddish brown when mature |
| Shapes | Erect cone ovoid or ellipsoidal, 7.5-12 cm long and 5- 8.7 cm in diameter with numerous fan-shaped scales arranged in spiral of 8 x 5 on persistent woody central axis |
| Taste | Pungent, bitter, Astringent |
| Health benefits | Treats Cough, Controls Fever, Cures Epilepsy & Neurological Disorders, Promotes Digestion, Rectifies Arthritis, Treats Skin Disease & Wounds, Cure Asthma, Alleviates Blood Disorders, Alleviates Backache, Good Utero-Tonic, Aids to Control Obesity, Stress and Anxiety, Treats Alopecia, Osteoarthritis, Fights Respiratory Issues, Aids in Weight Loss, Improves Cognitive Functioning |
| Name | Deodar |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Cedrus deodara |
| Native | Afghanistan, Tibet, Nepal, Pakistan, and India (Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Jammu-Kashmir and Uttar Pradesh) |
| Common Names | Deodar , Deodar cedar, Himalayan cedar, cedar, Devdar |
| Name in Other Languages | Afrikaans: Deodar, Deordar seder Albanian: Deodar, cedër Amharic: Deodar-ˈdēəˌdär Arabic: Dudar (دودار), arz dudari (أرز دوداري) Armenian: Deodar (դեոդար), mayri himalayan (մայրի հիմալայան) Azerbaijani: Deodar, Himalay sidri Basque: Himalayako zedroa Belarusian: Kedr himalaysʹkyy (Кедр гімалайскі) Bengali: Dēbadārū (দেবদারূ) Bulgarian: Khimalaĭski kedŭr (хималайски кедър) Burmese: Hkwayruu (ခွေးရူး) Catalan: Cedre de l’Himalaia Chinese: Dù dá (杜达),(xue song (雪松), Xǐmǎlāyǎ xuěsōng (喜马拉雅雪松) Croatian: Deodar, Himalajski cedar Czech: Deodar, Cedr himálajský Danish: Deodar, Himalaya-ceder Dutch: Deodar, Himalaya ceder, Deodarceder English: Deodar , Deodar cedar, Himalayan cedar, cedar Esperanto: Deodar, Himalaja cedro Estonian: Deodar Filipino: Deodar Finnish: Deodar, Himalajansetri French: Déodar, Cèdre de l’Himalaya, Cèdre sacré, cèdre deodar Galician: Cedro do Himalaia Georgian: Deodari (დეოდარი), himalaiuri k’edari (ჰიმალაიური კედარი) German: Deodar, Himalaja-Zeder, Deodarzeder Greek: Aposmitikó (αποσμητικό), kédros ton Imalaïon (κέδρος των Ιμαλαϊων) Gujarati: Diyōdara (દિયોદર) Hausa: Deodar Hebrew: Deodar, ארז הימלאי Hindi: Devadaar (देवदार), dedwar, deodar, diar, kelu, kilar Hungarian: Himalájai cédrusfa, Himalájai cédrus Icelandic: Deodar, Himalajasedrus Indonesian: Deodar Irish: Deodar Italian: Deodar, Cedro dell’ Himalaya, Cedro dell’Himalaia, cedro deodara Japanese: Deodar-ˈdēəˌdär, himaraya-shida (ヒマラヤシダ), himaraya-sugi (ヒマラヤスギ) Javanese: Deodar Kannada: Viḍiyōḍar (ವಿಡಿಯೋಡರ್), Dēvadāru (ದೇವದಾರು) Kazakh: Deodar (деодар) Komi: Gimalais’ syspu (Гималаись сыспу) Korean: Himallaya samnamu (히말라야 삼나무), gaeipgalnamu (개잎갈나무) Kurdish: Deodar Lao: Deodar (dēəˌdär) Latin: Deodar Latvian: Deodars, Himalaju ciedrs Lithuanian: Deodarą, Himalajinis kedras Lower Sorbian: Himalajaska cedra Macedonian: Deodar (деодар), himalajski kedar (хималајски кедар) Malagasy: Deodar Malay: Deodar Malayalam: Diyēāḍār (ഡിയോഡാർ), dēvadāru (ദേവദാരു) Maltese: Deodar Marathi: Devadaar (देवदार) Mongolian: Deodar (деодар) Nepali: Devadaar (देवदार), Deodaar (देवदार), Diyaar (दियार), Diyaal (दियाल) Netherlands: Himalaya-ceder Norwegian: Himalaiaseder Oriya: ଦେଓଡର୍ | Pakistan: Deodar, diar Pashto: ډیوډار Persian: دئودار Polish: Deodar, cedr himalajski Portuguese: Deodar, Cedro-deodara, Cedro-do-himalaia, Cedro-dos-himalaias Punjabi: Di ōḍara (ਦਿਓਡਰ) Romanian: Deodar, cedru de himalaia Russian: Gimalayskiy kedr (гималайский кедр), kedr gimalajskij (Кедр гималайский) Serbian: Deodar (деодар), himalajski kedar (хималајски кедар) Sindhi: ڏند Sinhala: Diyōḍār (ඩියෝඩාර්) Slovenian: Deodar, himalajska cedra Spanish: Deodar, Cedro del Himalaya, Cedro llorón, cedro de la India, Himalajska cedra Sudanese: Deodar Swedish: Deodar, himalaja-ceder Tajik: Deodar (деодар) Tamil: Ṭiyōṭar (டியோடர்) Telugu: Dēvadāru (దేవదారు) Thai: Deodar (dēəˌdär) Turkish: Himalaya sediri Ukrainian: Dezodar (дезодар), kedr himalaysʹkyy (кедр гімалайський) Upper Sorbian: Himalajaska cedra Urdu: Deodar, دیودار Uzbek: Deodar Vietnamese: Deodar, Tuyết tùng Himalaya Welsh: Deodar, Cedrwydden Ddeodar Zulu: Idikoni |
| Plant Growth Habit | Elegant, large, ornamental, evergreen, dioecious, coniferous tree |
| Soil | Thrives on most soils, being very tolerant of dry sites and of drought when it is established. Succeeds in very chalky soils. Prefers a rich loam or a sandy clay in full sun |
| Plant Size | 40–50 m (131–164 ft.) tall, exceptionally 60 m (197 ft.) with a trunk up to 3 m (10 ft.) in diameter |
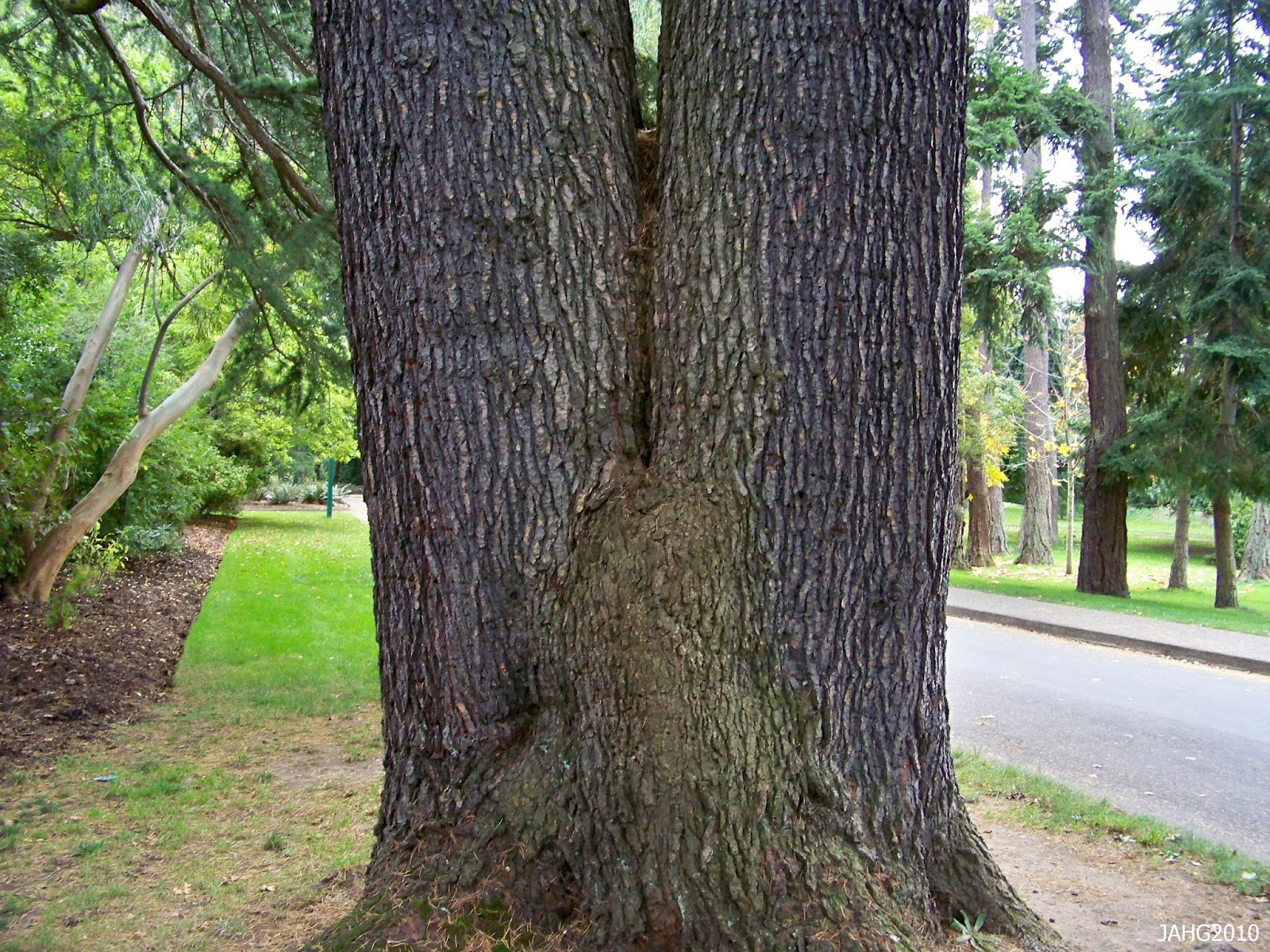
| Bark | Greyish brown, dark, almost black, with vertical and diagonal cracks dividing it into irregular oblong scales |
| Twigs | Slender, with numerous short spur shoots, branches droop with age; buds are very small and round. |
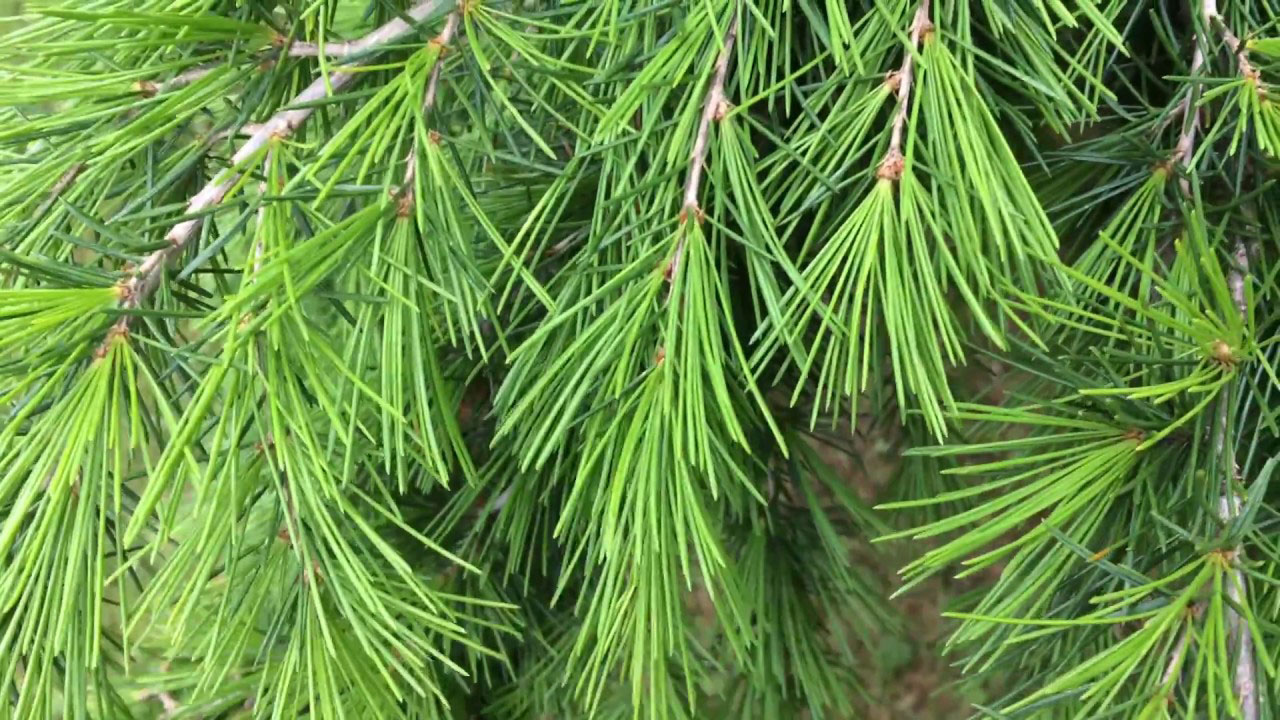
| Leaf | Solitary, acicular, stiff, sharp-pointed, needle-like, mostly 2.5–5 cm (0.98–1.97 in) long, occasionally up to 7 cm (2.8 in) long, slender and 1 mm (0.039 in) thick |
| Flowering season | October to November |
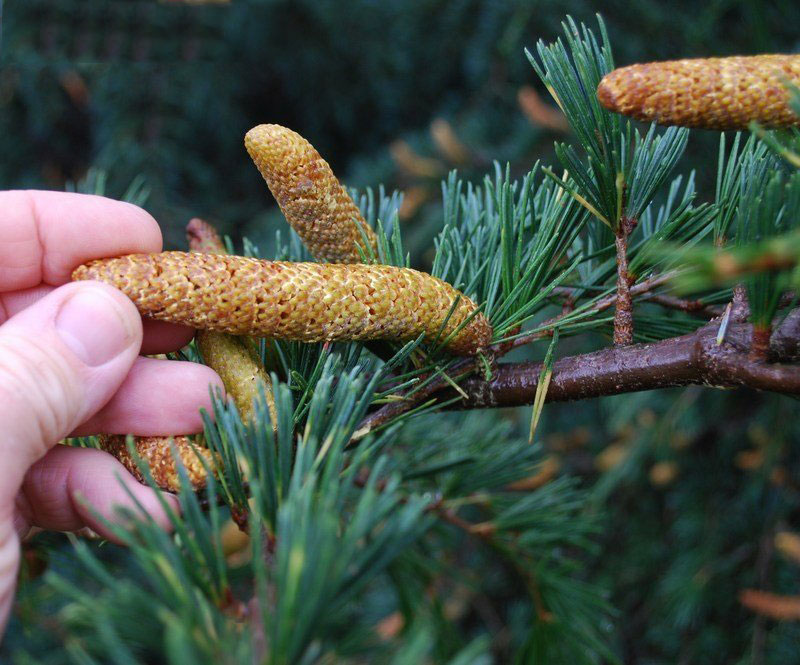
| Flower | Male flowers are solitary and erect catkins, pale green to yellowish green with purplish tinge, oblong, ovoid, and 2.5 to 4.6 cm long and 1 to 1.5 cm in diameter. The female flowers are solitary and erect at the end of arrested branchlets |
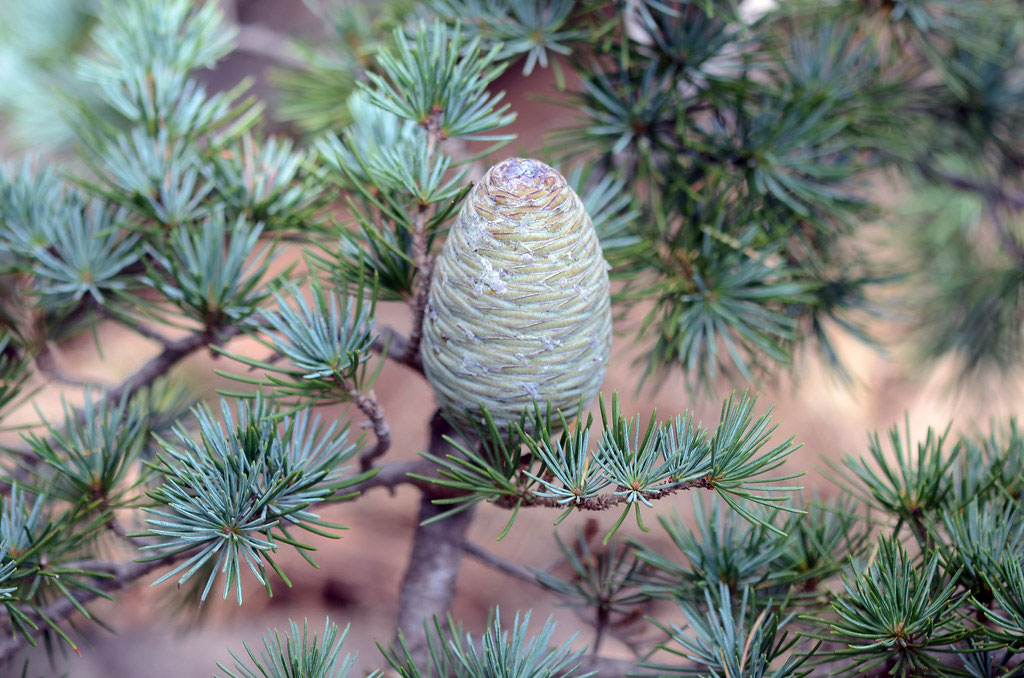
| Fruit Shape & Size | Cones solitary or in pairs, erect, ovoid or ellipsoidal, 7.5-12 cm long and 5- 8.7 cm in diameter with numerous fan-shaped scales arranged in spiral of 8 x 5 on persistent woody central axis |
| Fruit Color | Initially green and purplish, then later turning a reddish brown when mature |
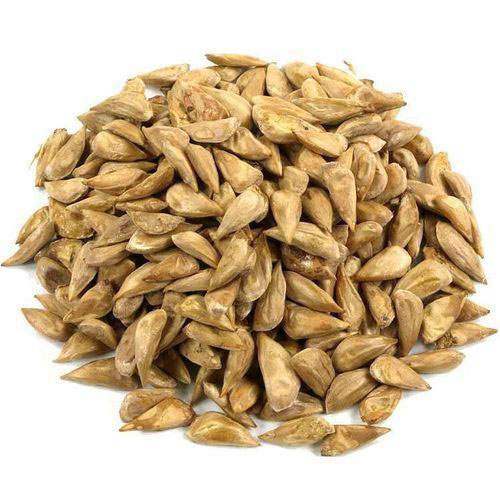
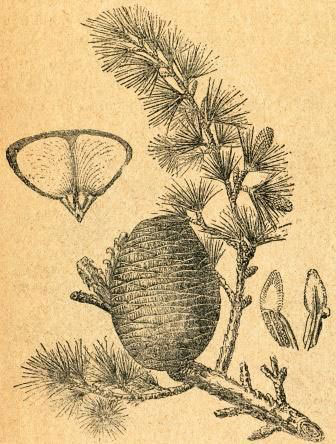
| Seed | Seed are triangular, winged, 2.5 to 3.7 cm long; wings with rounded corners and 2- 2.5 cm broad |
| Taste | Pungent, bitter, Astringent |
| Plant Parts Used | Wood, leaves, bark. Twigs, oil, seed, resin, pollen |
| Season | October to December |
| Health Benefits |
|
Plant Description
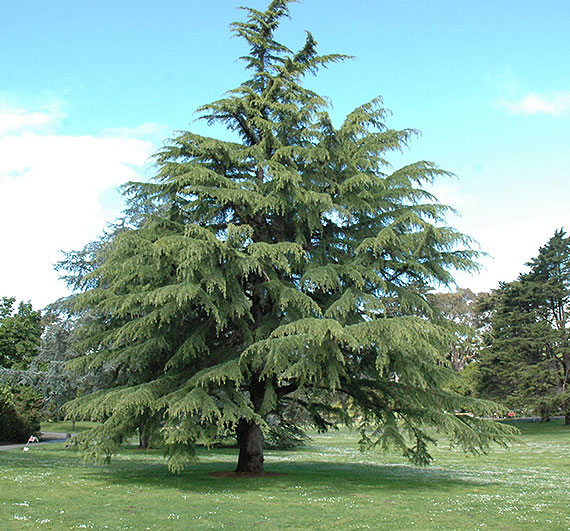
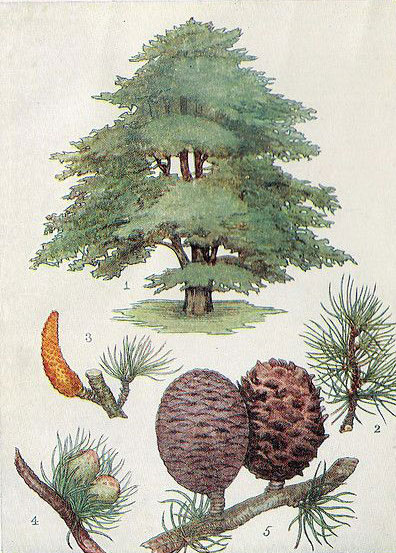
Deodar is an elegant, large, ornamental, evergreen, dioecious, coniferous tree that is pyramidal when young, maturing to flat-topped trees with broad-spreading horizontal branches. It is perhaps the most pendulous of the true cedars, with drooping branchlets and branching that is gracefully drooping at the tips. Lower branches typically remain on the tree as it ages; often touching the ground. The plant normally grows about 40-50 m tall, exceptionally 60 m, with a trunk up to 3 m diameter. The plant thrives on most soils, being very tolerant of dry sites and of drought when it is established. It succeeds in very chalky soils and prefers a rich loam or sandy clay in full sun. Bark is greyish brown, dark, almost black, with vertical and diagonal cracks dividing it into irregular oblong scales. Twigs are slender, with numerous short spur shoots, branches droop with age; buds are very small and round.
Leaves
Leaves are solitary, acicular, stiff, sharp-pointed, needle-like, mostly 2.5–5 cm (0.98–1.97 in) long, occasionally up to 7 cm (2.8 in) long, slender and 1 mm (0.039 in) thick, borne singly on long shoots, and in dense clusters of 20–30 on short shoots. They vary from bright green to glaucous blue-green in color.
| Leaf arrangement | Spiral |
| Leaf type | Simple |
| Leaf margin | Entire |
| Leaf shape | Needle-like (filiform) |
| Leaf venation | Parallel |
| Leaf type and persistence | Evergreen, needled evergreen |
| Leaf blade length | Less than 2 inches |
| Leaf color | Green, silver |
| Fall color | No color change |
| Fall characteristic | Not showy |
Flower
The plant is monoecious. Male flowers are solitary and erect catkins, pale green to yellowish green with purplish tinge, oblong, ovoid, and 2.5 to 4.6 cm long and 1 to 1.5 cm in diameter. On opening they elongate rapidly to 5-7.5 cm in length and become yellow with pollen. The female flowers are solitary and erect at the end of arrested branchlets; flowers, at the time of pollination, are oblong, ovoid, 1.2 to 2.0 cm long and 0.6 cm in diameter, pale glaucous green. The scales occur in a spiral of 8 x 5; at the time of pollination they stand perpendicular to the axis, exposing ovules and close after pollination. Flowers appear in between September and October.
| Flower color | Unknown |
| Flower characteristics | Not showy |
Fruit
Cones solitary or in pairs, erect, ovoid or ellipsoidal, 7.5-12 cm long and 5- 8.7 cm in diameter with numerous fan-shaped scales arranged in spiral of 8 x 5 on persistent woody central axis, rounded at the apex. It is bluish when young, reddish-brown when ripe. Fruit starts maturing from September to November and the seed shed from September to December. Seed scales are 5-6 cm wide, usually glabrous on the upper side. On each scale rests a pair of winged seeds. Seed are triangular, winged, 2.5 to 3.7 cm long; wings with rounded corners and 2- 2.5 cm broad.
| Fruit shape | Oval, cone |
| Fruit length | 3 to 6 inches |
| Fruit covering | Dry or hard |
| Fruit color | Brown |
| Fruit characteristics | Does not attract wildlife; showy; fruit/leaves not a litter problem |
Health benefits of Deodar
Since ancient times, deodar plants have been used extensively in Ayurvedic medicine. Moreover, all parts of this tree like heartwood, leaves, bark, oil, resin, etc. have numerous types of medicinal benefits and antiseptic properties. Listed below are some of the valued benefits of Deodar
1. Treats Cough
Accumulation of mucus in the airways may cause cold-related cough. Deodar helps to reduce cough by effectively removing mucus from the airways, and it is also extensively recommended in the treatment of tuberculosis. Consuming the mixture of Deodar powder and hot water also help to cure cough. Apart from that mix 1 drop of Davana oil with 1 drop of cedarwood oil in warm water and inhale its vapor to expel mucus from the trachea. Thus inhalation of vapor cures sinusitis, colds, fever, and cough.
2. Controls Fever
Traditional medicine use deodar to treat viral fever and acute fevers. Inner bark of the deodar tree are finely powdered, and prepare decoction by boiling this bark powder in water or by adding some other herbal products with deodar bark powder. By consuming this distilled water for fever you can also gain energy and stability.
3. Cures Epilepsy & Neurological Disorders
Epilepsy is considered one of the most common disorders of the central nervous system, mostly affecting brain function and result in sensations, seizures, and loss of awareness. Deodar extract can significantly reduce the nature of epilepsy and its effects and helps in curing it over time.
Additionally, the alcoholic extract derived from the hardwood of Deodar greatly helps to regulate the levels of Kapha found in the nervous system, thus providing the body with antidepressant properties. Himalayan Cedar oil is very helpful in balancing the Vata dosha which is the main cause of various neurological disorders. Deodar oil is used to treat all nerve-related problems including stroke, nerve pain.
4. Promotes Digestion
Mild carminative and digestive properties of the Deodar helps to cure all the problems relating to digestive system. Anti-flatulent property helps to reduce the formation of gas in the alimentary canal, thus reducing flatulence, bloating, constipation, and abdominal distension. Similarly antacid property of the herb prevents the formation of excessive acids in the stomach thus treating indigestion, ulcer, and gastritis and promotes better absorption of nutrients in the body. Additionally, it improves the peristaltic movements of the gut and helps in complete removal of stools and prevents the formation of Ama.
5. Rectifies Arthritis
Arthritis is caused by the severity of the maximum Vata that gathers in the body, causing swelling, pain, and difficulty in movement. Deodar tree extract has strong anti-inflammatory properties and is used to treat arthritis. Extract also has the feature of balancing the Vata and provides relief for body aches and joint pains caused by arthritis. Heartwood oil prevents leukotriene synthesis and helps stabilize mast cells. In addition, Deodar can help relieve erections in cervical spondylosis.
6. Treats Skin Disease & Wounds
Oil extracted from the Deodar plant is rich in anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory properties. This oil when applied topically helps to treat wounds and pruritus. Apart from that its oil consists of two types of chemical compounds called Benzyl Benzoate and OCD, which kill active acaricides and effectively kill parasites and germs. Similarly, its oil is effective against Sarcoptes skin infections, including psoriasis, scabies, and eczema.
Mix Deodar, Guggulu, and Turmeric well and apply the paste to intolerant swellings. This combination is also recommended for use in the treatment of leprosy, and fungal skin infections.
7. Cure Asthma
Deodar is the most important ingredient in vegetable oil and is used to treat asthma and shortness of breath due to its anti-allergic properties. Since it consists of allergens it is used to treat hiccups, sinusitis, and runny nose.
8. Alleviates Blood Disorders
Toxins and impurities in the body and blood are excluded by ingesting Deodar bark powder or extract orally. When taken internally it can effectively improve liver function. Deodar is considered an excellent cure for vascular disorders, excessive bleeding, and infections in the blood such as sepsis.
9. Alleviates Backache
Topical formulas made with Deodar are very effective in treating back pain after childbirth and during menstruation. Additionally, its juice is taken orally to relieve back pain and strengthen the spinal cord.
10. Good Utero-Tonic
When Himalayan cedar bark’s extract is taken regularly, it strengthens the uterus and improves our health. When taken internally, some of the active compounds present in it stimulate the release of eggs from the ovary. This spontaneous process can effectively treat uterine dysfunction, amenorrhea, leucorrhoea, anovulation and dysmenorrhea.
11. Aids to Control Obesity
Unhealthy eating habits and delicate lifestyles are primary causes for weight gain, which can lead to poor digestion and various diseases. Deodar wood helps to reduce obesity by helping to expel excess fat and triglycerides deposited in the body.
Similarly antioxidants in Himalayan Cedar help greatly in reducing the toxin called Ama and improving the metabolism. All these processes are carried out by their digestive properties called Pachan and appetizer properties called Deepan.
12. Stress and Anxiety
Essential oil obtained from Deodar, plays a significant role in discomforting off stress and eliminating various symptoms of anxiety like uneasiness, restlessness, cold hands, and feet, etc. Calming and grounding properties of the plant also actively help to uplift the mood and promote feelings of hope and joy.
Just pour a few drops of the cedarwood oil in the potpourri and relax in the aromatic environment or get a head massage with a few drops of this oil to get rid of stress and insomnia.
13. Treats Alopecia
Alopecia areata is a term used to describe the circular baldness or occurrence of sudden hair loss in both men and women. Deodar oil is a good natural medicine with no side effects to cure alopecia and control hair loss. This oil cures scalp irritation, excessive dandruff, hair loss, etc. and promotes healthy hair growth.
14. Osteoarthritis
Deodar is beneficial in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis may cause pain, swelling and difficulty in moving. It has Vata balancing property and gives relief from the symptoms of osteoarthritis-like pain and swelling in the joints.
15. Fights Respiratory Issues
Due to its potent anti-inflammatory, anti-biotic, and anti-asthmatic properties, Deodar helps in treating a host of respiratory troubles. It is extensively used for treating the common cold, sore throat, cough and flu symptoms. It also thins and loosens the rheum particles within the chest and nasal cavities and therefore eases breathing and helps the body to get rid of mucus. It is also beneficial in treating bronchitis and asthmatic conditions.
16. Aids in Weight Loss
Abundance of flavonoids in Deodar helps the body shed excess weight faster. Due to the presence of fiber and anti-obesity action, Deodar satisfies sudden hunger pangs and prevents overeating and thus plays a pivotal role in one’s weight loss regimen. The herb also improves metabolism and helps the body to maintain a proper weight.
17. Improves Cognitive Functioning
Deodar is an ancient and traditional remedy to increase the functioning of the brain. Antioxidants present in the bark improve the memory capacity, focus, concentration, calmness, alertness of an individual. Several research conclude that people taking deodar in powdered or decoction form regularly, have improved memory, reasoning, problem-solving, and other cognitive abilities. It also helps in treating epilepsy, memory loss, stress, anxiety, depression, Alzheimer’s and other neuro-degenerative disorders.
Traditional uses and benefits of Deodar
- Heartwood is carminative, diaphoretic, diuretic and expectorant.
- Decoction of the wood is used in the treatment of fevers, flatulence, pulmonary and urinary disorders, rheumatism, piles, kidney stones, insomnia, diabetes etc.
- It has also been used as an antidote to snake bites.
- Essential oil obtained by distillation of the wood is used in the treatment of bronchitis, blenorrhagia, phthisis, tuberculosis, gonorrhea and skin eruptions.
- Resin obtained from the wood is used externally to treat bruises, skin diseases and Joint injuries.
- It has been proved beneficial in the treatment of diarrhea and dysentery.
- Leaves are used in the treatment of tuberculosis in Ayurvedic medicines.
- It is applied externally to treat skin diseases.
- Oil obtained from the seed is used externally and orally for the treatment of Syphilis.
- In Traditional Ayurvedic medicine, bark is used to cure cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, cold, cough and hiccups.
- Pollen also treats sexual problems of both male and female.
- Paste of deodar helps to relieve swelling inflammation, pain, cleansing infected wounds and in skin disorders associated with pain and itching.
- Its paste is applied to relieve breast pain and mastitis.
- Decoction of deodar wood pieces is made and taken twice a day in hiccups and breathlessness.
- Paste is mixed with turmeric and Guggulu and applied on indolent swellings.
Ayurvedic Health benefits of Deodar
- Diarrhea: Make a decoction of Deodar bark. Take it, twice a day.
- Skin Diseases: Apply Deodar seed oil to the infected skin, locally.
- Kidney Stones: Prepare a decoction of Deodar bark. Take it, twice a day for one week.
- Tuberculosis: Prepare a decoction of Deodar leaves. Take it, twice a day for 15 days.
Other Facts
- It is a wind-tolerant tree and can be used in shelterbelt plantings.
- It is a valuable timber, but a poor fuel, producing a lot of smoke as it burns.
- Inner part of the wood is used for making essential oils used in aromatherapy.
- The deodar is the national tree of Pakistan.
- It is worshiped as a divine tree among Hindus.
- Deodar wood was used extensively for construction of public buildings, canals, bridges, barracks and railway cars during British colonial period in India and British.
- Inner wood is aromatic and used to make incense.
- Essential oil is used as insect repellent on the feet of horses, cattle and camels.
- It is used in house building, beams, floorboards, door and window frames, furniture, general carpentry and boats. It also produces quality plywood.
- It’s a soil conservation and erosion control species in the Himalayas.
Precautions
- It may cause allergy or skin irritation to some people.
- Always take oral medicine after food as it may lead to stomach upset in empty stomach in some individuals.
- People taking oral preparations of Deodar should be careful of pre-existing gastritis problems. Individuals with pre-existing gastric problems should start medication in low doses orally and then graduate up. Always take expert opinion before starting.
- Oral preparations may not be safe in pregnancy but acceptable in the lactation phase. Since Deodar has emmenagogue action and it acts of female hormones, pregnancy is not the right time to take it. So strict medical supervision is advisable.
- Deodar has a hot potency and so not advisable for people with serious Pitta dosha.
- Some Ayurvedic texts recommend avoiding the use of Deodar in girls below 18 yrs. of age.
- Its formulation of Chandraprabha vati contains salt during preparation and hence should be used with caution in patients with high blood pressure.
References:
https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Cedrus+deodara
http://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?kempercode=b442
http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/record/kew-2707322
https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=CEDE2
https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=183408#null
https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/ST134
https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/12436
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cedrus_deodara
https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/CEUDE
http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Devdar.html