| Egg Mango Quick Facts | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Egg Mango |
| Scientific Name: | Mangifera laurina |
| Origin | Myanmar, Indochina (Kampuchea, Vietnam) and Malesia, from peninsular Thailand to New Guinea |
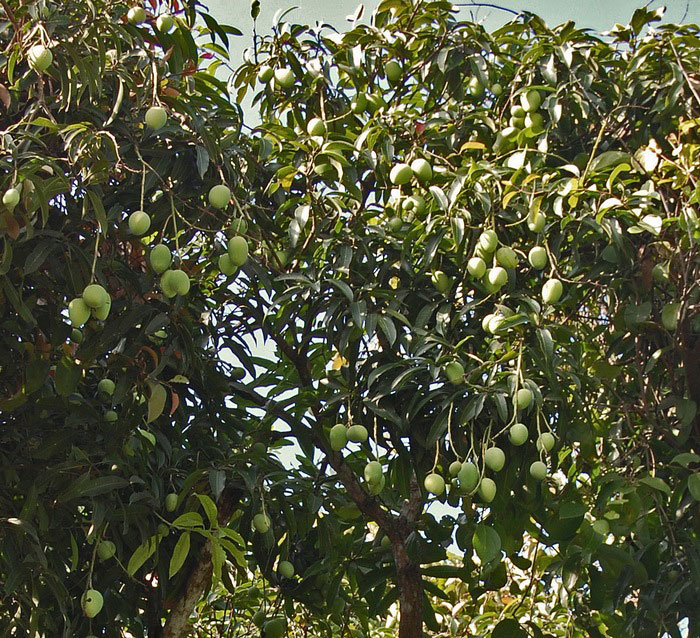
| Colors | Green when young turning to greenish yellow to yellow at maturity |
| Shapes | Ovoid, or kidney-shaped drupe-like small mango, 5–7 cm long and 4 cm thick |
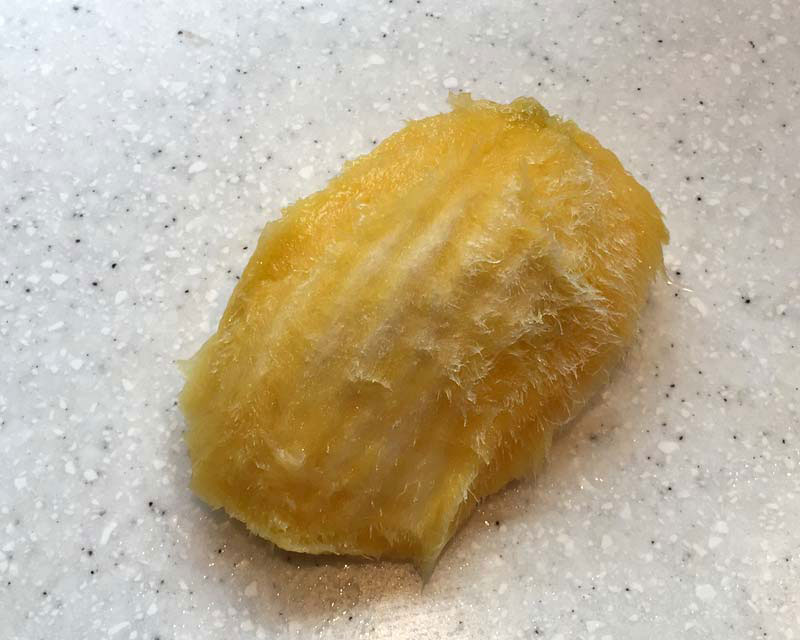
| Flesh colors | Intense yellow |
| Taste | Sweet taste, slightly acidulous |
| Name | Egg Mango |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Mangifera laurina |
| Native | Myanmar, Indochina (Kampuchea, Vietnam) and Malesia, from peninsular Thailand to New Guinea |
| Common Names | Egg Mango, Padi Mango, Water Mango, mangga aer |
| Name in Other Languages | Burma: Thayet The Nee, Thayet China: Chang Geng Mang Guo English: Egg Mango, Padi Mango, Water Mango, mangga aer Indonesia: Mangga Pari, Parih, Pelem Kecik, Empelem, Asam Pun, Ampelan Dotan, Empelem, Mangga Tiakar, Pauh Gadang, Pauh Pong Malay: Bachang Api, Machang, Machang Api Malaysia: Mempelam, Emplam, Tanh Chai, Mangga Telur, Mempelam Melur, Mempelam Padi, Pauh Telur, Pauh Padi, Mangga Ayer, Manga Hutan, Pauh Kijang Philippines: Apali Sabah: Mangga Air Thailand: Mamuang Kaleng, Mamuang Khee Kwaang Vietnam: Cây Nui, Xoái Nui, Queo |
| Plant Growth Habit | Medium-sized, evergreen, erect tree |
| Growing Climates | Lowland evergreen forests, Lowland tropical rainforest |
| Plant Size | 20–30 m high, with 40–190 cm diameter |
| Bark | Bark surface longitudinally cracked, peeling off in small, narrow strips, pinkish-brown to blackish |
| Trunk | Rough, greyish trunk |
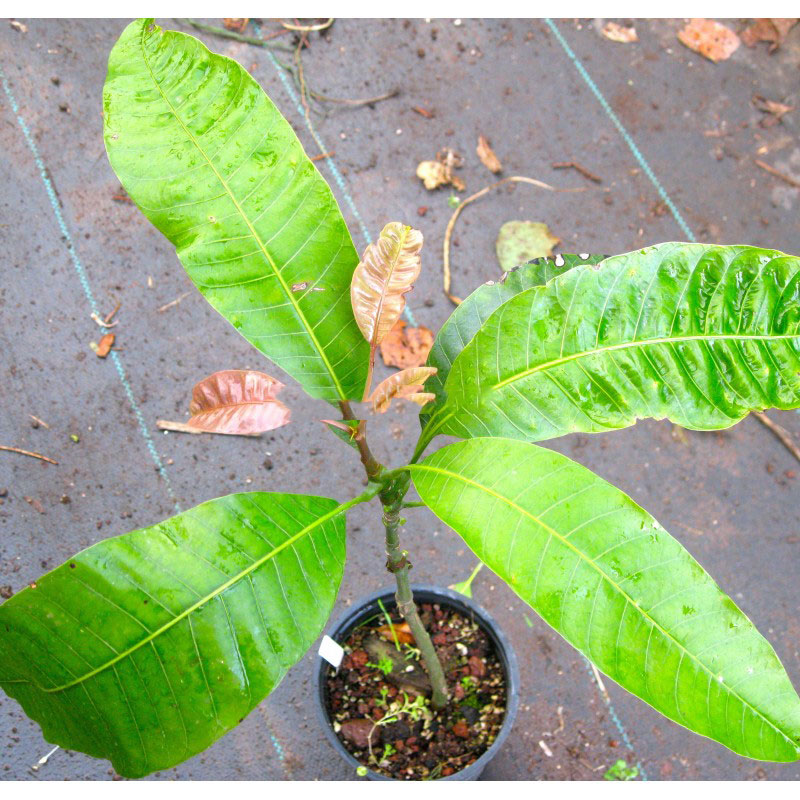
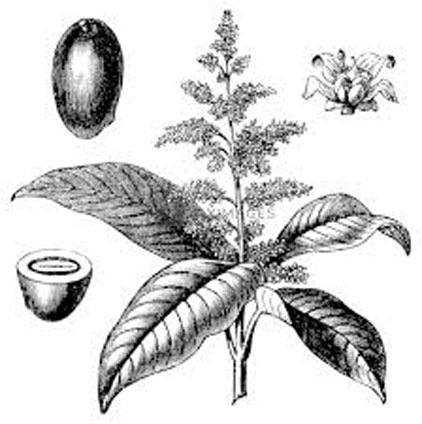
| Leaf | Borne on slender, 2.5–5.5 cm long petiole that is grooved above and inflated at the base. Lamina is oblong-lanceolate, elliptic-lanceolate to lanceolate, 15–26 cm long and 4–6 cm wide |
| Inflorescence | Paniculate, sub-terminal to terminal, 40 cm long, with slender primary branches; pedicels are about 1.5 mm long, sparsely pubescent to sub glabrous, lax and loosely flowered |
| Flower | Whitish-green to pale yellow, pentamerous, small and fragrant on long pedicel; calyx 5-lobed with acute sepals |
| Fruit Shape & Size | Ovoid, or kidney-shaped drupe-like small mango, 5–7 cm long and 4 cm thick, not beaked |
| Fruit Color | Medium green turning greenish yellow to yellow at maturity |
| Stone | Large, 4–5 cm by 2–3 cm |
| Flesh | Intense yellow, juicy, very acid and fibrous |
| Seed | Oval, often polyembryonic |
| Propagation | From seeds |
| Taste | Sweet taste, slightly acidulous, with a slight taste of turpentine |
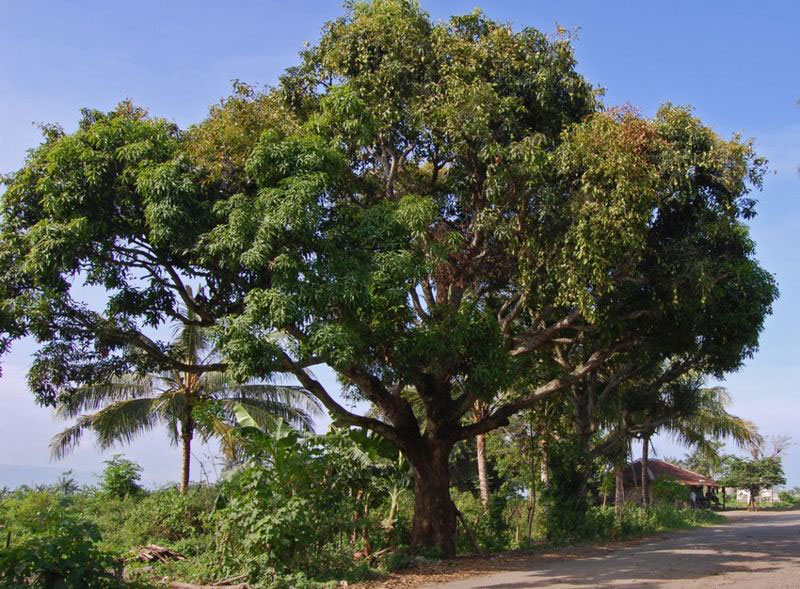
Plant Description
Mangifera laurina is a medium-sized, evergreen, erect tree with a massive, globose crown; which normally grows about 20–30 m tall. The bole can be 80 – 100 cm in diameter with rough, greyish trunk. The plant is found growing in lowland evergreen forests and lowland tropical rain forest. Bark surface of the tree is longitudinally cracked, peeling off in small, narrow strips, pinkish-brown to blackish. Leaves are borne on slender, 2.5–5.5 cm long petiole that is grooved above and inflated at the base. Lamina is oblong-lanceolate, elliptic-lanceolate to lanceolate, 15–26 cm long and 4–6 cm wide, leathery, glabrous, base cuneate to broadly cuneate, margin entire and slightly undulate, apex acuminate or caudate-acuminate, lateral veins prominent on both sides. It is glossy green on the upper page, dark green on the inferior side.
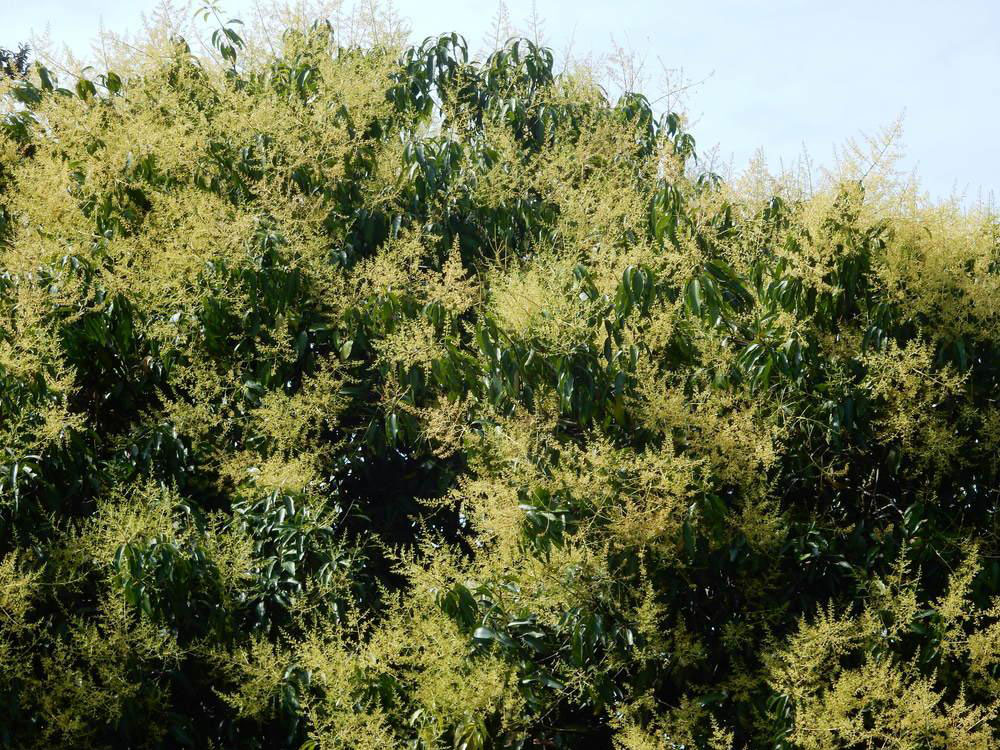
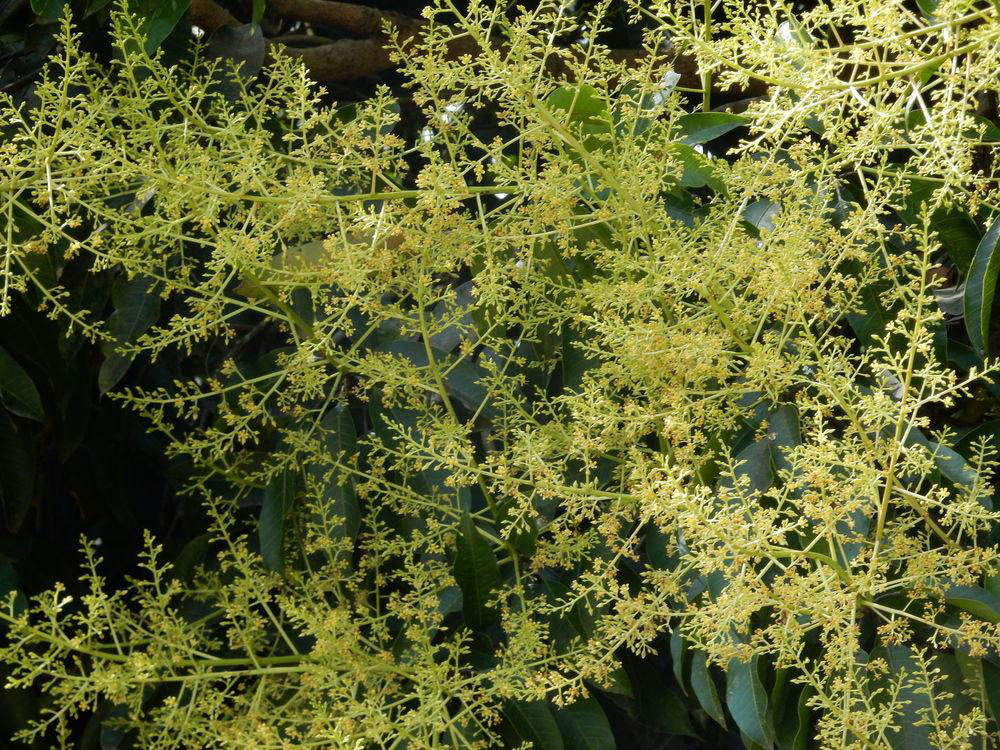
Flower
Inflorescence is paniculate, sub-terminal to terminal, 40 cm long, with slender primary branches; pedicels are about 1.5 mm long, sparsely pubescent to sub glabrous, lax and loosely flowered. Flowers are whitish-green to pale yellow, pentamerous, small and fragrant on long pedicel. Calyx is 5-lobed with acute sepals. Petals is 5 and are linear-oblong. About 5 stamens are present but only 1 is fertile and rest are staminodes. Ovary is ovoid to sub globose and style sub terminal.
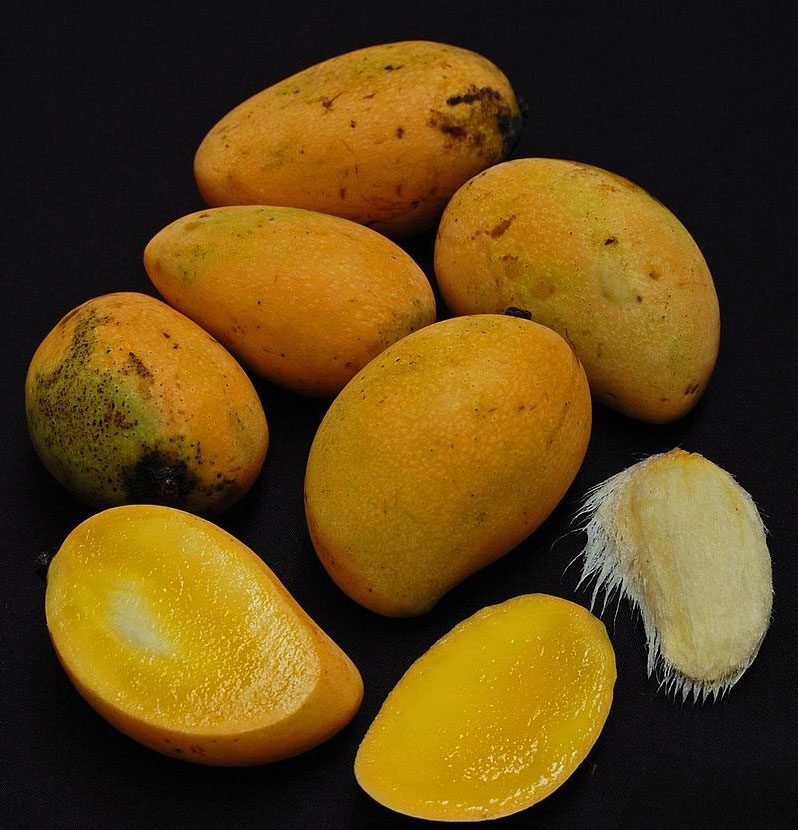
Fruits
Fertile flowers are followed by an ovoid or kidney-shaped drupe-like small mango, 5–7 cm long and 4 cm thick, not beaked. Fruits are initially green turning to medium green turning greenish yellow to yellow at maturity. Flesh is intense yellow, juicy, very acid and is fibrous. Stone is found on the center of the fruits that is large about 4–5 cm long and 2–3 cm wide. Seed is oval and is often polyembryonic.
History
Wild distribution of this species is found in Myanmar, Indochina (Kampuchea, Vietnam) and Malesia, from peninsular Thailand to New Guinea, in lowland tropical rain forest. It was probably brought into cultivation long before the introduction of Mangifera indica L. in the region. In most parts of Borneo it is still widely cultivated, but it is now losing ground in Peninsular Malaysia, Sumatra and Java, since the fruit is inferior to that of M. indica cultivars. It was probably introduced into the Philippines.
Culinary Uses
- Mature, ripe and unripe fruit are edible.
- The ripe fruit is very acid and has been processed into drinks with sugar or honey.
- More often the fruit is harvested immature, sliced and served in fruit salads with a spicy sauce.
- Mature, unripe fruits are halved or sliced for use in pickles and chutney.
- The slices are also dried and salted as preserves and consumed as snacks.
Other facts
- Seeds being polyembryonic are used often as root stocks for the common mango, Mangifera indica in Malaysia.
- The wood is used as machang.
- The heartwood is reported to be grayish to pale red but also chocolate brown.
References:
http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Mangifera+laurina
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mangifera_laurina
https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?315701
https://www.monaconatureencyclopedia.com/mangifera-laurina/?lang=en
https://uses.plantnet-project.org/en/Mangifera_laurina_(PROSEA)
https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q15544945